Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Dec 27, 2021; 13(12): 1673-1684
Published online Dec 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i12.1673
Published online Dec 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i12.1673
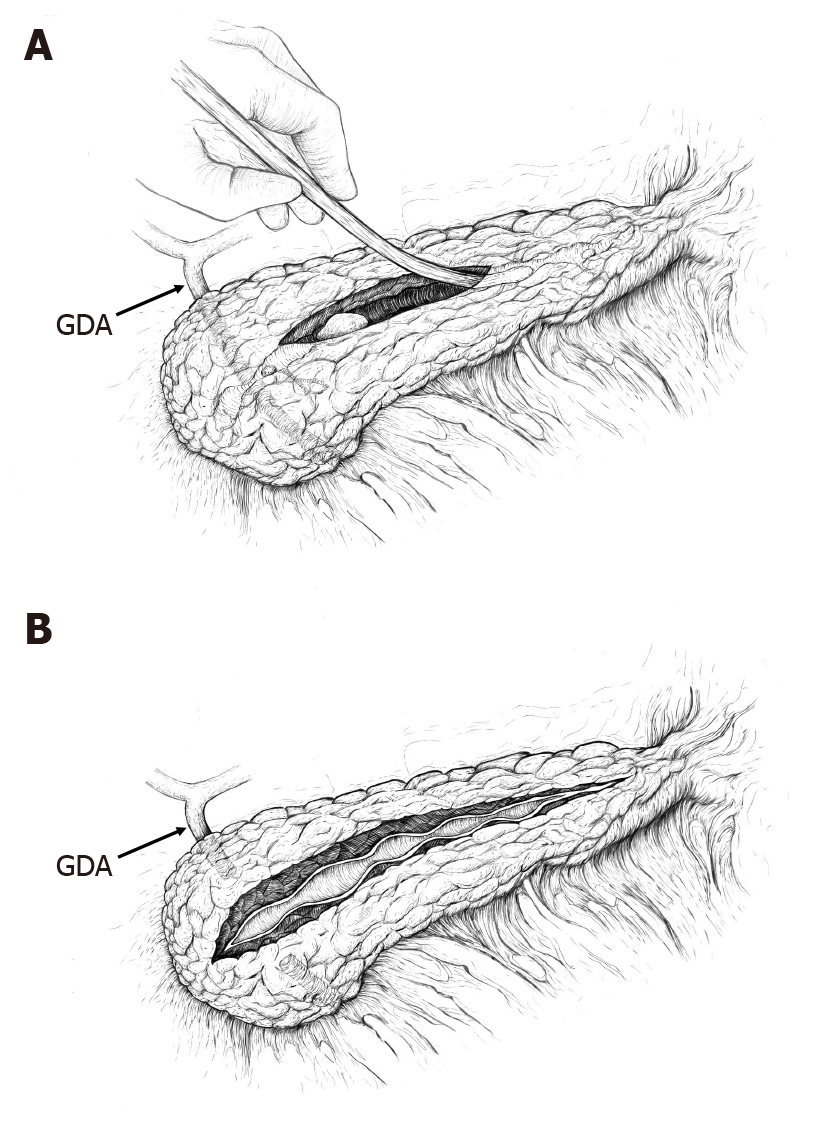
Figure 1 Two surgical options: ‘Short’ and ‘long’ ductotomy.
A: ‘Short’ ductotomy (median length 40 mm), probing of the pancreatic duct; B: ‘Long’ ductotomy (length up to 100 mm). GDA: Gastroduodenal artery.
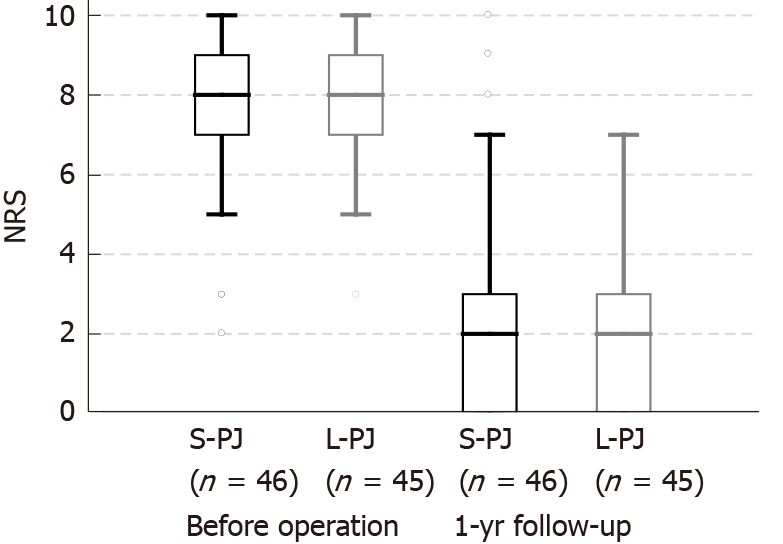
Figure 2 Box plot of the intensity of pain according to the numerical rating scale (0-10) before surgery and 1 yr after surgical treatment of chronic pancreatitis.
NRS: Numerical rating scale; S-PJ: Short pancreaticojejunostomy; L-PJ: Long pancreaticojejunostomy.
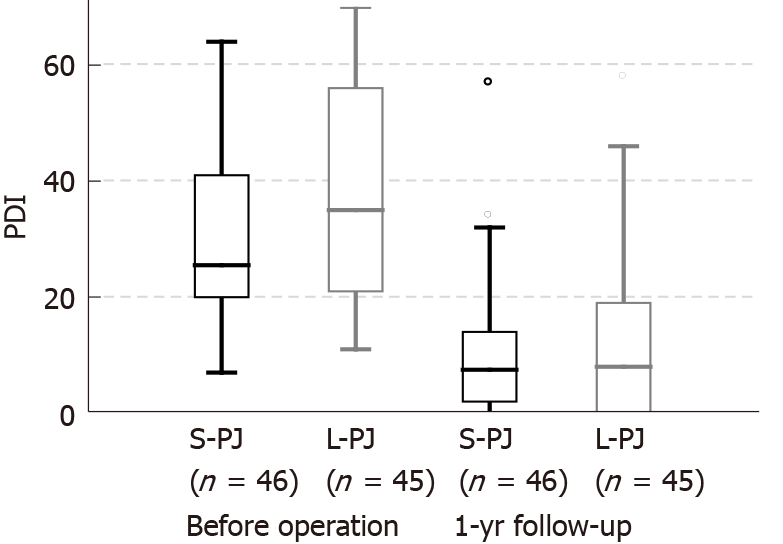
Figure 3 Box plot of the pain disability index (0-70) before surgery and 1 yr after surgical treatment of chronic pancreatitis.
PDI: Pain disability index; S-PJ: Short pancreaticojejunostomy; L-PJ: Long pancreaticojejunostomy.
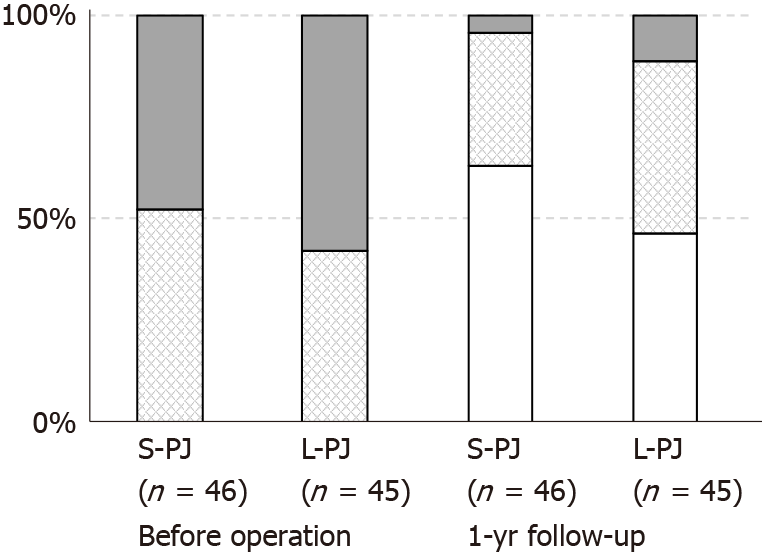
Figure 4 Data on pain treatment before surgery and 1 yr after surgical treatment of chronic pancreatitis.
Gray bars, opioid users; diamond-filled bars, users of non-opioid painkillers; white bars, non-users of any painkillers. S-PJ: Short pancreaticojejunostomy; L-PJ: Long pancreaticojejunostomy.
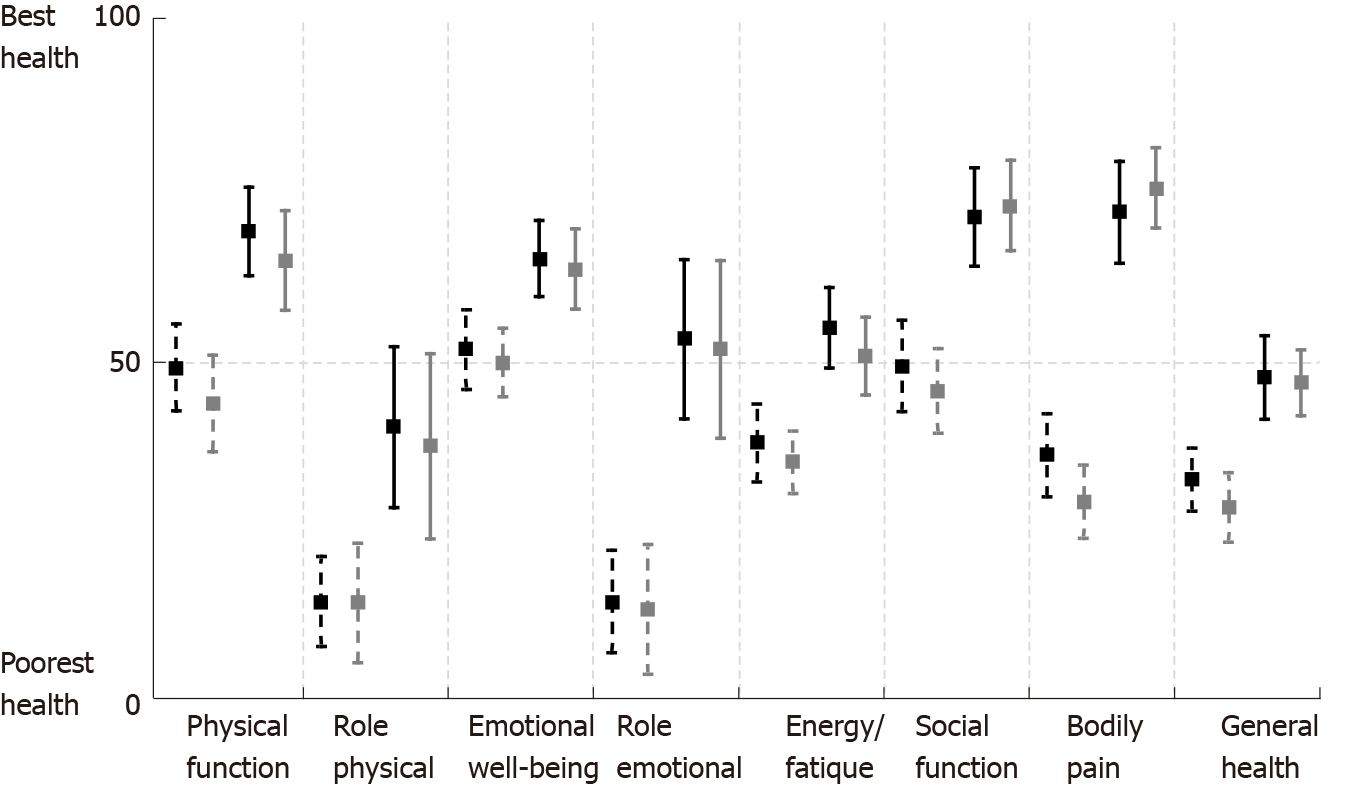
Figure 5 Quality of life RAND SF-36 mean scores, with 95% confidence interval, before surgery and 1 yr after surgical treatment of chronic pancreatitis.
Black, short pancreaticojejunostomy (n = 46), gray, long pancreaticojejunostomy (n = 45); dashed lines, before surgery; solid lines, 1 yr after surgical treatment of chronic pancreatitis.
- Citation: Murruste M, Kirsimägi Ü, Kase K, Veršinina T, Talving P, Lepner U. ‘Short’ pancreaticojejunostomy might be a valid option for treatment of chronic pancreatitis in many cases. World J Gastrointest Surg 2021; 13(12): 1673-1684
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v13/i12/1673.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v13.i12.1673