Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Surg. May 27, 2022; 14(5): 482-493
Published online May 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i5.482
Published online May 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i5.482
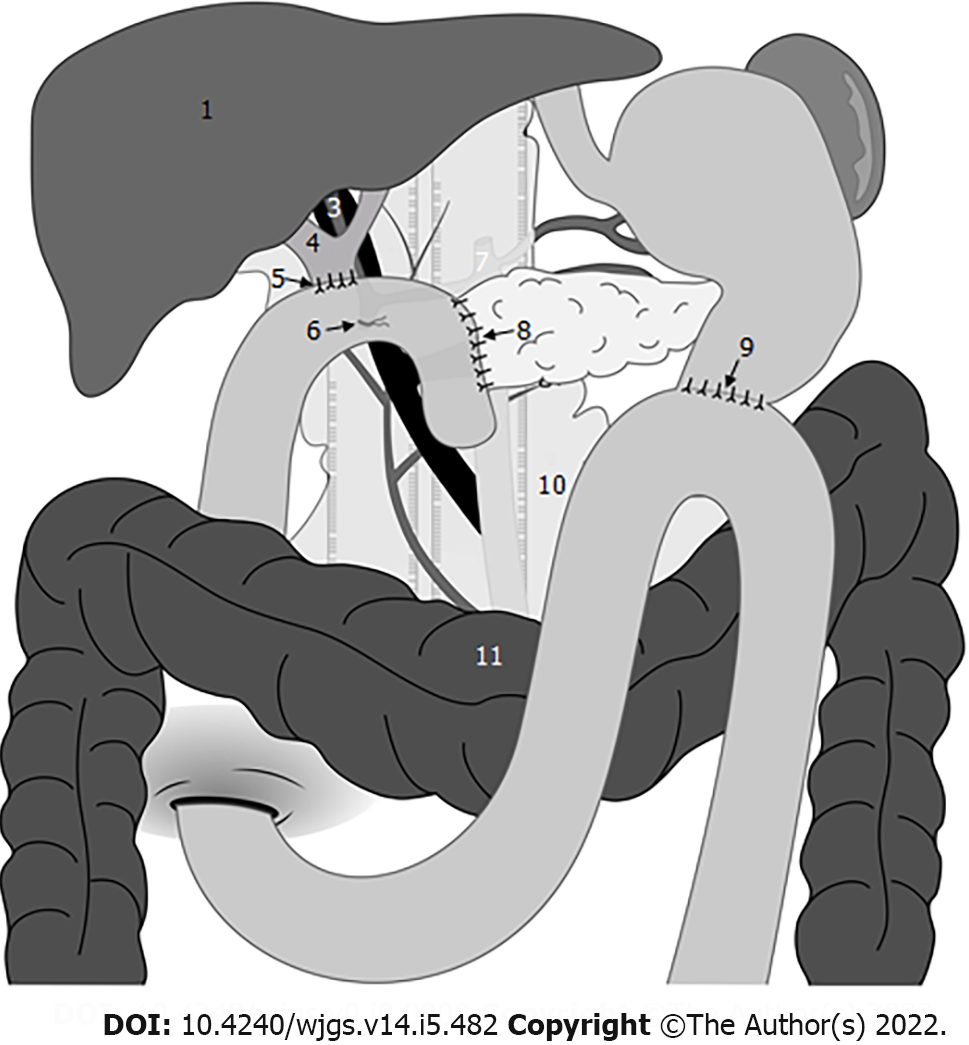
Figure 1 Omental interposition was placed in front of the adjacent vessels and behind the anastomosis where the pancreas stump was fixed to the jejunum.
1: Liver; 2: Portal vein; 3: Hepatic artery; 4: Common bile duct; 5: Hepaticojejunostomy; 6: Gastrojejunostomy; 7: Celiac artery; 8: Pancreaticojejunostomy site; 9: Gastrojejunostomy. site; 10: Omental interposition; 11: Transverse colon.
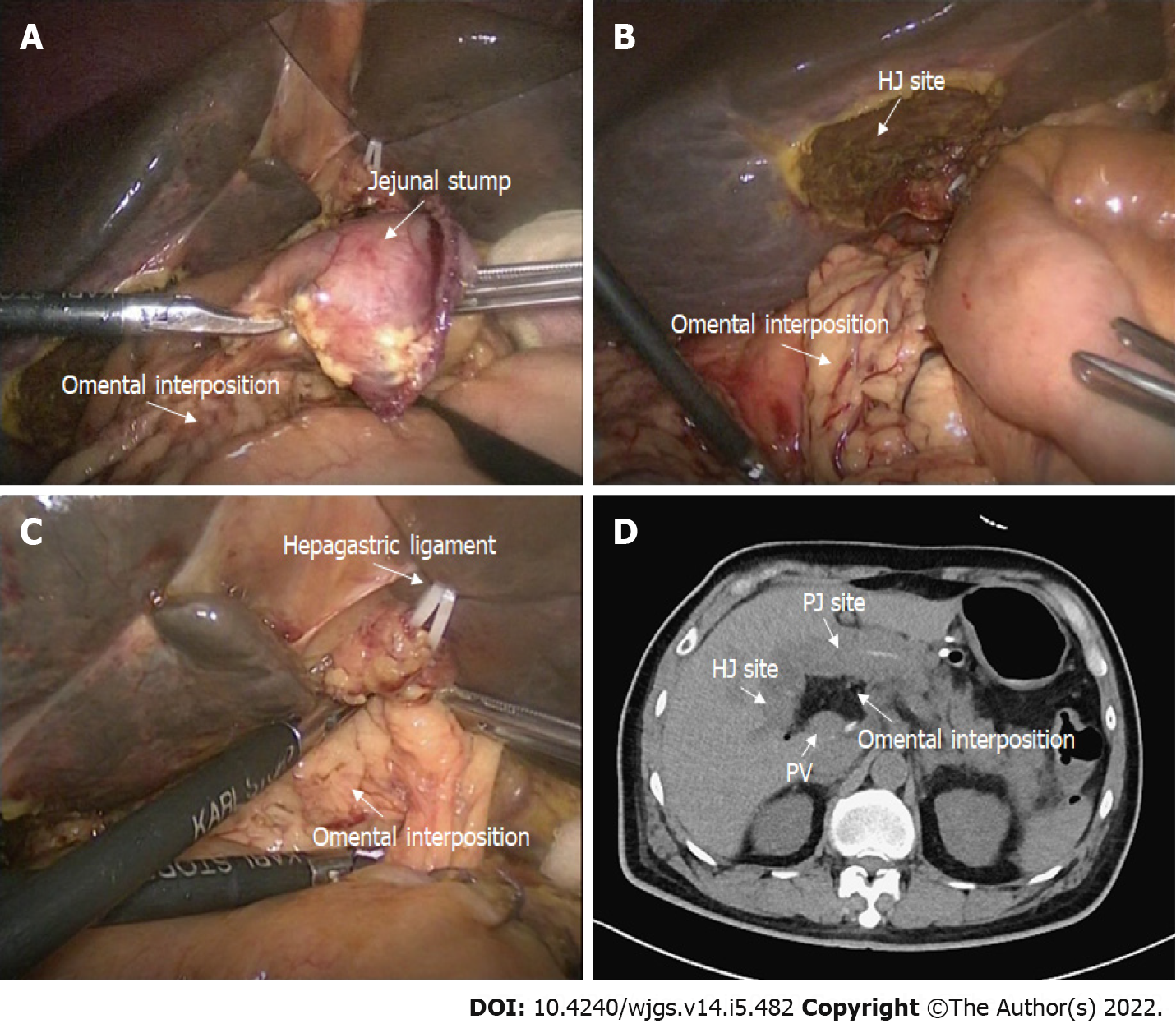
Figure 2 Application of the omental interposition in pancreaticoduodenectomy.
A: The pedicled omental interposition was placed in front of the adjacent vessels (hepatic artery, portal vein, and gastroduodenal artery stump) and behind the pancreaticojejunostomy site; B: The right boundary of the omental interposition was the right margin of the inferior vena cava; C: The upper boundary of the omental interposition was the hepatogastric ligament; the omental interposition was fixed to the hepatic portal and hepatogastric ligament with several sutures to prevent postoperative mobilization; D: Postoperative computed tomography images. The omental interposition elevated the hepaticojejunostomy site and filled the potential cavity.
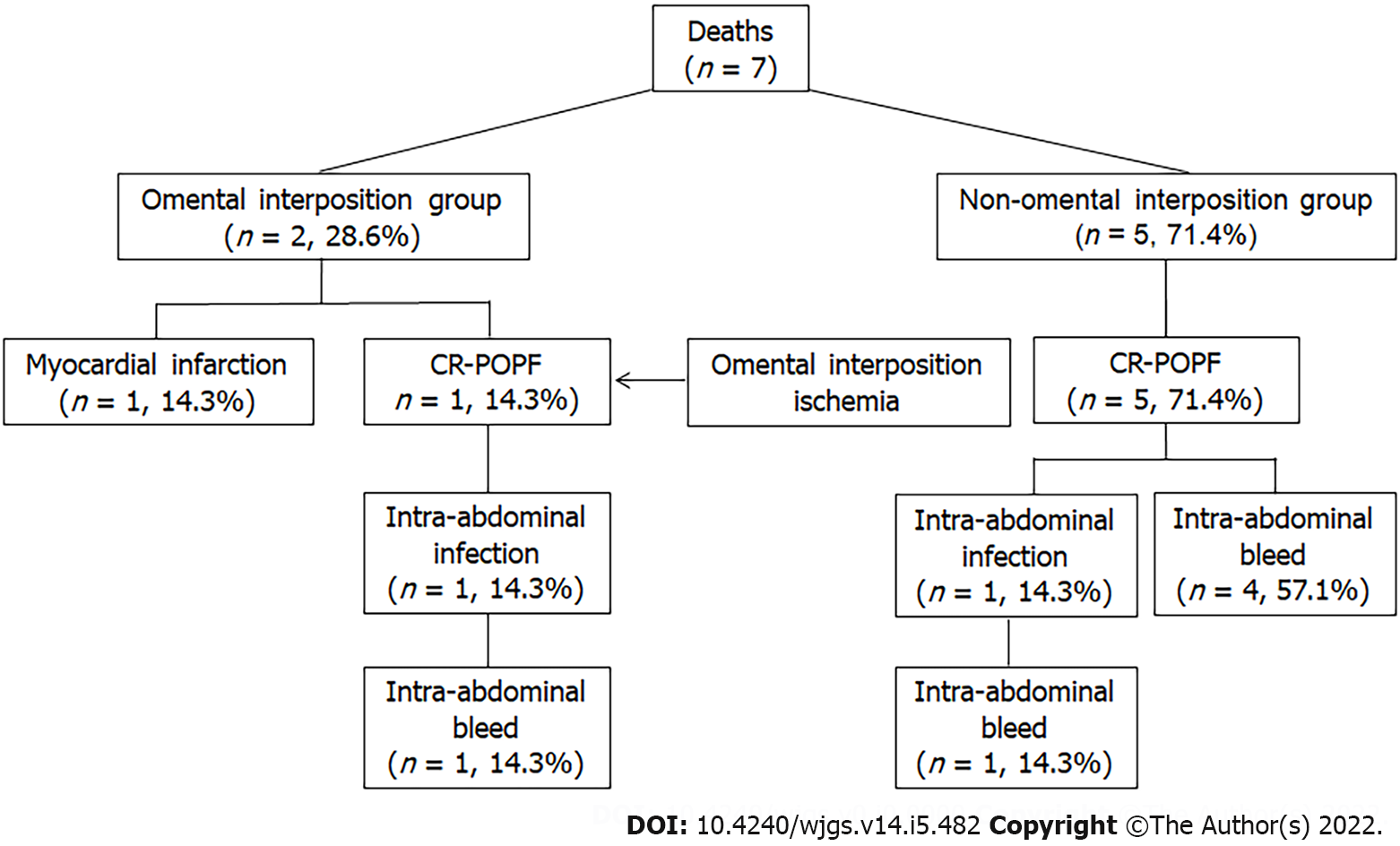
Figure 3
Causes of death in the two groups.
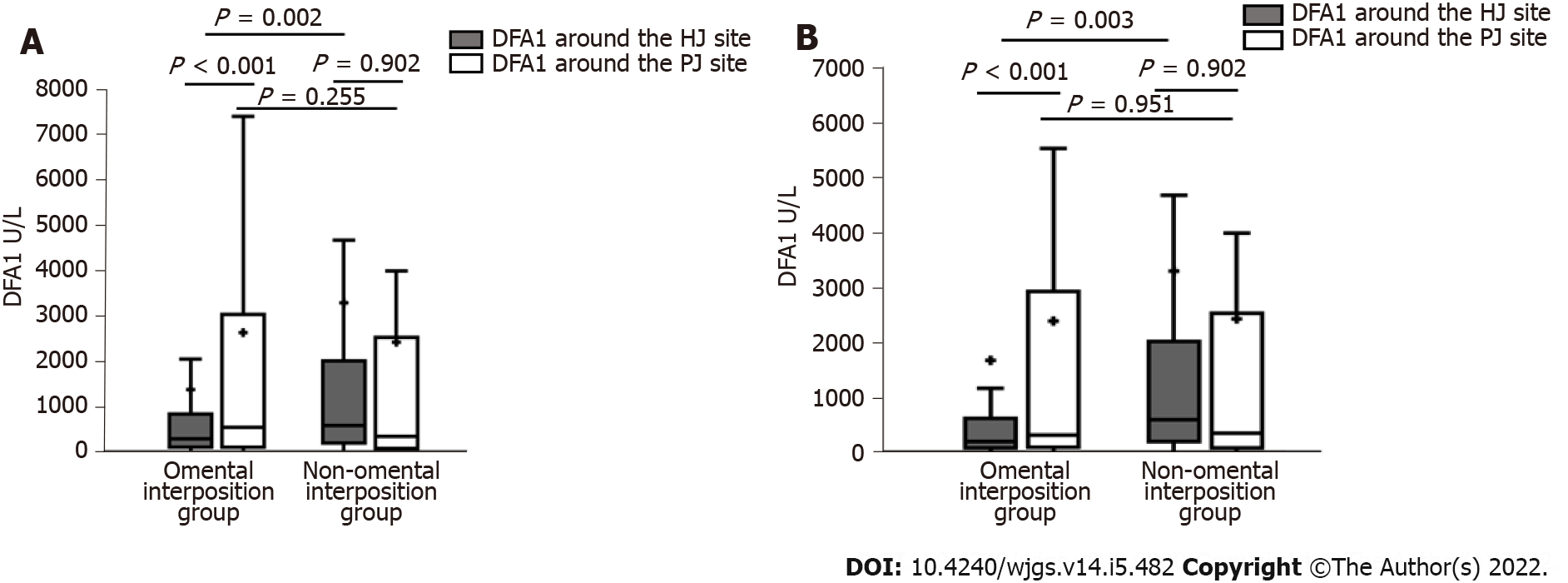
Figure 4 Differences between the two groups.
A: Drain fluid amylase obtained on the first postoperative day (DFA1) before propensity score-matching (PSM); B: DFA1 after PSM.
- Citation: Li Y, Liang Y, Deng Y, Cai ZW, Ma MJ, Wang LX, Liu M, Wang HW, Jiang CY. Application of omental interposition to reduce pancreatic fistula and related complications in pancreaticoduodenectomy: A propensity score-matched study. World J Gastrointest Surg 2022; 14(5): 482-493
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v14/i5/482.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v14.i5.482