Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Oct 27, 2022; 14(10): 1169-1178
Published online Oct 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i10.1169
Published online Oct 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i10.1169
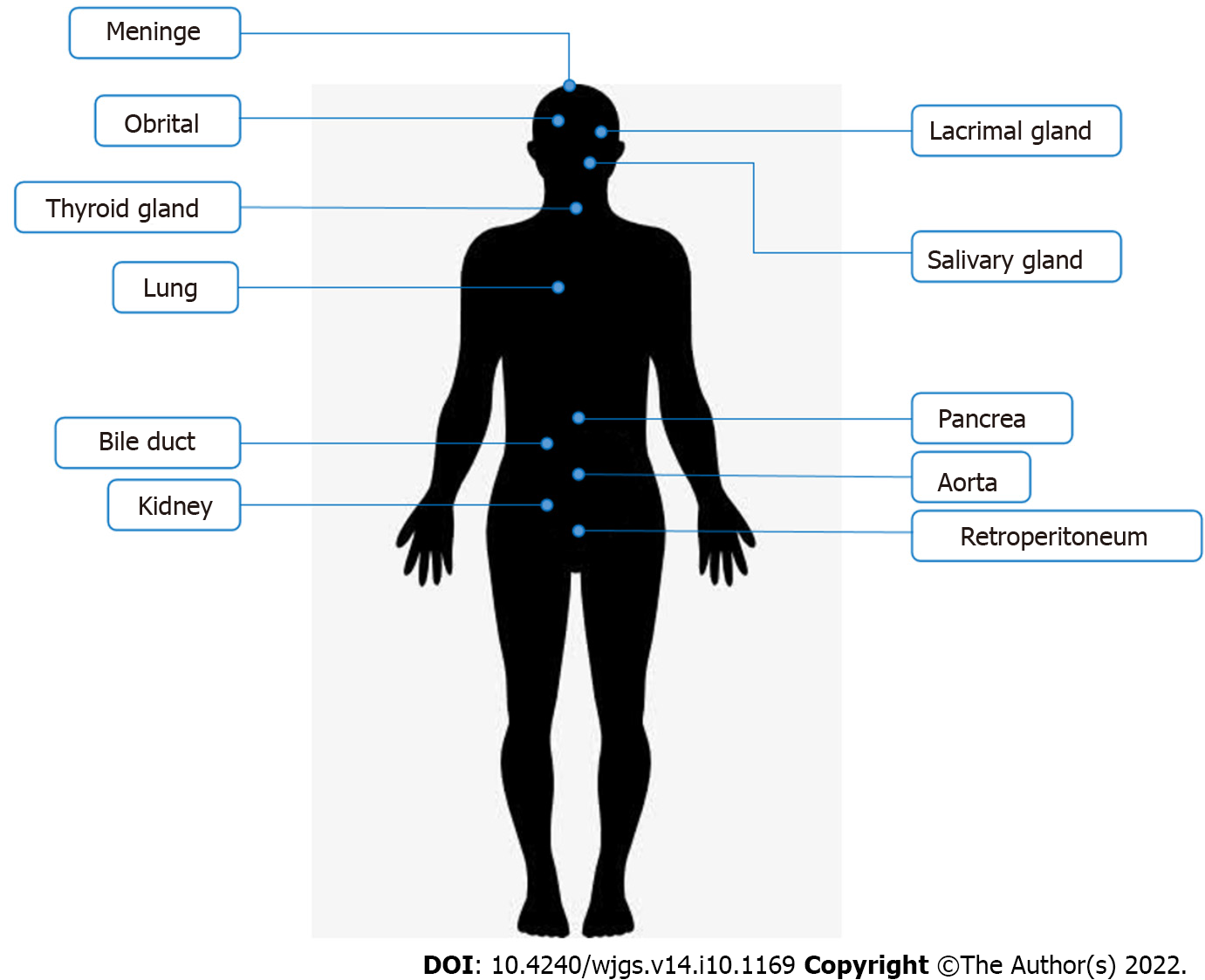
Figure 1 Commonly affected organs in immunoglobulin G4-related disease.
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease often appears in salivary glands, lacrimal glands, pancreas, and biliary tract.
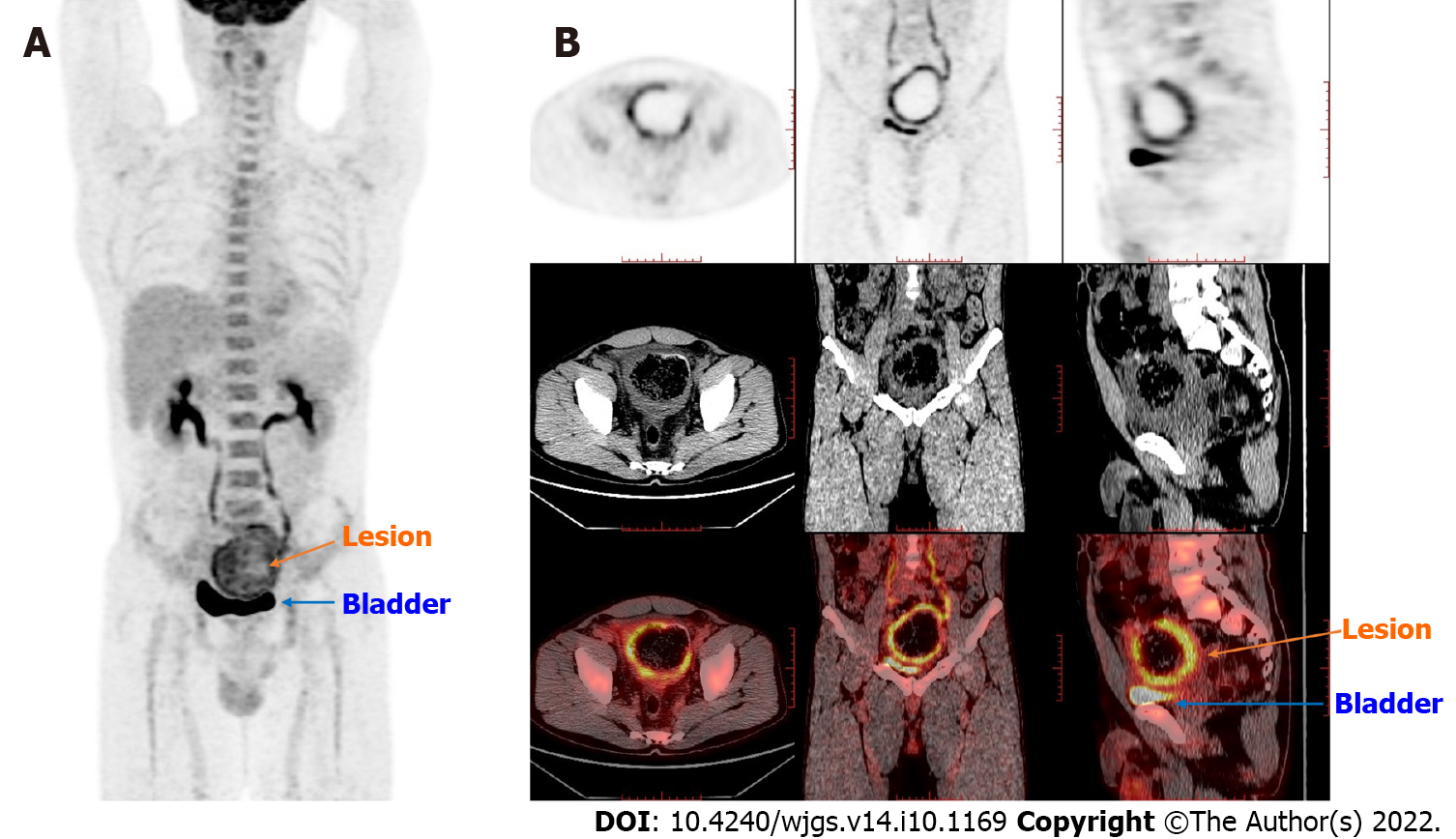
Figure 2 Positron emission tomography/computed tomography findings.
The thick-walled cystic structure above the bladder could be seen, the radioactive uptake was significantly increased, and the maximum standard uptake value reached 6.5. The diagnosis was considered inflammatory or a neoplastic lesion on the sigmoid colon adherent to the bladder. A: Coronal whole-body imaging showing high uptake values at the lesion site; B: Detailed imaging pictures of the lesion, including horizontal, sagittal and coronal.
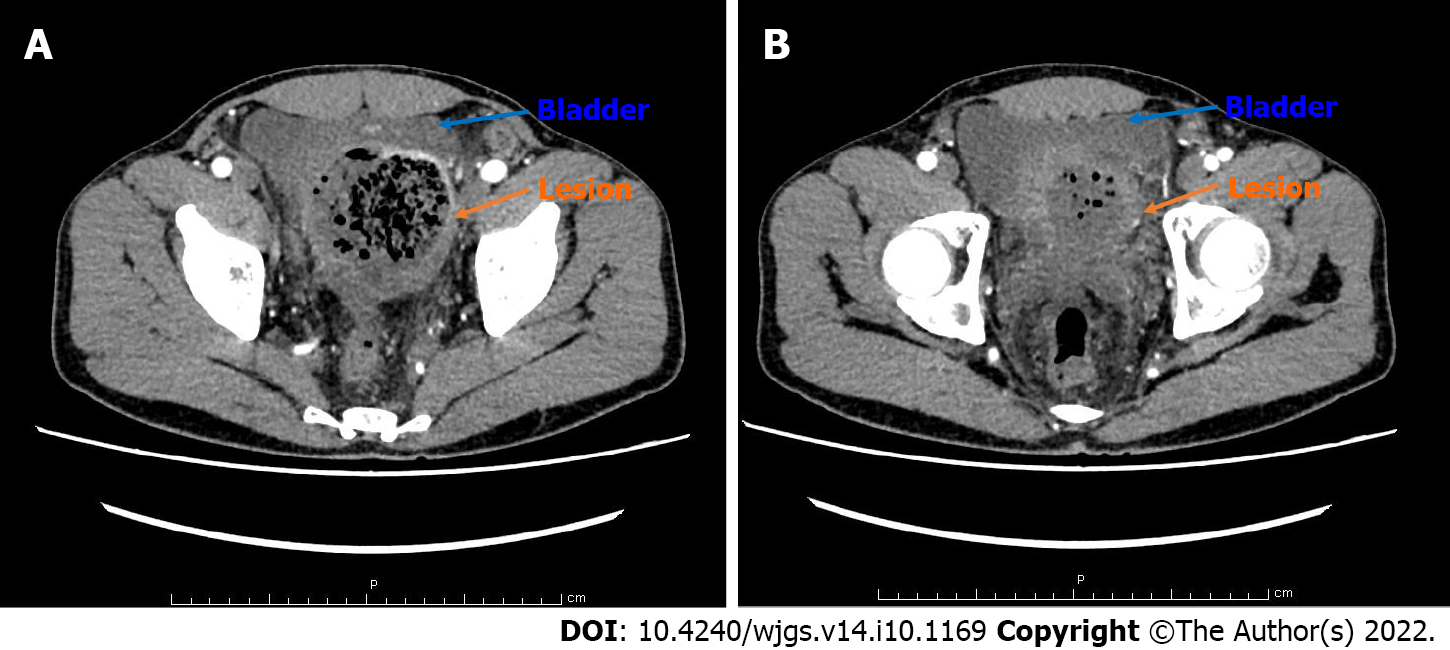
Figure 3 Contrast-enhanced computed tomography scan of the abdomen findings.
A: The proximal sigmoid colon was dilated. The middle colon wall was thickened. It was markedly enhanced in the arterial phase, representing the characteristics of neoplastic lesions or chronic abscesses; B: The sigmoid colon mass compressed the bladder, and the boundary between the bladder and the mass was unclear.
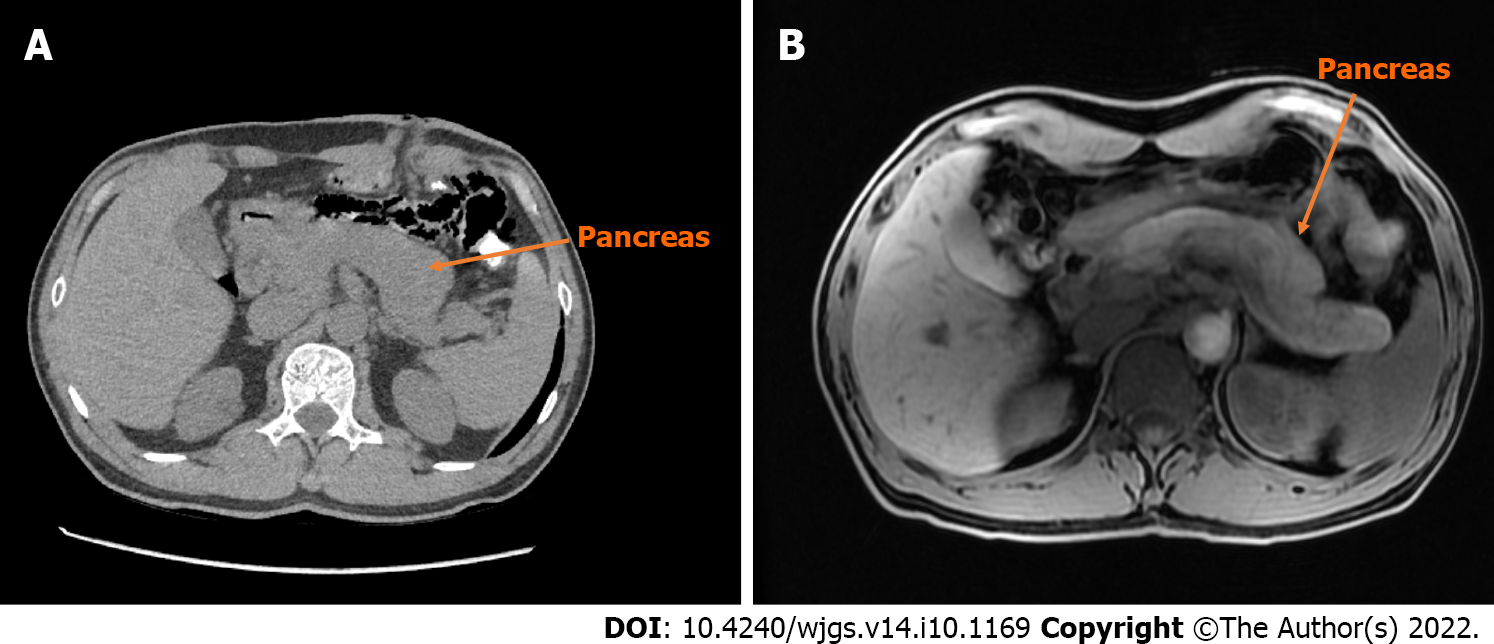
Figure 4 Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging scan of the pancreas.
A: The pancreas of the patient is diffusely enlarged, surrounded by capsule-like edema in computed tomography (CT) image; B: Magnetic resonance imaging image of the patient’s pancreas is similar to CT.
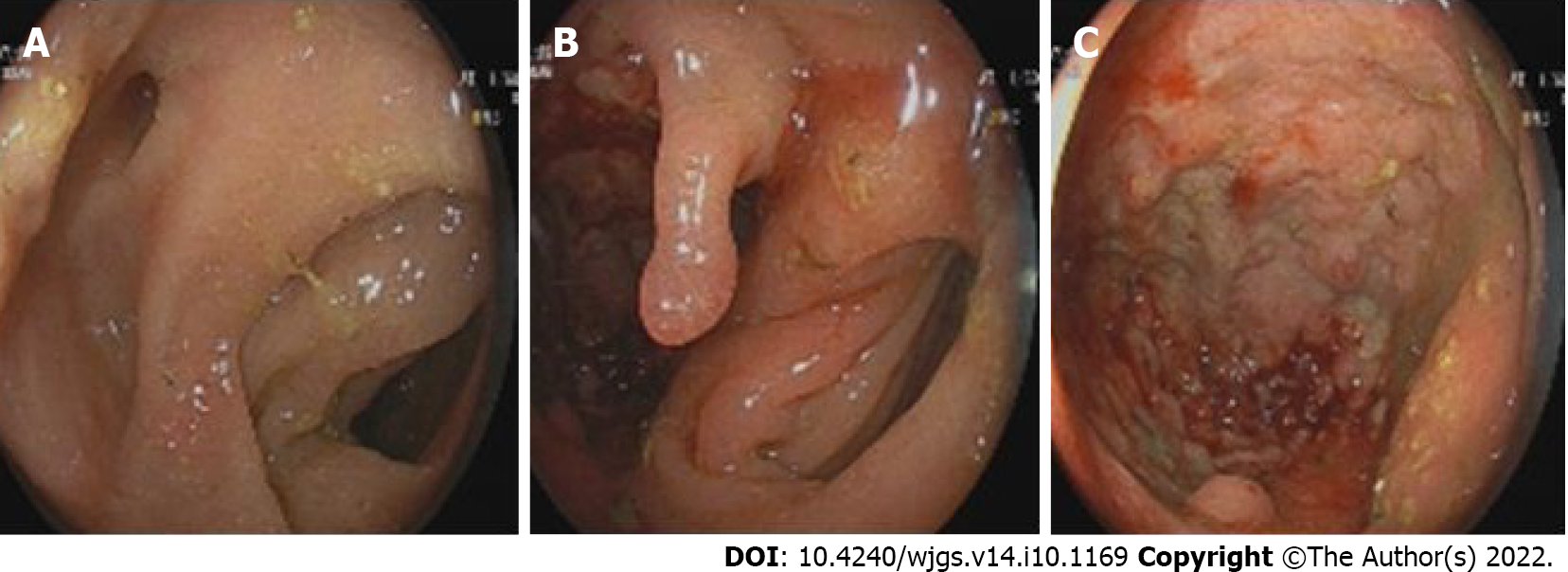
Figure 5 Findings of the colonoscopy.
A and B: From different angles, it could be seen that there were two cavities in the sigmoid colon, one of which was a blind cavity; C: It could be seen that the diseased colon was thickened and rough, and the tissue was so hard to do a biopsy.
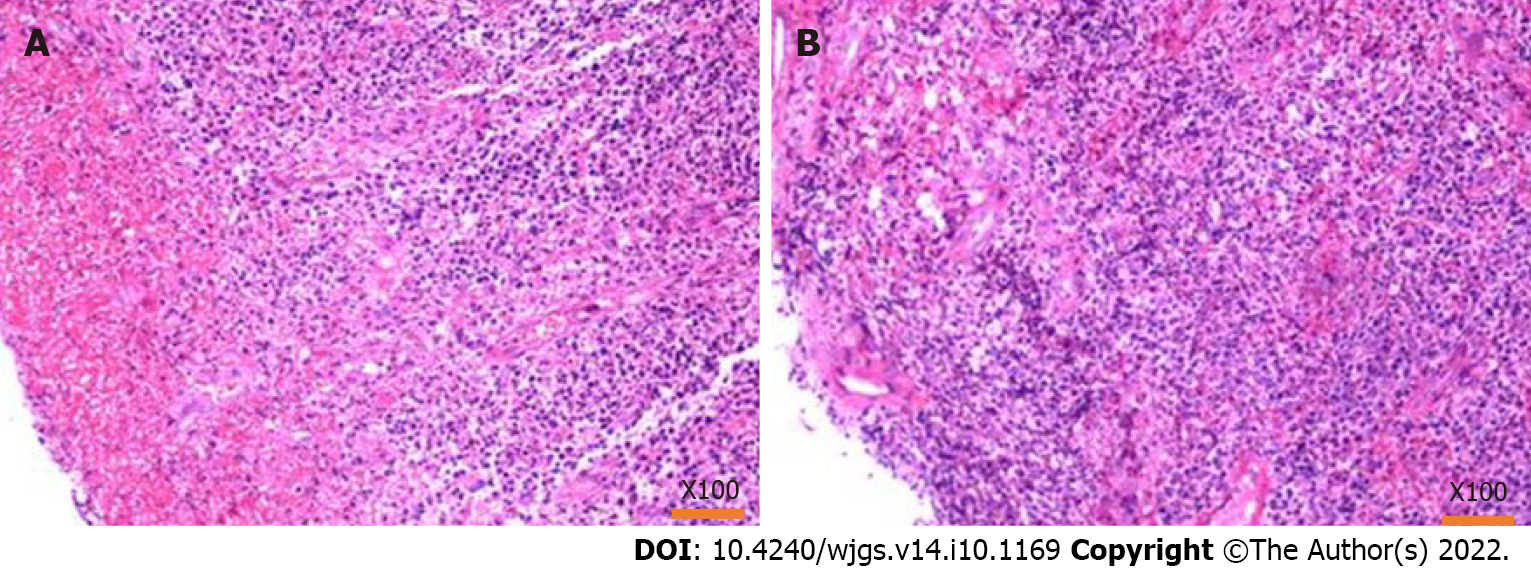
Figure 6 Pathology of the biopsy by colonoscopy.
A: Hematoxylin-eosin staining showed that the tissues were inflammatory hyperplasia changes, and a large number of inflammatory cells were infiltrated; however, there were no tumor cells; B: Results from different sampling sites.
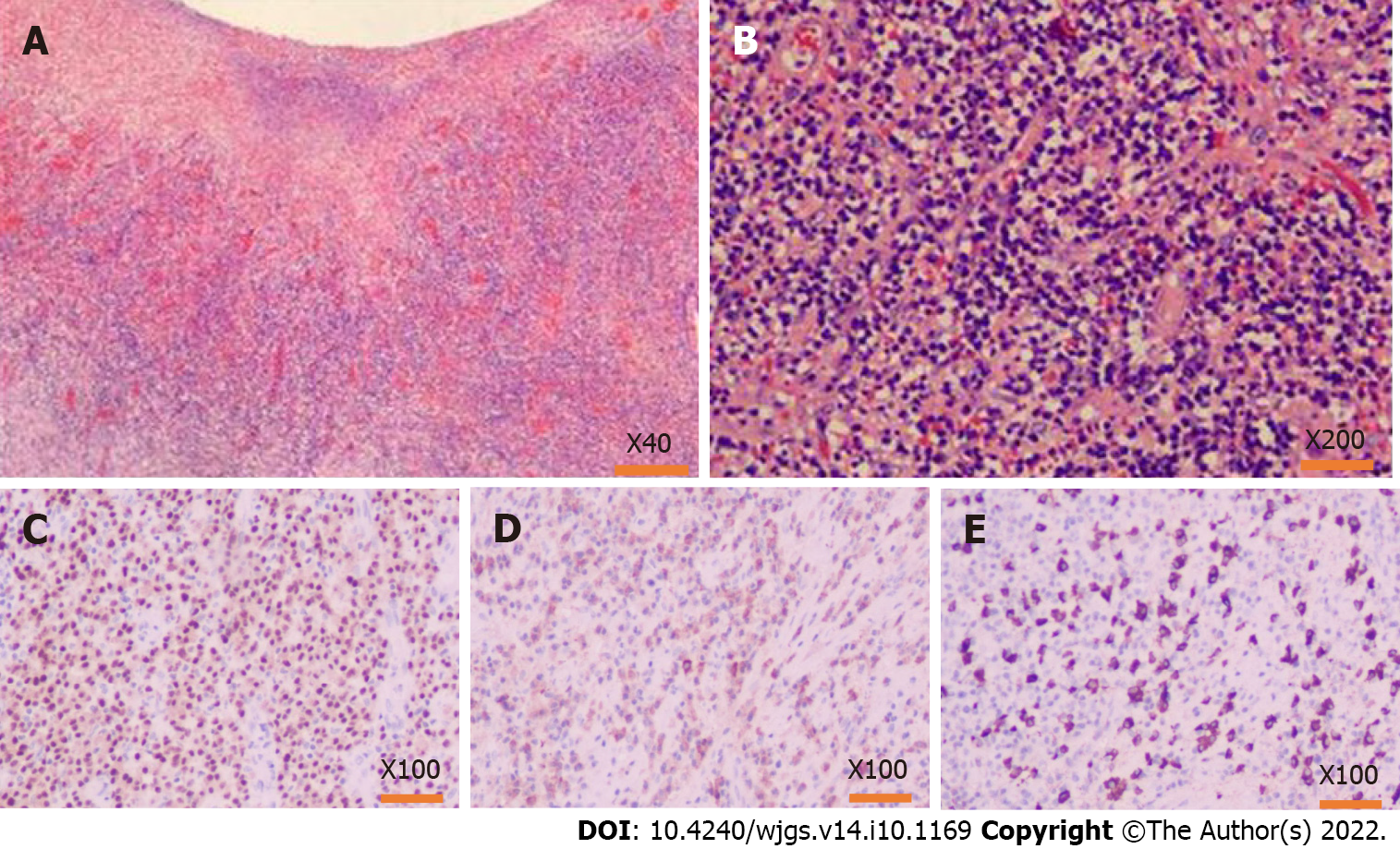
Figure 7 Pathology findings after the operation.
A and B: Hematoxylin-eosin staining of the lesion tissues, inflammatory cell infiltration with plasma cells and neutrophils and increased immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) positive cells could be seen in the resection colonic mass, accompanied by tissue fibrosis and obliterative phlebitis; C: MMU1 staining showed a high expression state, suggesting a large number of plasma cells infiltration; D: Immunohistochemistry showed a lot of positive IgG staining in the lesion area; E: IgG4 also showed much positive staining in the lesion area, and the number of IgG4-positive cells in the main core area was as high as 110/HPF.
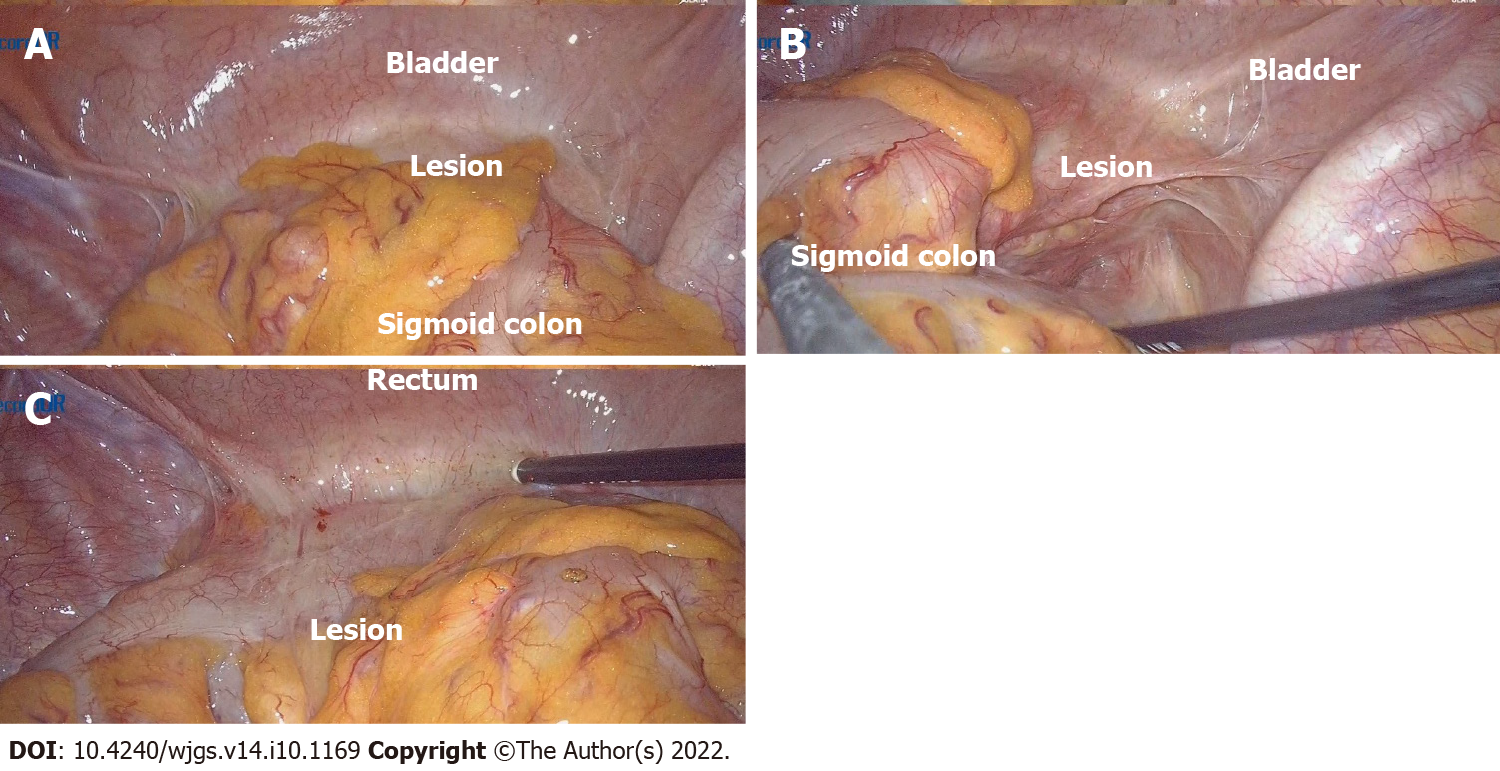
Figure 8 Operation images from laparoscopy.
A: Explore its relationship to surrounding tissue: Dense adhesion of the sigmoid colon to the bladder was observed during the laparoscopic surgery, and it was tough to separate the adhesion; the mass was on the sigmoid colon wall between the bladder and colon; B and C: View the location of the lesion from different angles.
- Citation: Zhan WL, Liu L, Jiang W, He FX, Qu HT, Cao ZX, Xu XS. Immunoglobulin G4-related disease in the sigmoid colon in patient with severe colonic fibrosis and obstruction: A case report. World J Gastrointest Surg 2022; 14(10): 1169-1178
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v14/i10/1169.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v14.i10.1169