Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Surg. May 27, 2022; 14(5): 470-481
Published online May 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i5.470
Published online May 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i5.470
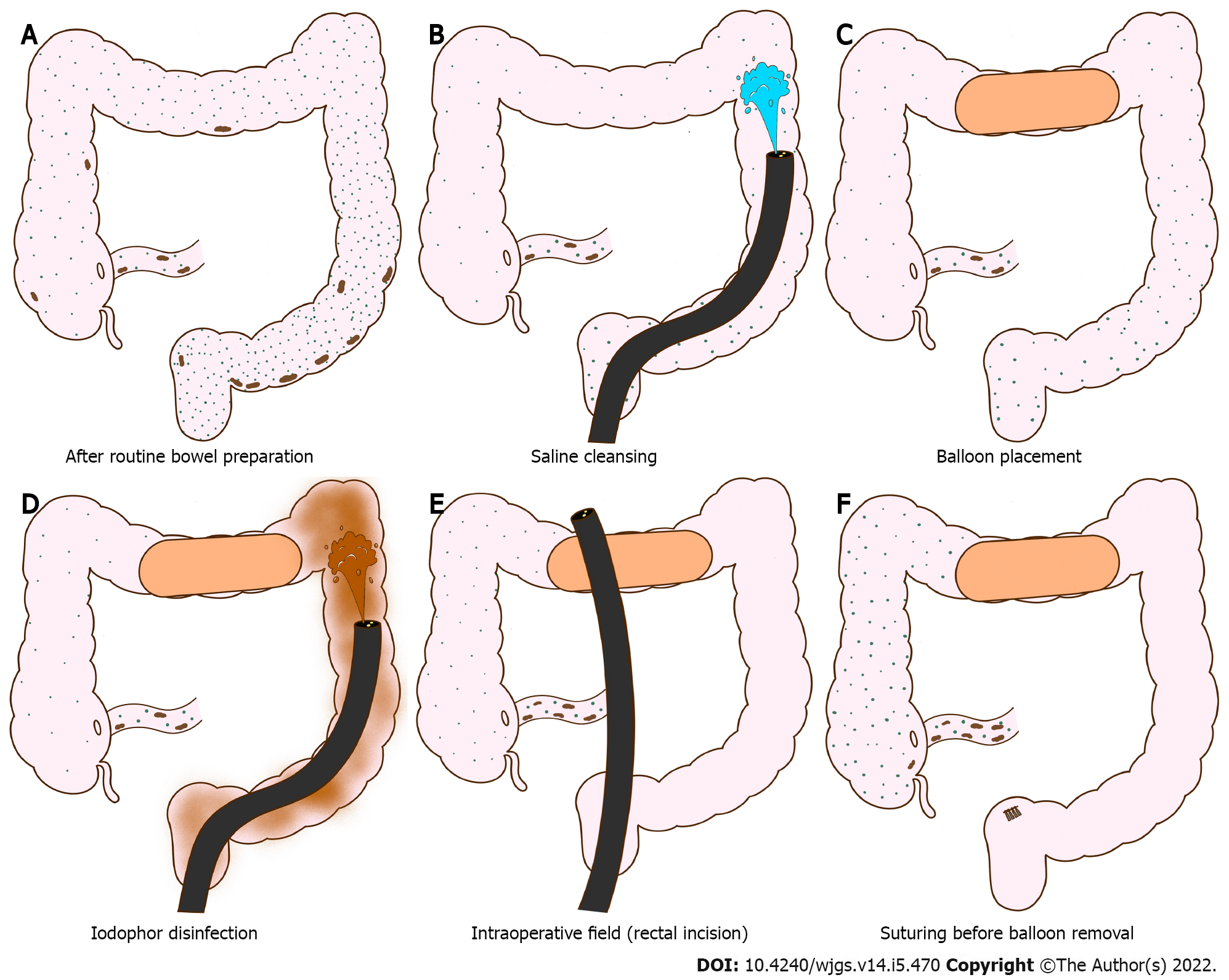
Figure 1 Schematic of colonic cleansing, detachable balloon placement, and colonic disinfection.
A: Colon after bowel preparations; B: Colon cleansing using saline solution; C: Placement of detachable balloon in the transverse colon; D: Distal colon disinfection using iodophor; E: Endoscopy insertion to peritoneal cavity via rectal incision; F: Suturing of rectal incision before balloon removal.
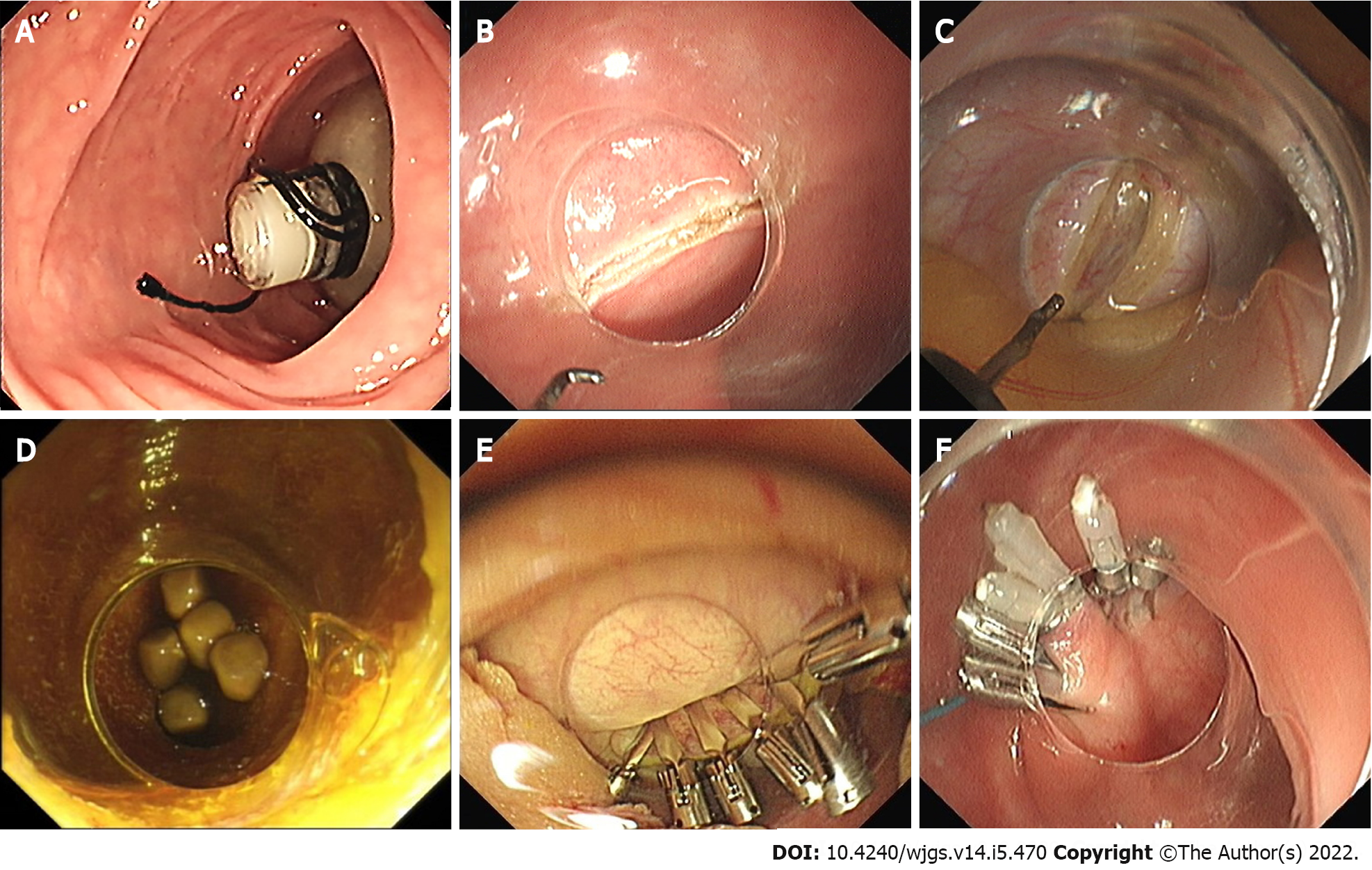
Figure 2 Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery trans-rectal gallbladder preserving cholecystolithotomy.
A: Detachable balloon placement in the colonic lumen; B: Rectum incision for trans-rectal access; C: Gallbladder incision; D: Visualization of gallbladder stones; E: Closure of the gallbladder wall with endoclips; F: Closure of the rectal incision with endoclips and endoloops.
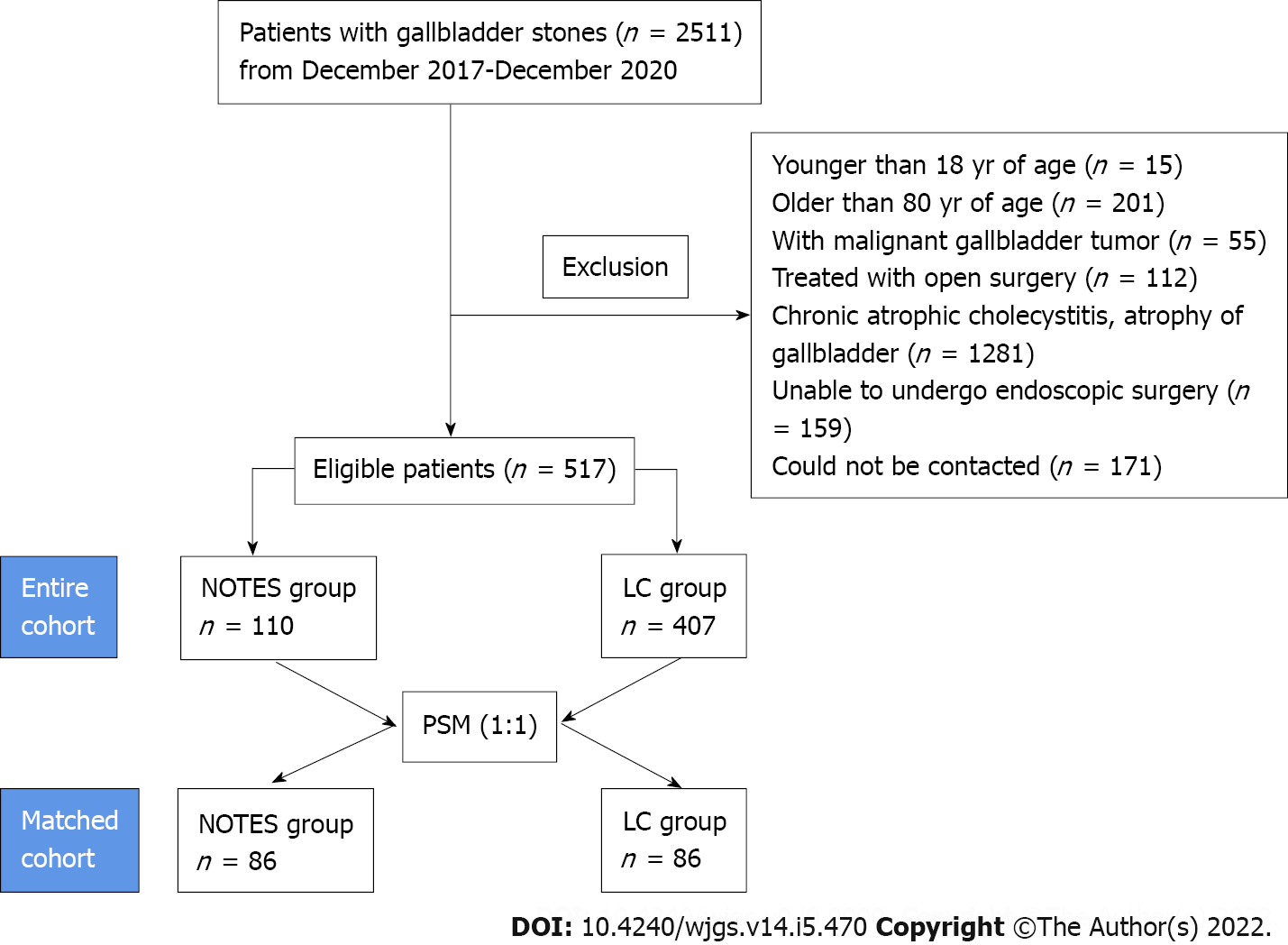
Figure 3 Flow chart of the entire and matched cohort.
NOTES: Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery.
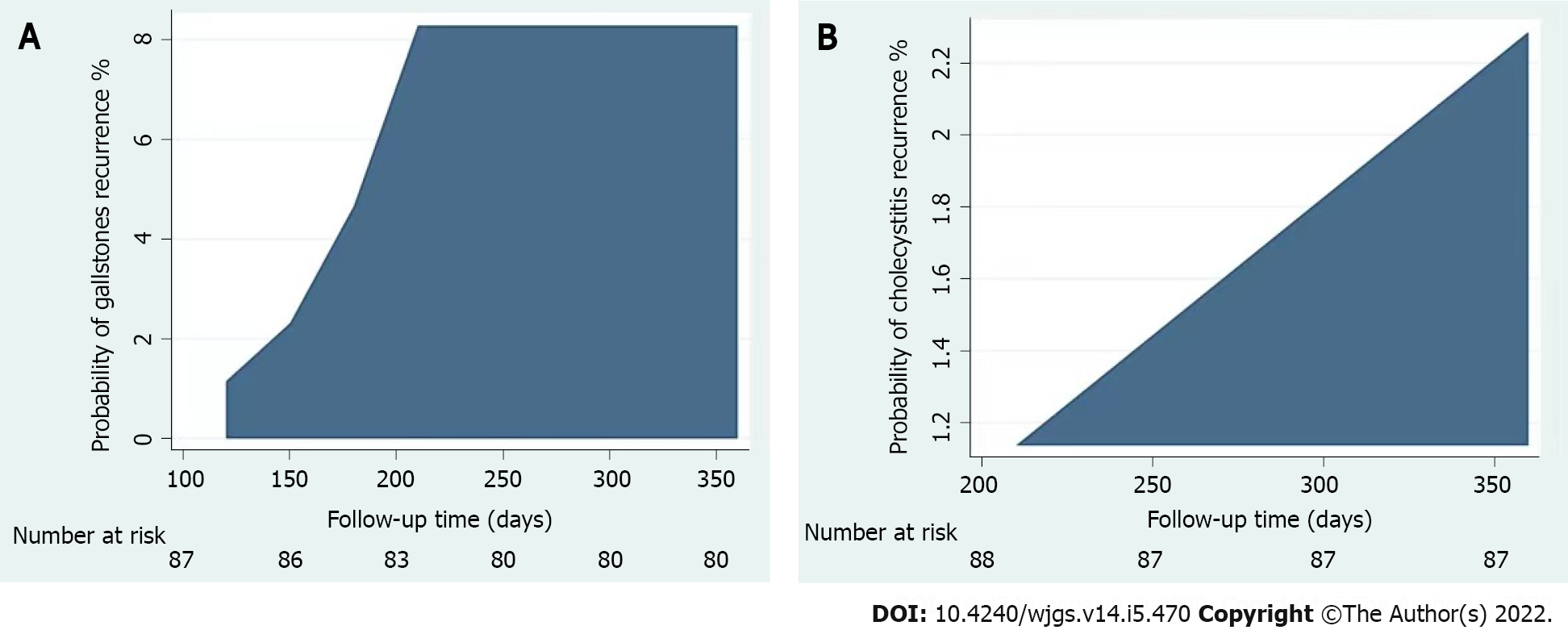
Figure 4 The cumulative incidence of recurrent gallbladder stones and recurrent cholecystitis in the natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery group.
A: Cumulative incidence of recurrent gallbladder stones in natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES) patients; B: Cumulative incidence of recurrent cholecystitis in the NOTES patients.
- Citation: Ullah S, Yang BH, Liu D, Lu XY, Liu ZZ, Zhao LX, Zhang JY, Liu BR. Are laparoscopic cholecystectomy and natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery gallbladder preserving cholecystolithotomy truly comparable? A propensity matched study. World J Gastrointest Surg 2022; 14(5): 470-481
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v14/i5/470.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v14.i5.470