Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jan 27, 2023; 15(1): 1-8
Published online Jan 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i1.1
Published online Jan 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i1.1
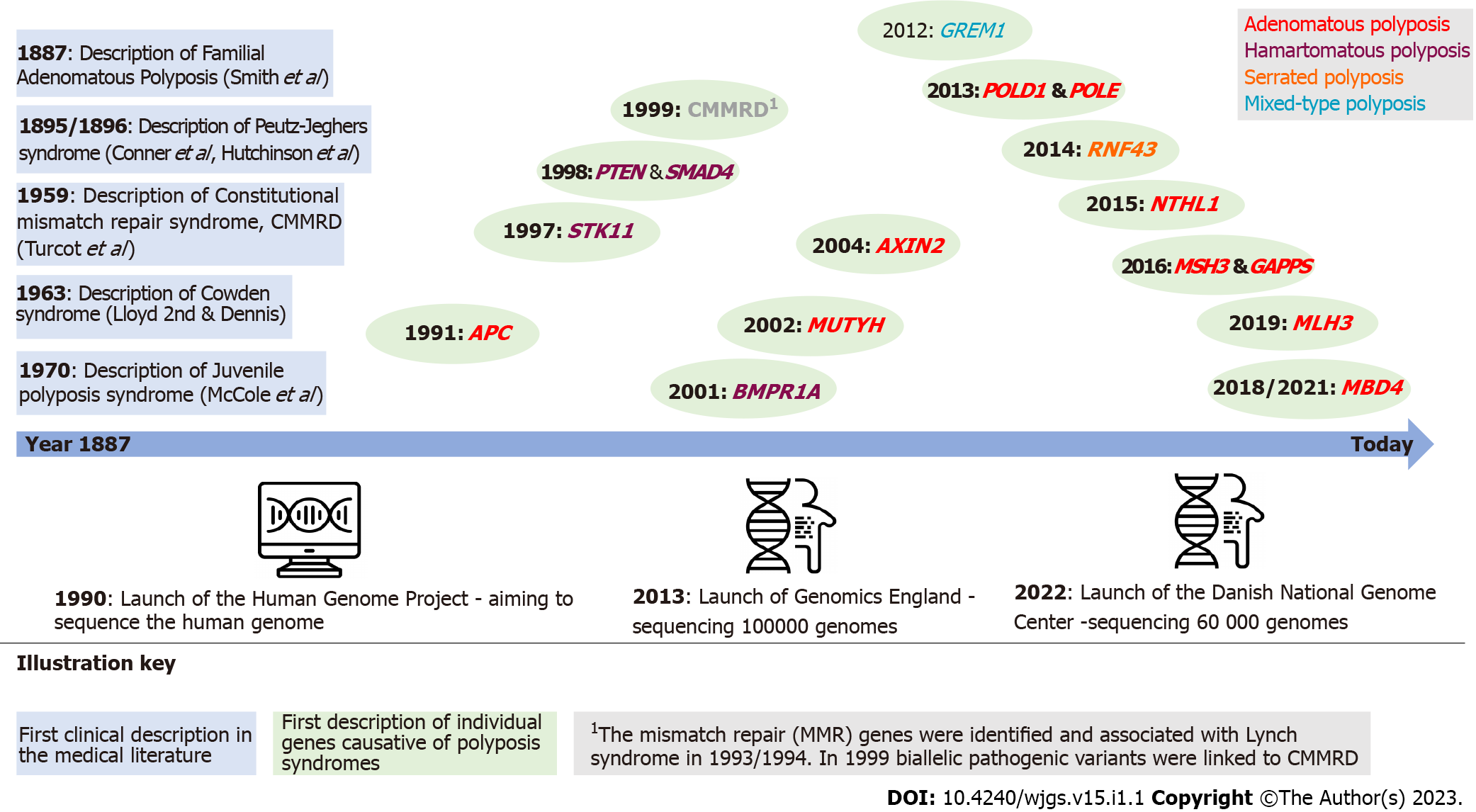
Figure 1 Timeline of hereditary polyposis syndromes and identification of causative gene.
APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli; AXIN2: Axis inhibition protein 2; BMPR1A: Type IA bone morphogenetic protein receptor; CMMRD: Constitutional mismatch repair deficiency; POLD1: Polymerase delta 1; POLE: Polymerase-epsilon; MLH: MutL homolog; MUTYH: MutY homologue; RNF43: Ring finger 43.
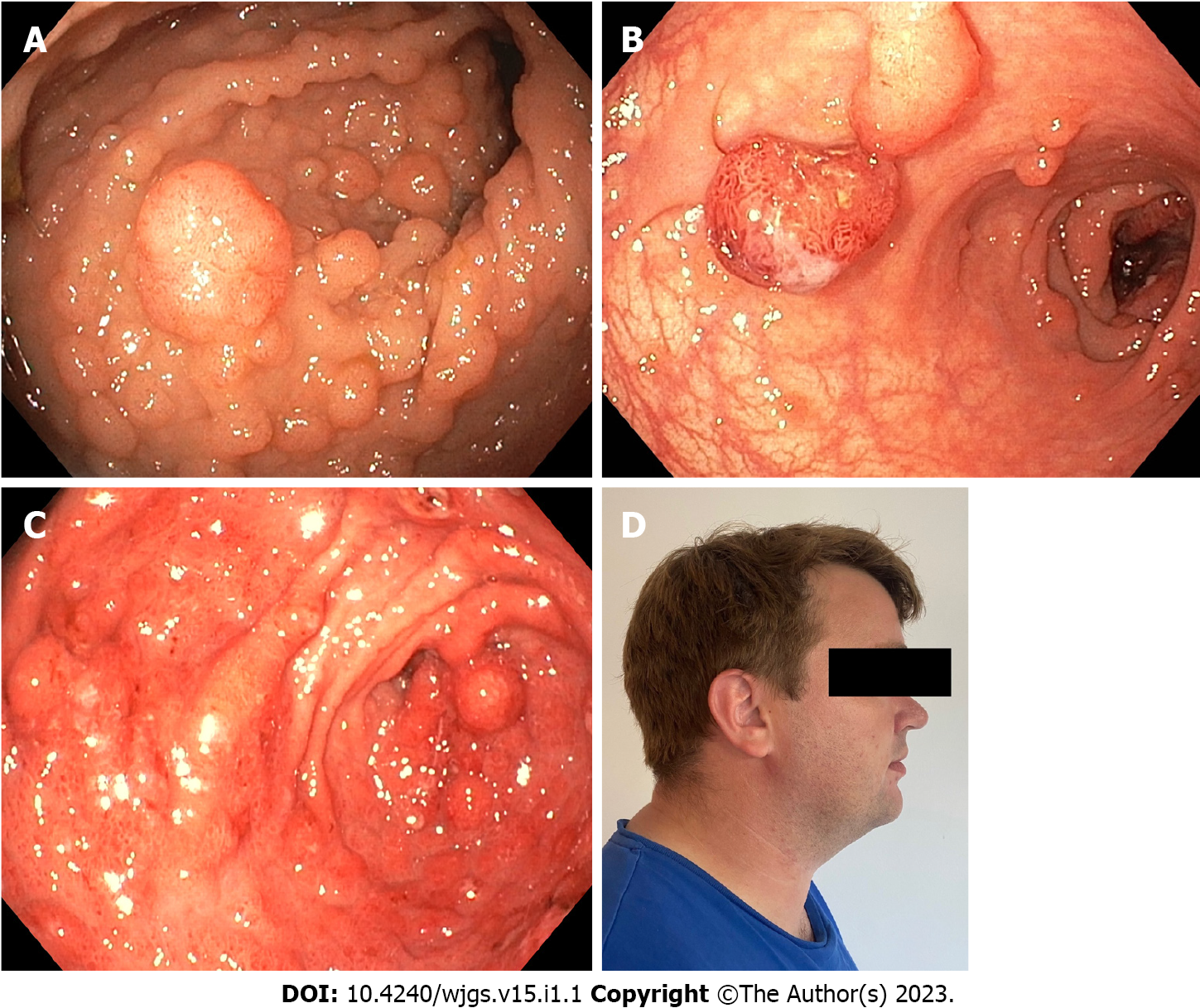
Figure 2 Polyps and extraintestinal manifestations in patients with hereditary polyposis syndromes.
A: Severe colonic adenomatosis in a patient with familial adenomatous polyposis; B: Colonic polyposis in patient with Peutz-Jegher syndrome; C: Severe gastric polyposis in patient with SMAD4-related juvenile polyposis syndrome; D: Patient with Cowden syndrome and macrocephaly.
- Citation: Pachler FR, Byrjalsen A, Karstensen JG, Jelsig AM. Hereditary polyposis syndromes remain a challenging disease entity: Old dilemmas and new insights. World J Gastrointest Surg 2023; 15(1): 1-8
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v15/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v15.i1.1