Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Feb 27, 2021; 13(2): 210-221
Published online Feb 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i2.210
Published online Feb 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i2.210
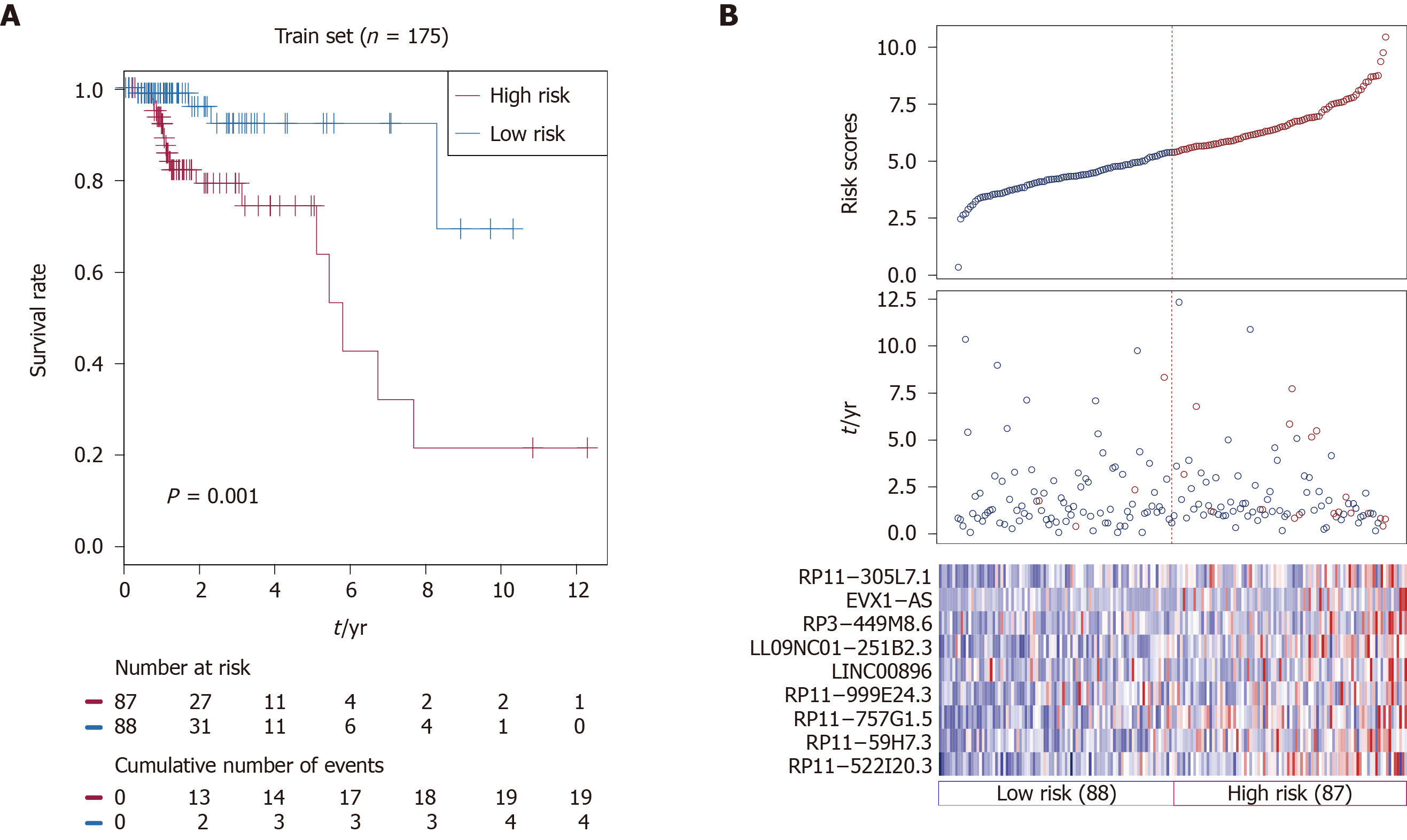
Figure 1 Construction of the nine-long non-coding ribonucleic acid signature in the training set.
A: Kaplan-Meier overall survival analysis in the training set between patients in the high-risk group and low-risk group; B: Distribution of risk score, overall survival and long non-coding ribonucleic acid expression for the patients in the training set. Columns represent patients.
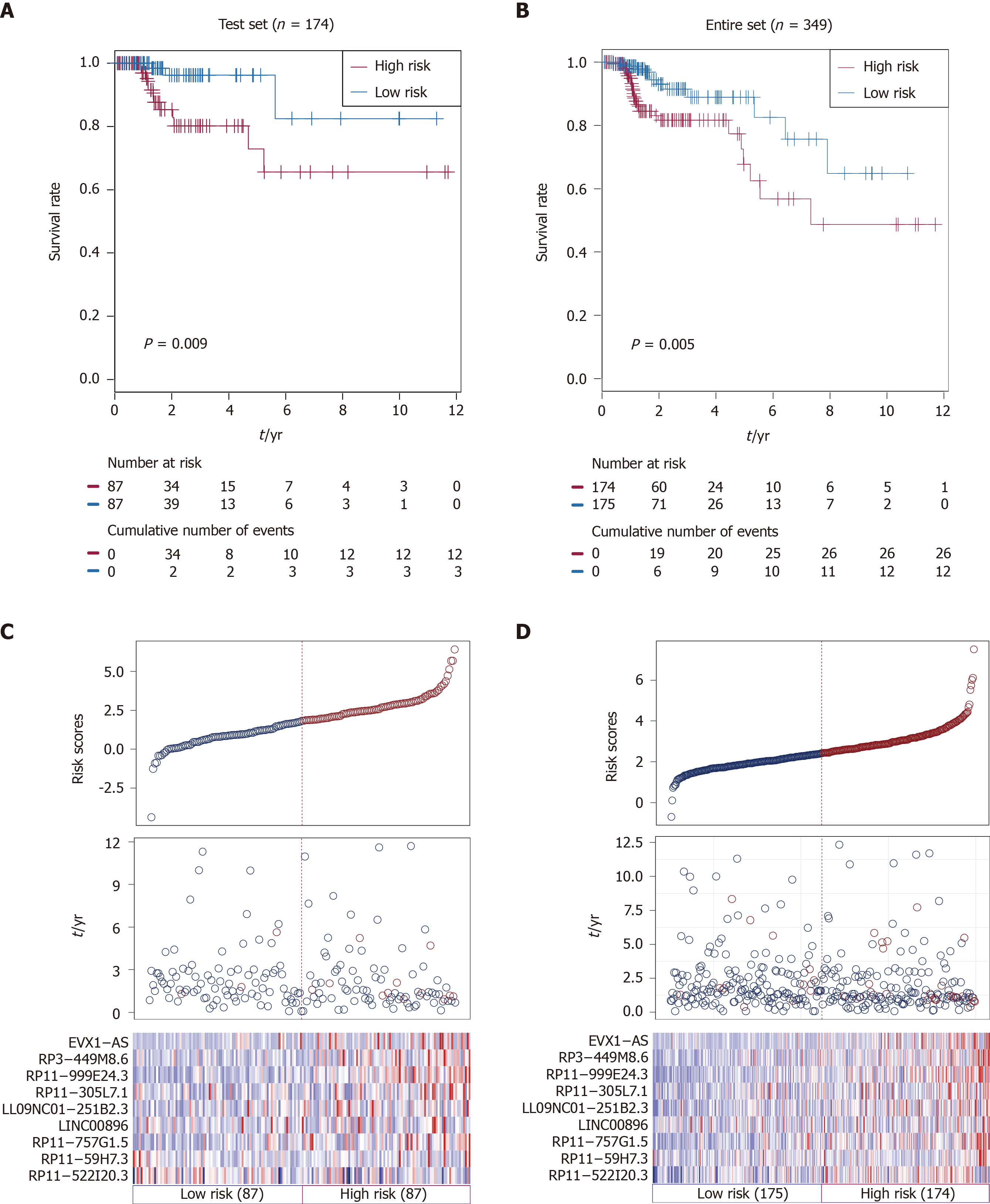
Figure 2 Validation of the nine-long noncoding ribonucleic acid signature in the testing set and entire set.
A: Kaplan-Meier overall survival (OS) analysis in the testing set between patients in the high-risk group and low-risk group; B: Kaplan-Meier OS analysis in the entire set between patients in the high-risk group and low-risk group; C: Distribution of risk score, OS and long noncoding ribonucleic acid expression for the patients in the testing set; D: Distribution of risk score, OS and long non-coding ribonucleic acid expression for patients in the entire set. Columns represent patients.
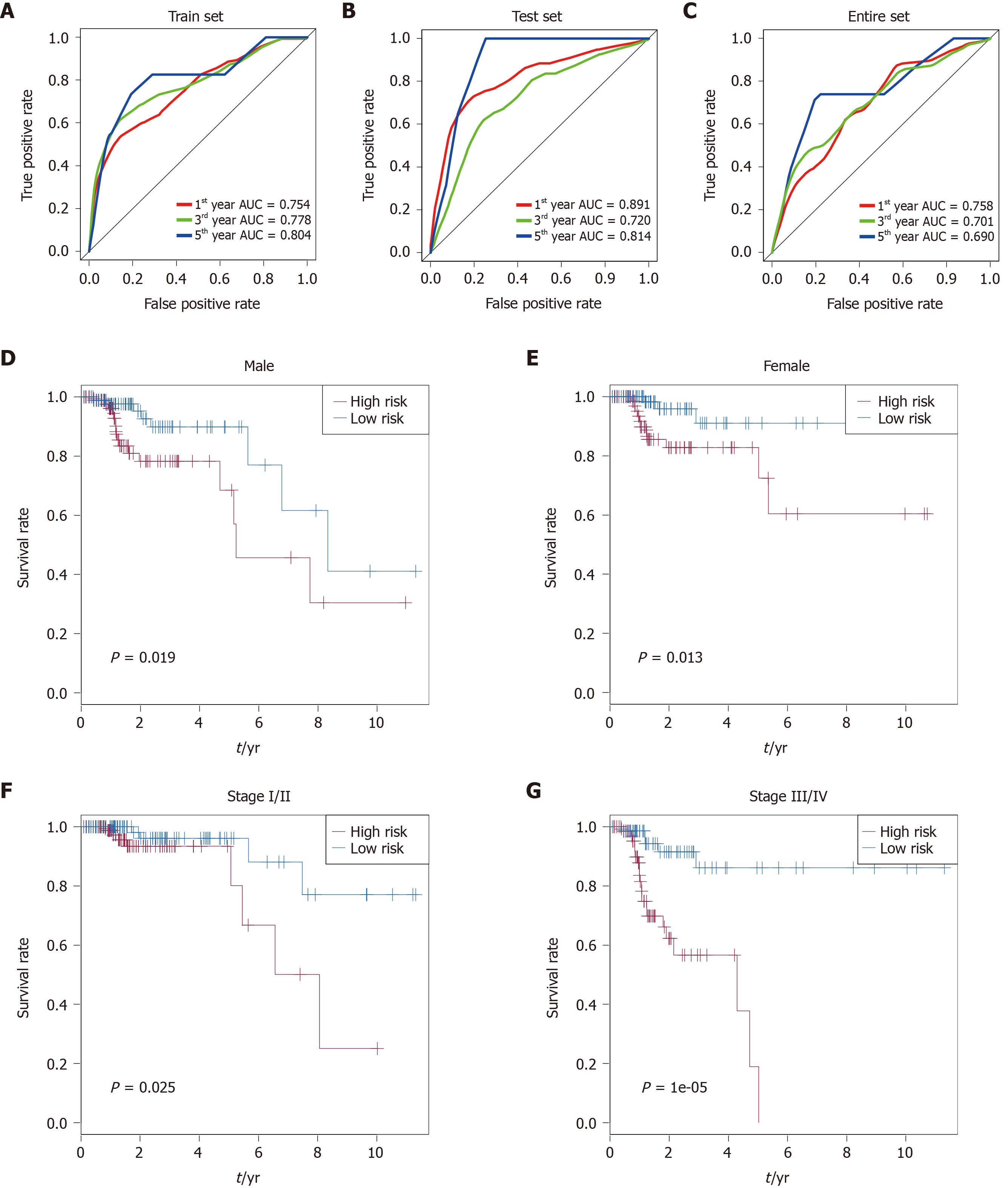
Figure 3 Performance assessment and comparison of the nine-long non-coding ribonucleic acids signature by survival receiver operating characteristic and stratification analyses.
A-C: Receiver operating characteristic analysis of overall survival for the nine-long noncoding ribonucleic acid signature in the training set, testing set and entire set; D: Kaplan-Meier curves for male patients; E: Kaplan-Meier curves for female patients; F: Kaplan-Meier curves for patients with stage I/II disease; G: Kaplan-Meier curves for patients with stage III/IV disease.
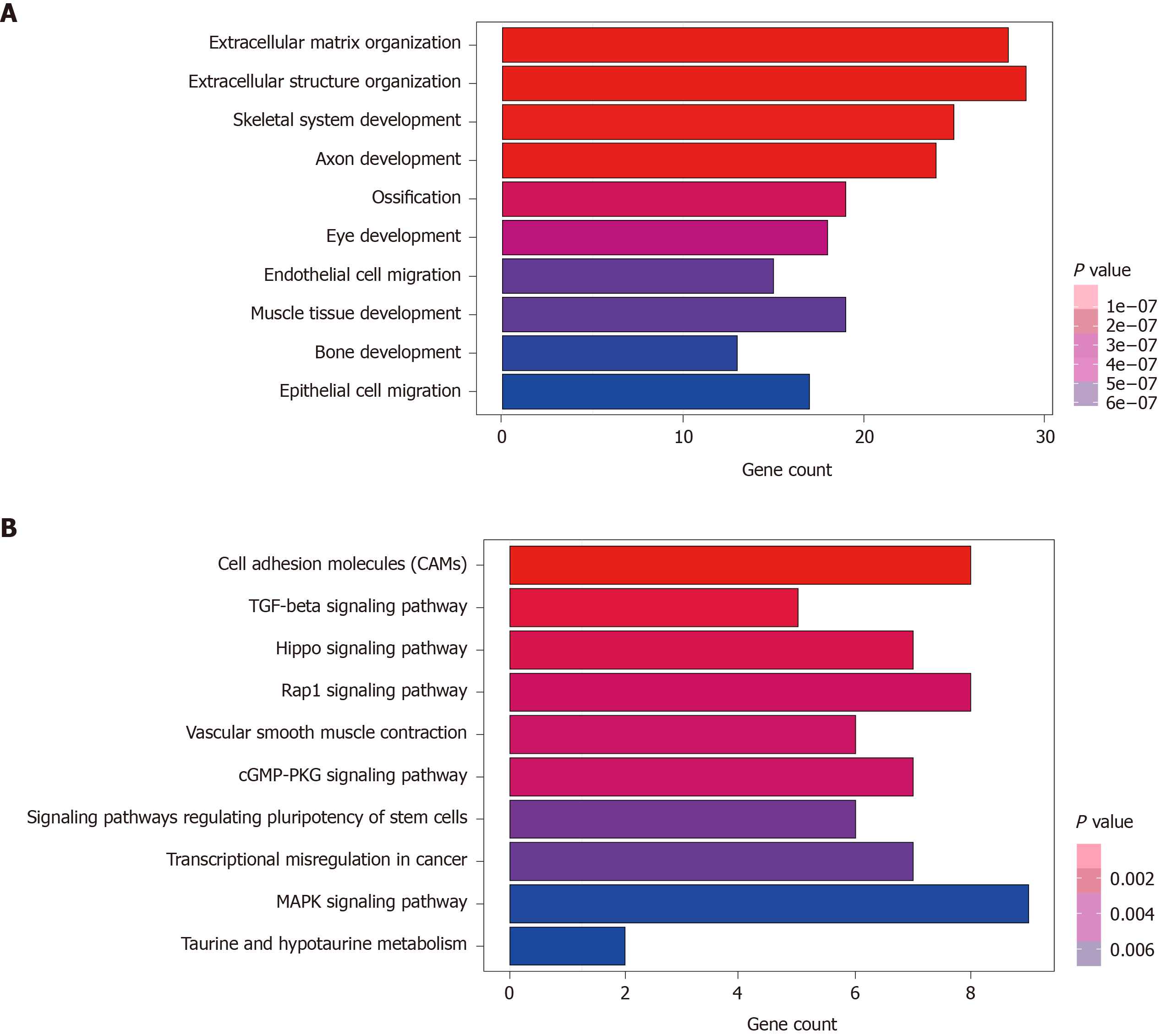
Figure 4 Functional annotation of predicted target genes of the nine long noncoding ribonucleic acids.
A: Gene Ontology enrichment (biological process) of predicted target genes; B: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways of predicted target genes.
- Citation: Zong Z, Hu CG, Zhou TC, Yu ZM, Tang FX, Tian HK, Li H, Wang H. Nine-long non-coding ribonucleic acid signature can improve the survival prediction of colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Surg 2021; 13(2): 210-221
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v13/i2/210.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v13.i2.210