Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Dec 27, 2021; 13(12): 1638-1650
Published online Dec 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i12.1638
Published online Dec 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i12.1638
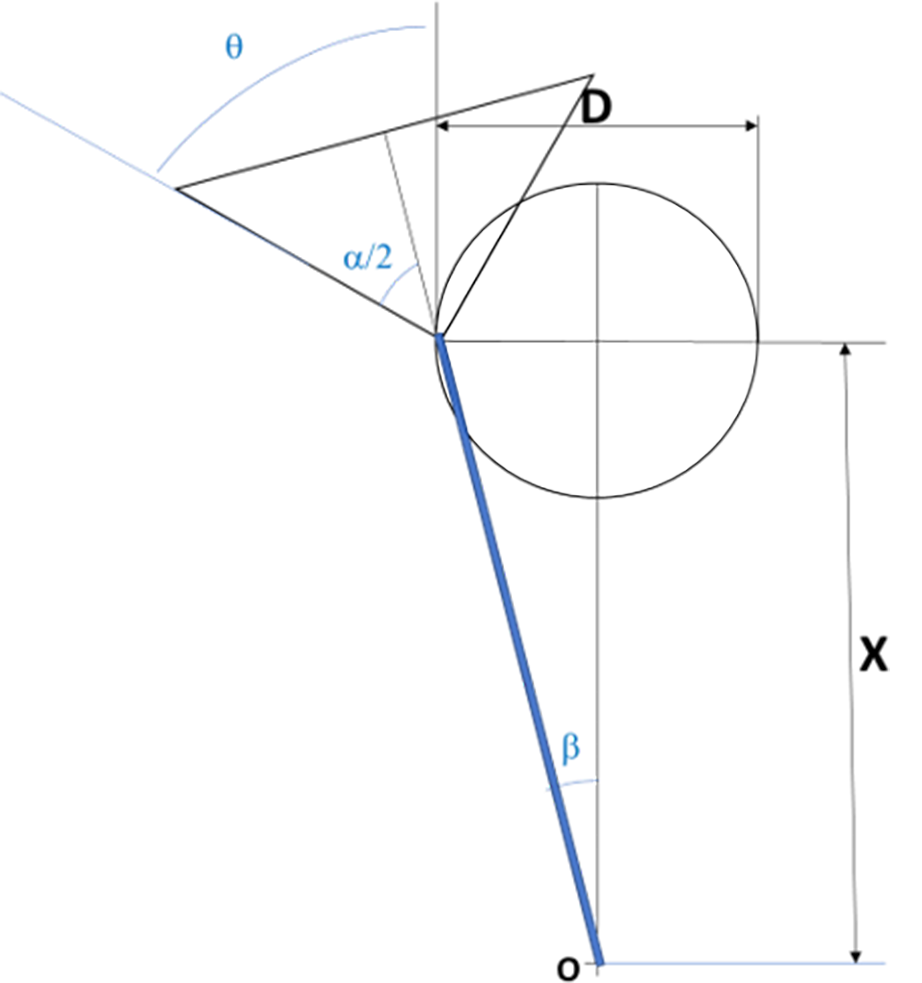
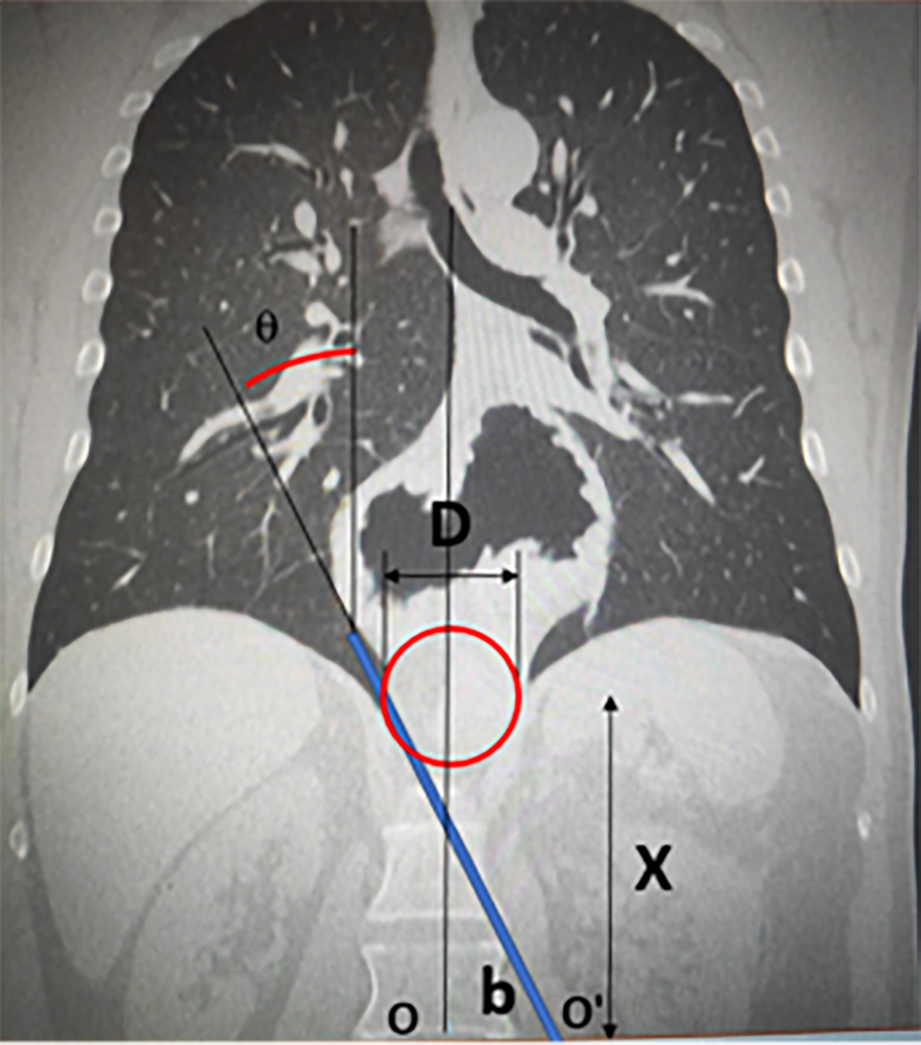
Figure 1 Geometric model for laparoscopy camera field of vision, 0º.
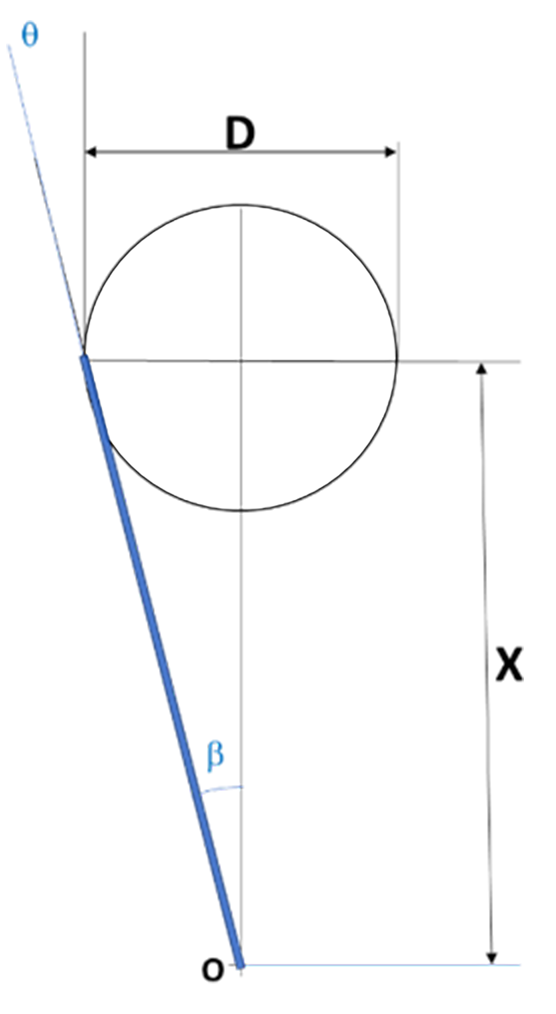
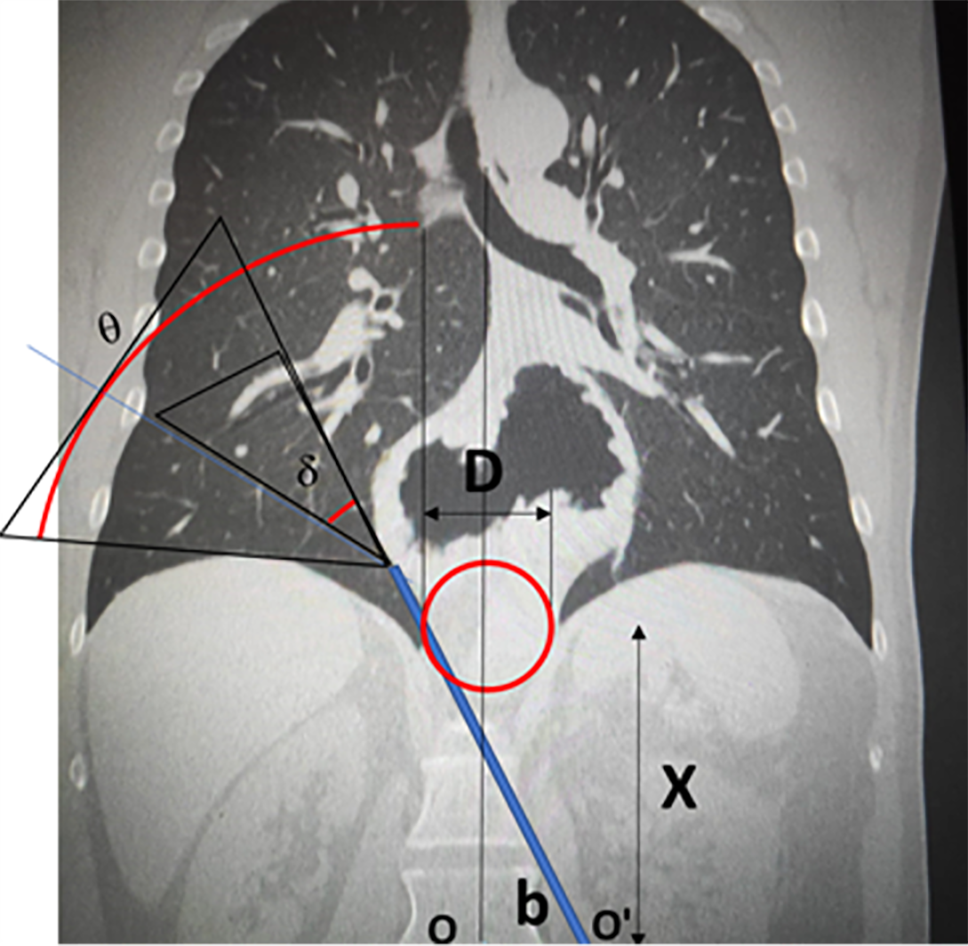
Figure 2 Angle of vision for 0º and 30º camera and geometric model (30º).
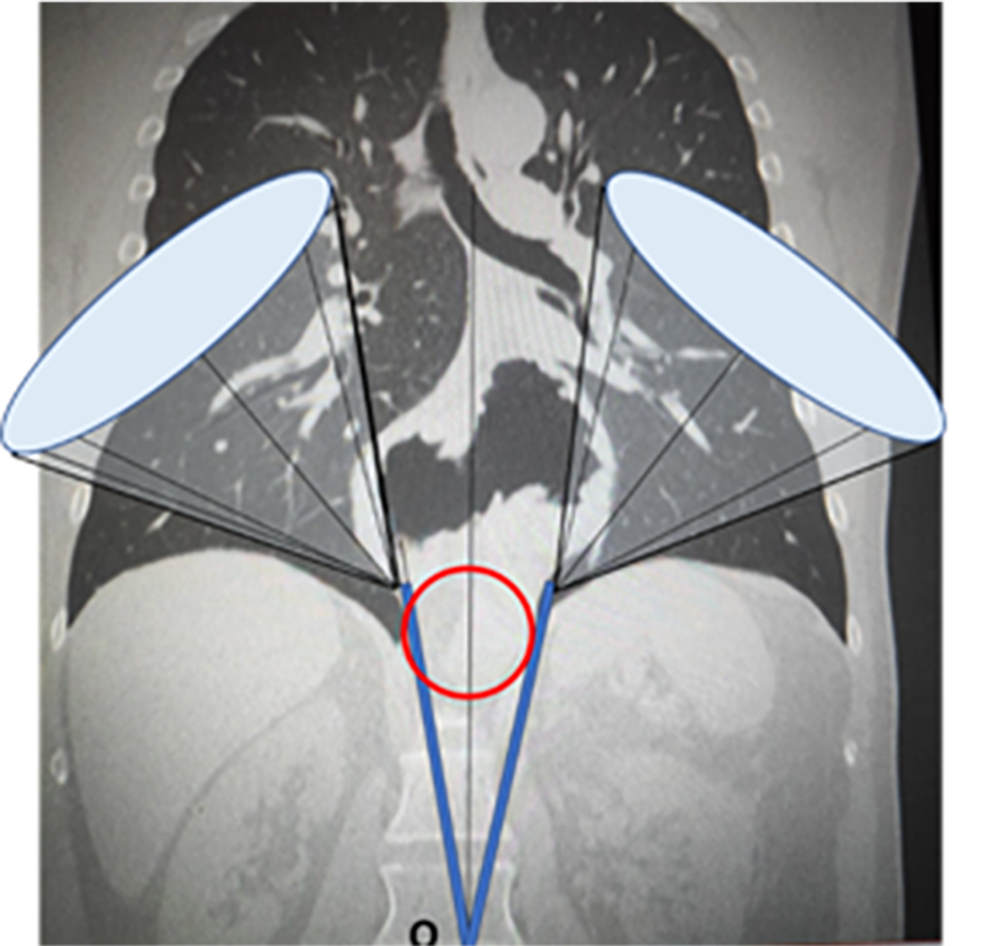
Figure 3 Projections of the operating field cones of vision.
Figure 4 Geometric model of working area with laparoscopic operative instruments.
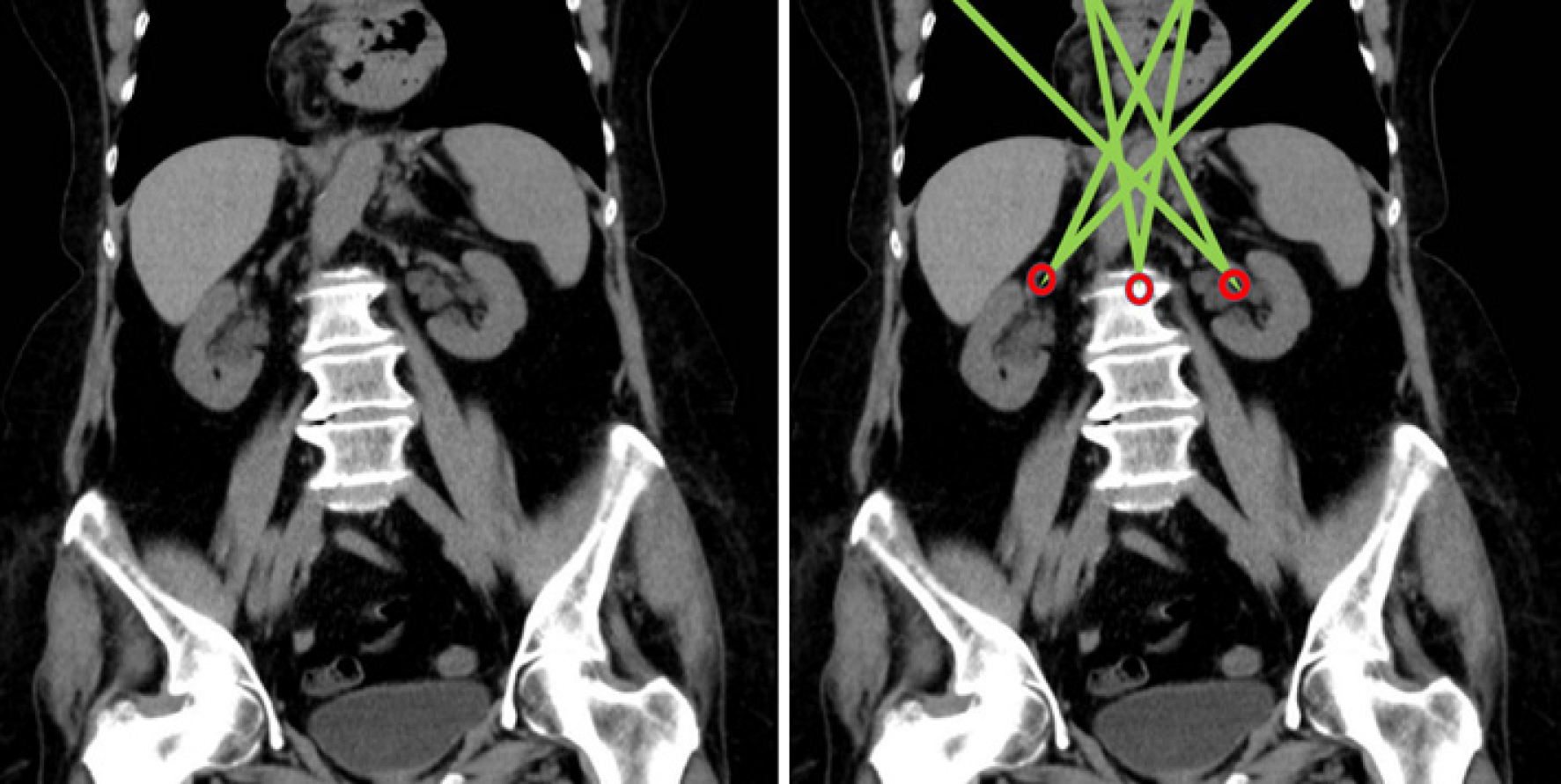
Figure 5 Model superimposed on image: Working area and field of vision with central trocar.
Figure 6 Working area with lateral displacement of the trocar.
Figure 7 Field of vision with lateral displacement of the trocar and camera at 30º.
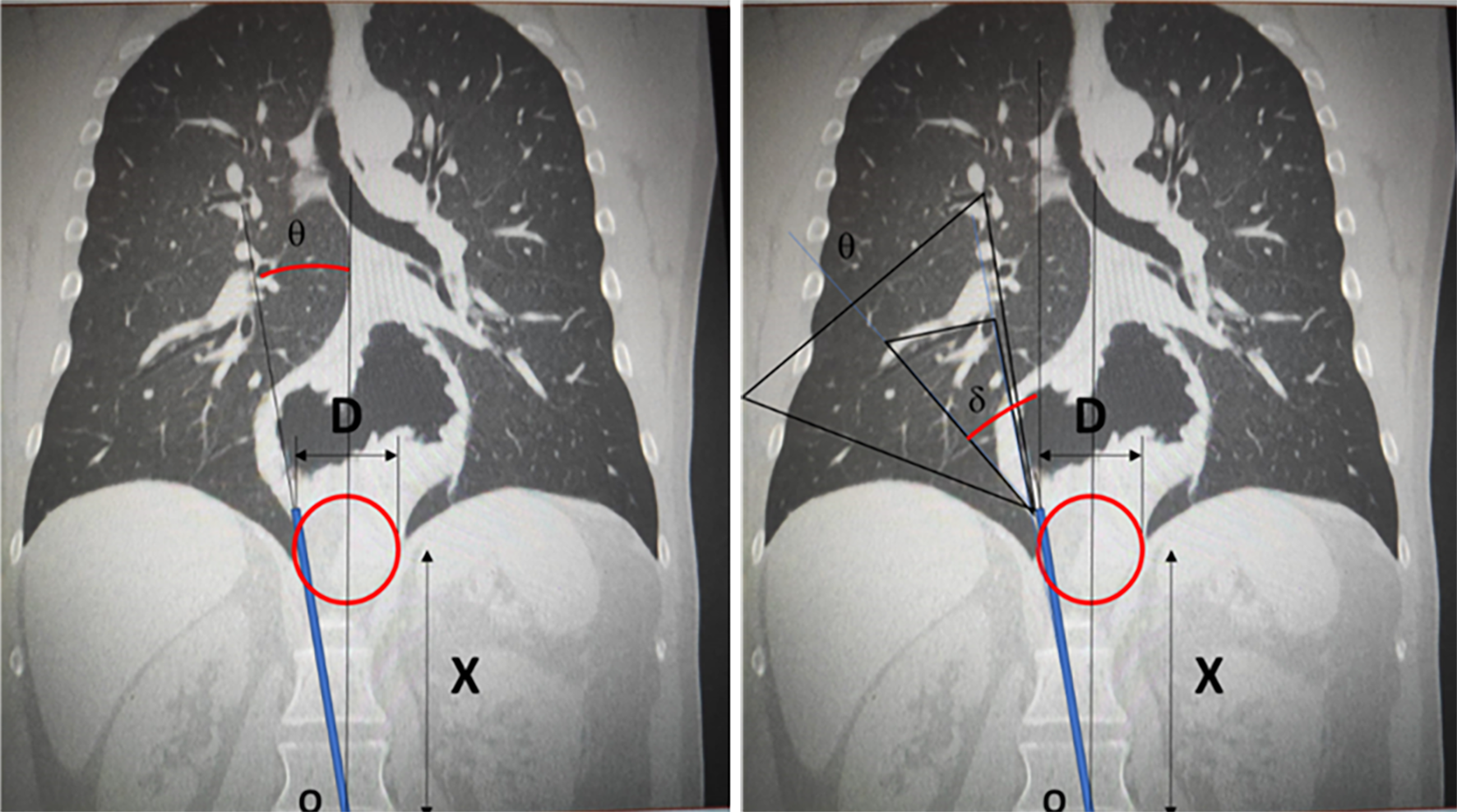
Figure 8 Simulation of the working area with different entry trocars, in a laparoscopically accessible giant hiatal hernia.
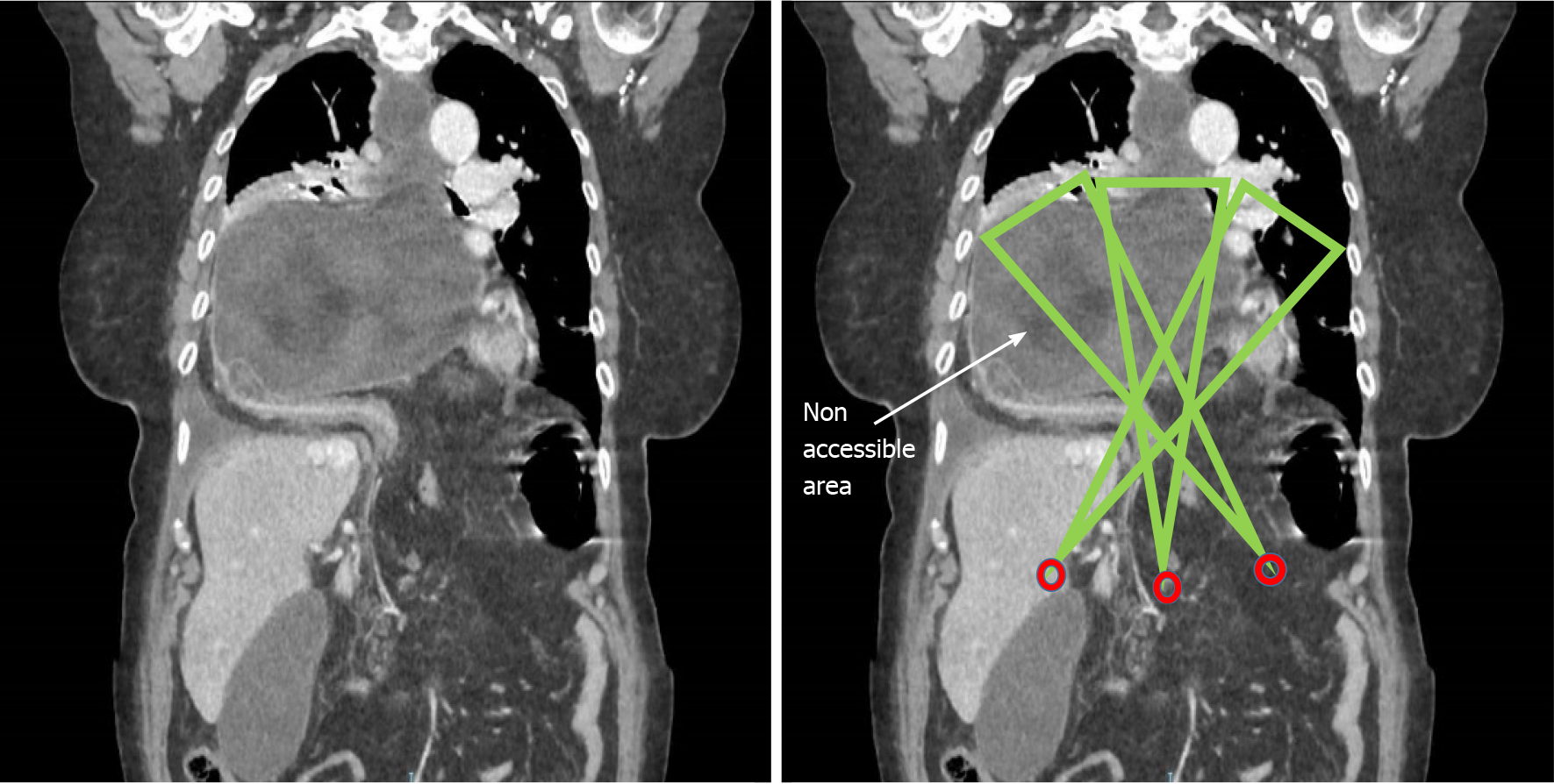
Figure 9 Simulation of the working area with different entry trocars, in a giant hiatal hernia for which the laparoscopic approach is impractical (the arrow shows the area non-accessible to instruments).
- Citation: Lara FJP, Zubizarreta Jimenez R, Moya Donoso FJ, Hernández Gonzalez JM, Prieto-Puga Arjona T, del Rey Moreno A, Pitarch Martinez M. Preoperative calculation of angles of vision and working area in laparoscopic surgery to treat a giant hiatal hernia. World J Gastrointest Surg 2021; 13(12): 1638-1650
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v13/i12/1638.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v13.i12.1638