Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Dec 27, 2022; 14(12): 1375-1386
Published online Dec 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i12.1375
Published online Dec 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i12.1375
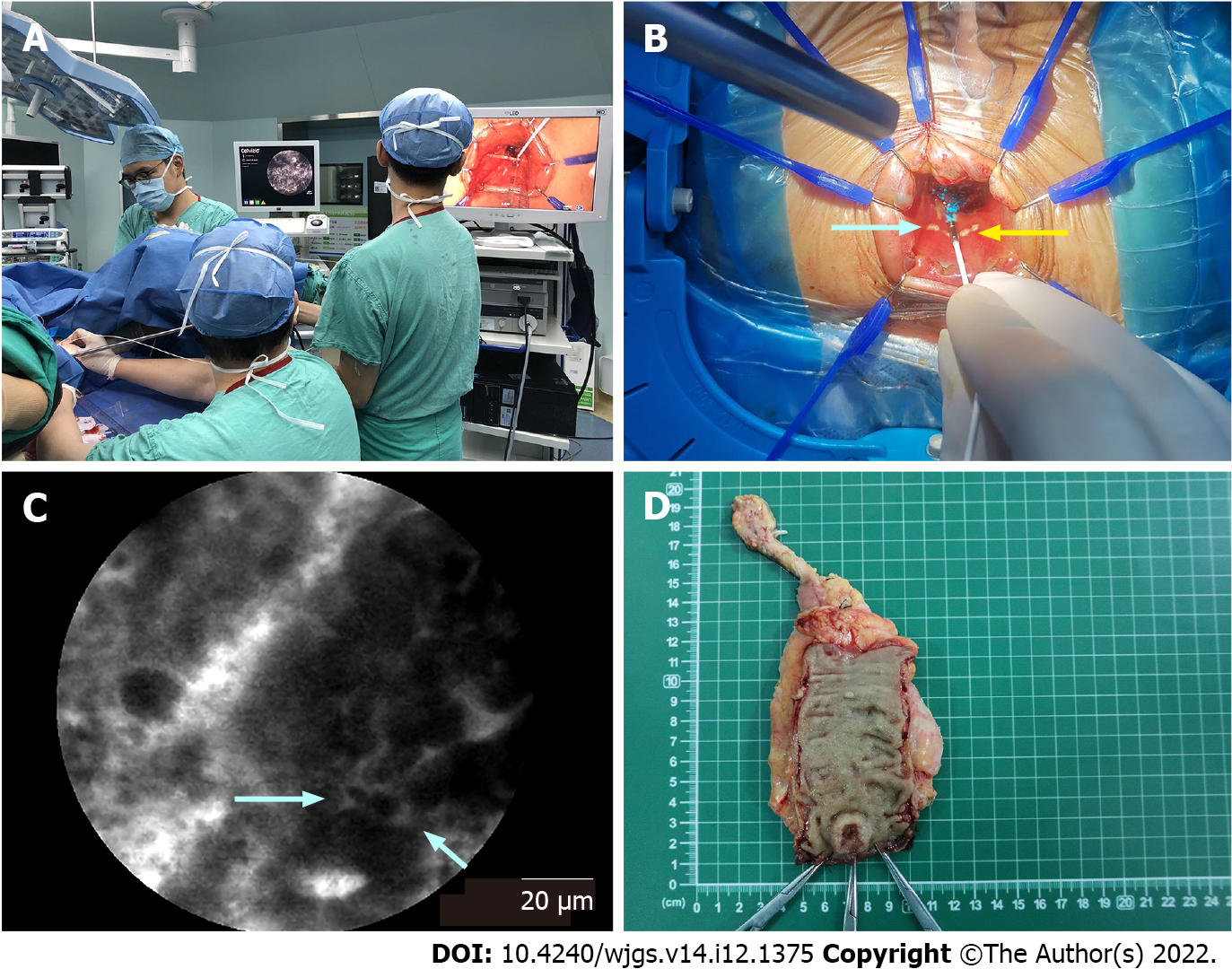
Figure 1 Selection of the distal resection margin guided by probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy.
A: During transanal total mesorectal excision, the surgeon used the tip of the probe in direct contact with the tissues. In the meantime, the pathologist analyzed the real-time probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (pCLE) videos; B: A dot (white arrow) was marked by an electric scalpel at the distal edge of the tumor, which was determined by pCLE optical biopsy. Then, the distal resection margin (DRM) (yellow arrow) was marked 5-10 mm below the marked dot; C: In pCLE videos, the distal edge of the tumor (white arrow) was determined at the end of the distorted structures (dark, irregularly thickened epithelium); D: Conventional samples were collected for histology at the marked dot and DRM after surgery.
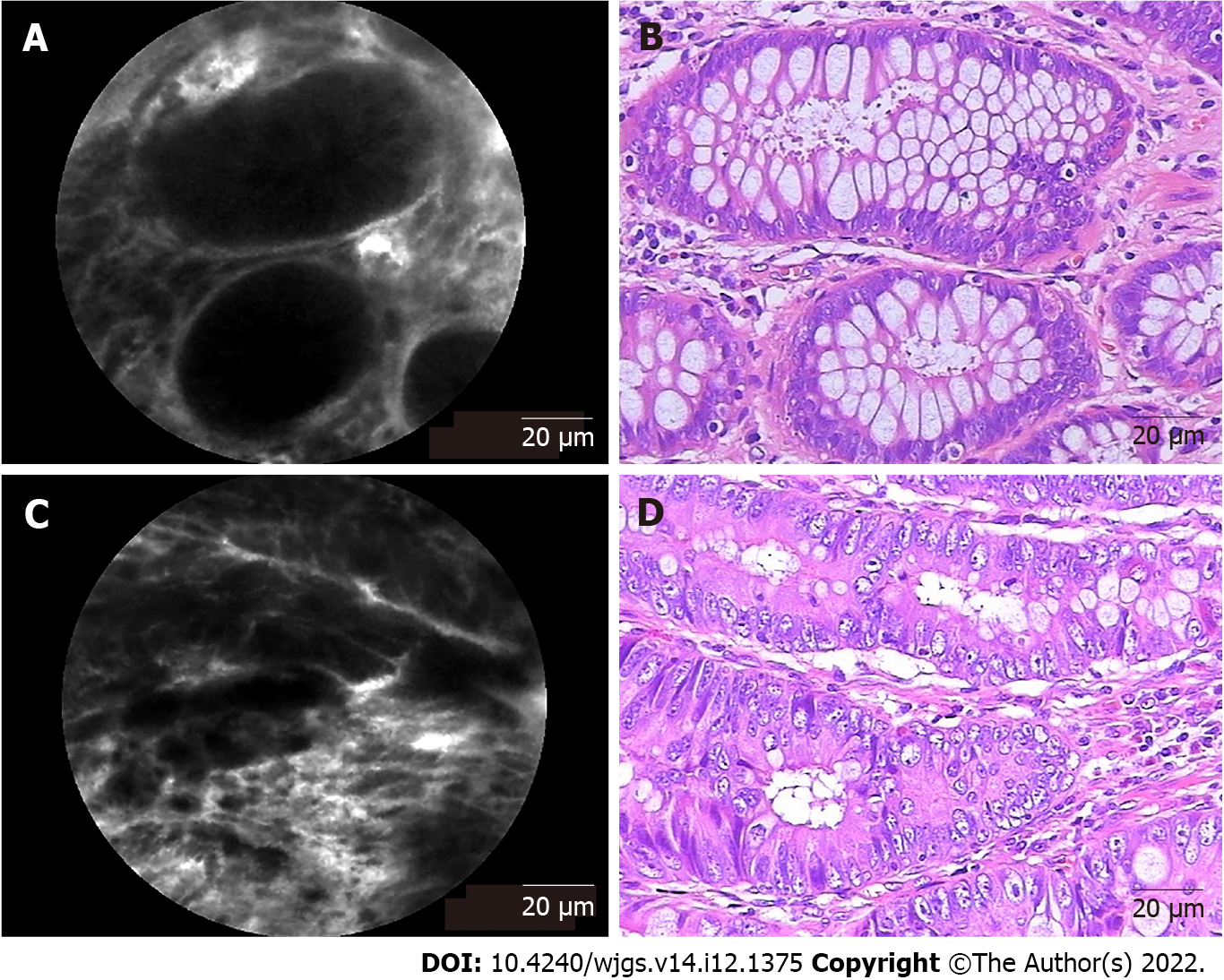
Figure 2 Representative probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy images and corresponding hematoxylin and eosin-stained images of rectal tissues.
A: Probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (pCLE) image of normal tissue presenting normal round crypt structures with regular luminal openings covered by a homogeneous single-cell-layered epithelium with dark goblet cells and regular narrow vessels with hexagonal, honeycomb appearance surrounding crypts; B: Corresponding image of normal rectal tissue stained by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E); C: pCLE image of rectal neoplastic tissues manifesting as dark and irregularly thickened epithelium with decreased volume of lamina propria and dilated, distorted vessels with elevated leakage. The epithelium was dark and irregularly thickened, and the vessels were dilated; D: Corresponding image of H&E-stained rectal adenocarcinoma tissue.
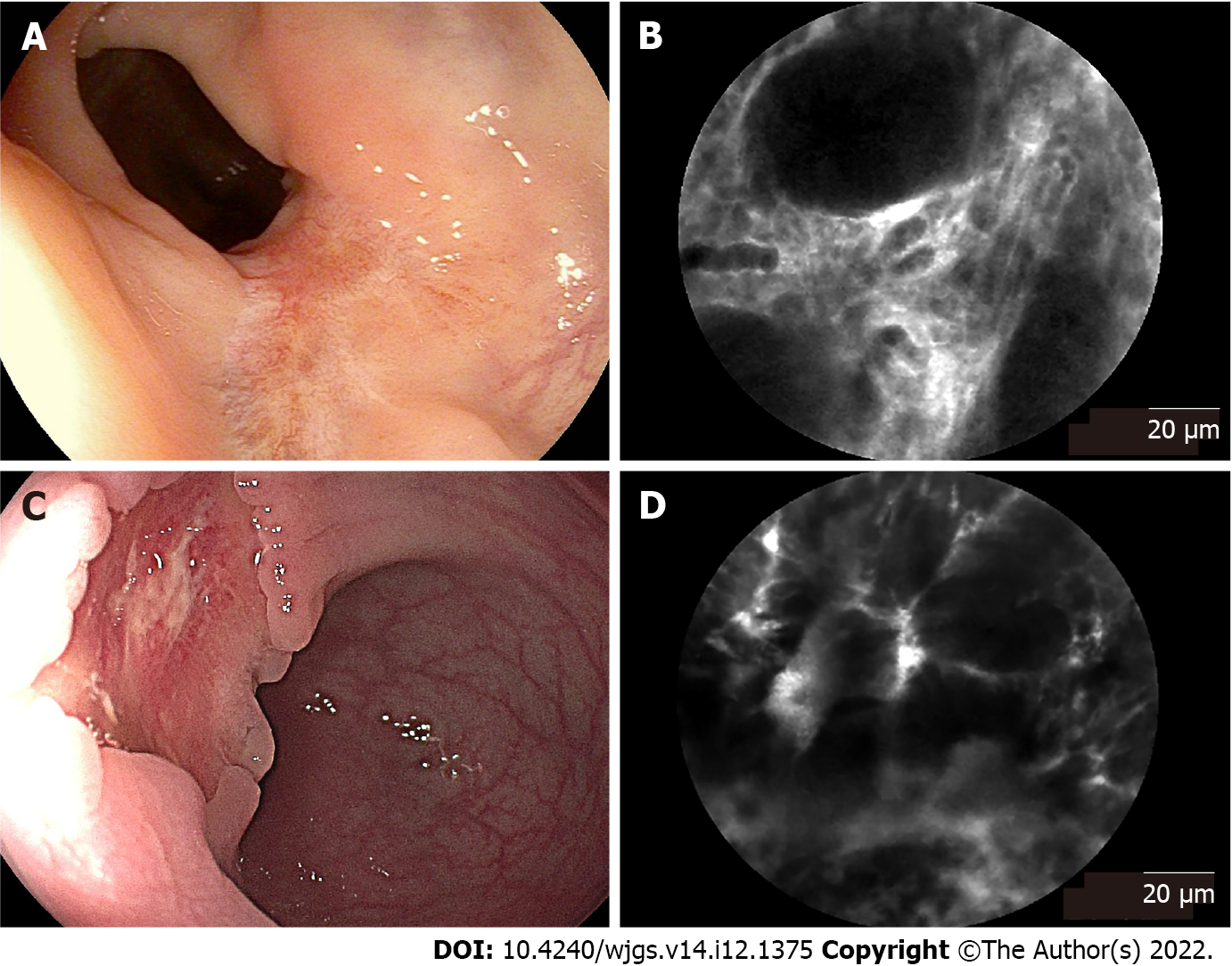
Figure 3 Endoscopic images and corresponding probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy images of rectal tissues after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy.
A: Endoscopic image of rectal tissue with complete response, presenting a residual scar; B: Corresponding probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (pCLE) image showed regular crypts with thickening epithelium and enlarged vessels with fibrotic stroma; C: Endoscopic image of rectal tissue with partial response, presenting a residual tumor lesion; D: Corresponding pCLE image showed atypical glands with dark and irregular crypts and enlarged twisty vessels.
- Citation: Tan J, Ji HL, Hu YW, Li ZM, Zhuang BX, Deng HJ, Wang YN, Zheng JX, Jiang W, Yan J. Real-time in vivo distal margin selection using confocal laser endomicroscopy in transanal total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Surg 2022; 14(12): 1375-1386
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v14/i12/1375.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v14.i12.1375