Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Nov 27, 2021; 13(11): 1315-1326
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i11.1315
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i11.1315
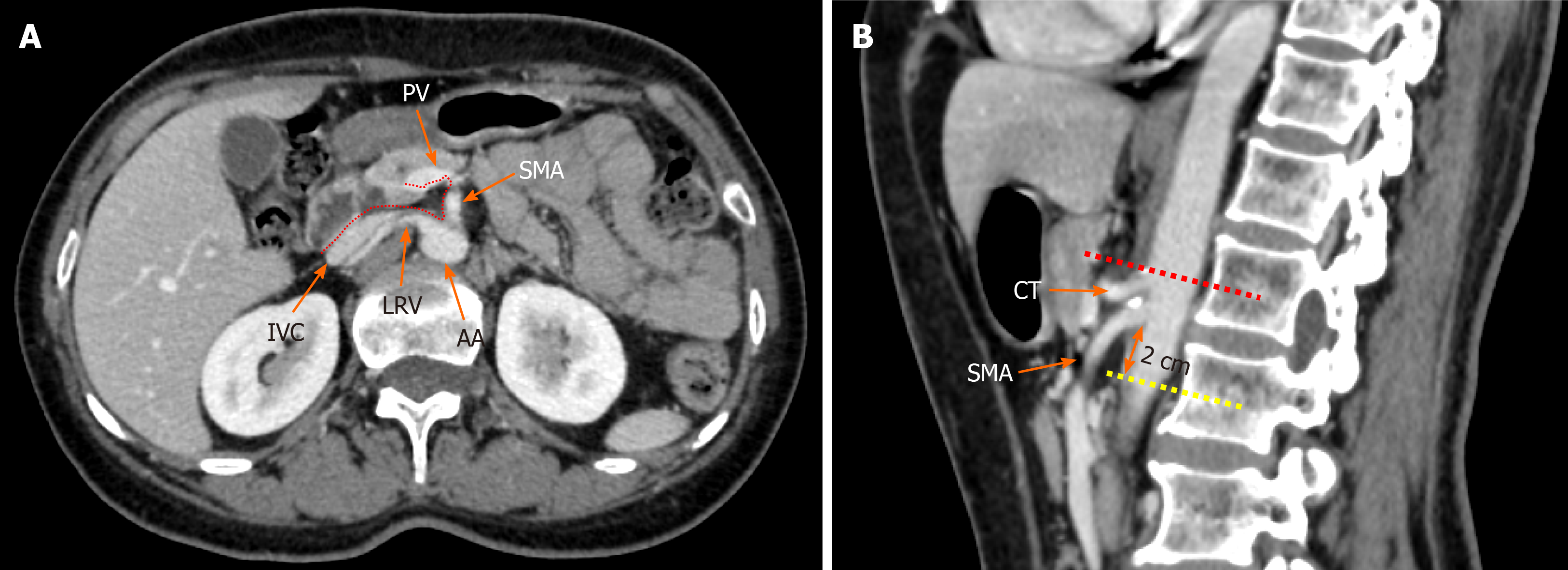
Figure 1 Radiological depiction of the mesopancreas in computed tomography.
A: The dotted line outlines the boundary of the mesopancreas, a region identified as the retro pancreatic retro portal tissue; B: The inferior boundary of the mesopancreas is 2 cm below the origin of superior mesenteric artery. PV: Portal vein; SMA: Superior mesenteric artery; LRV: Left renal vein; IVC: Inferior vena cava; AA: Aorta artery; CT: Celiac trunk.
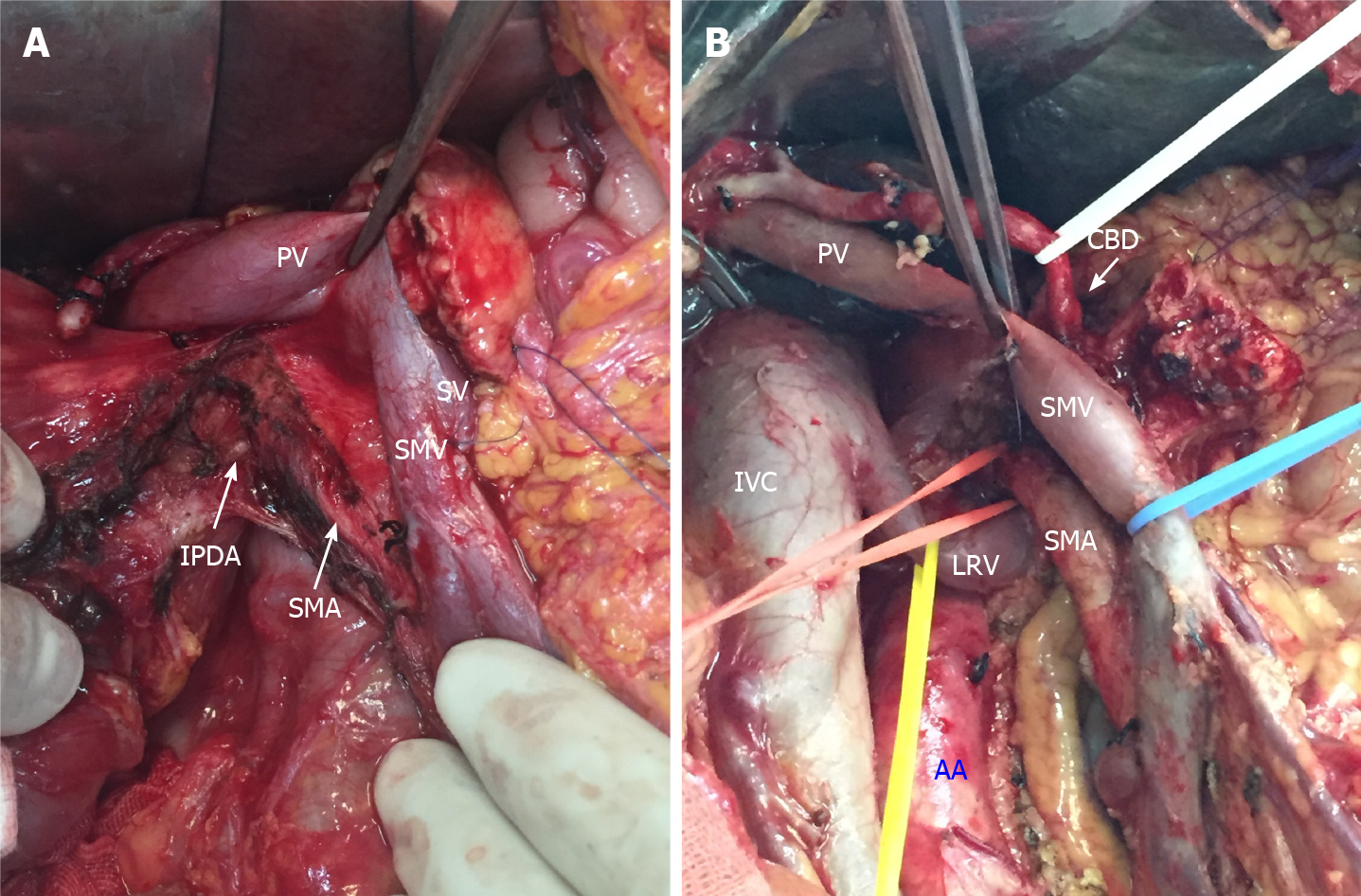
Figure 2 Key steps of total mesopancreas excision.
A: Dissection of the right semi-circumference of the superior mesenteric artery and celiac trunk; B: Clearance of the retropancreatic retroportal space (mesopancreas triangular). PV: Portal vein; SV: Splenic vein; SMV: Superior mesenteric vein; SMA: Superior mesenteric artery; IPDA: Inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries; IVC: Inferior vena cava; LRV: Left renal vein; AA: Aorta artery; CBD: Common bile duct.
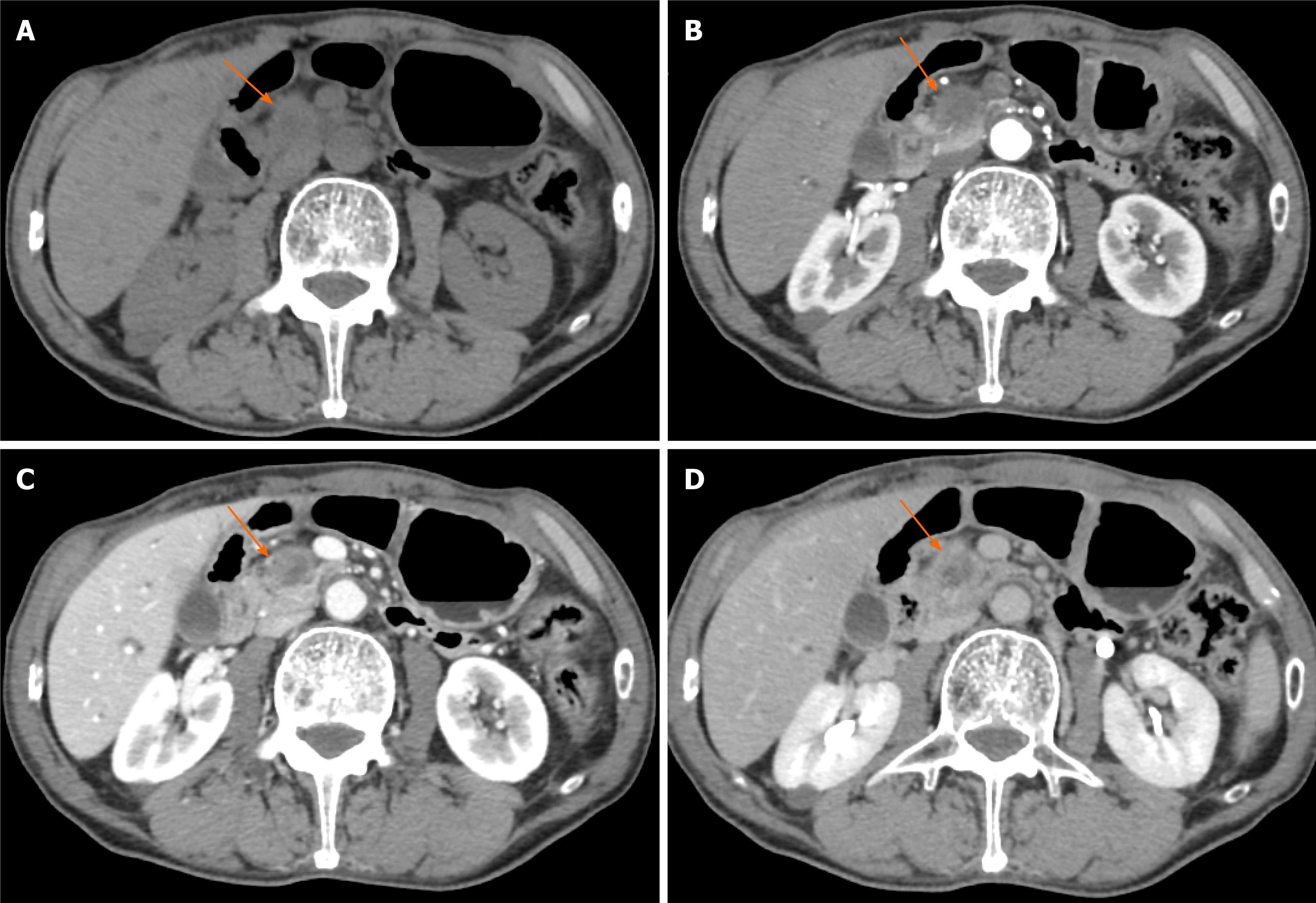
Figure 3 Typical CT features of pancreatic head carcinoma in a 73-year-old male patient.
A: On noncontrast CT imaging a slightly low-density mass (arrow) in the pancreatic head area was identified; B–D: On contrast CT images, the tumor shows an avascular tumor with a lower density than normal pancreatic parenchyma on arterial phase (B), venous phase (C), and delay phase (D). CT: Computed tomography.
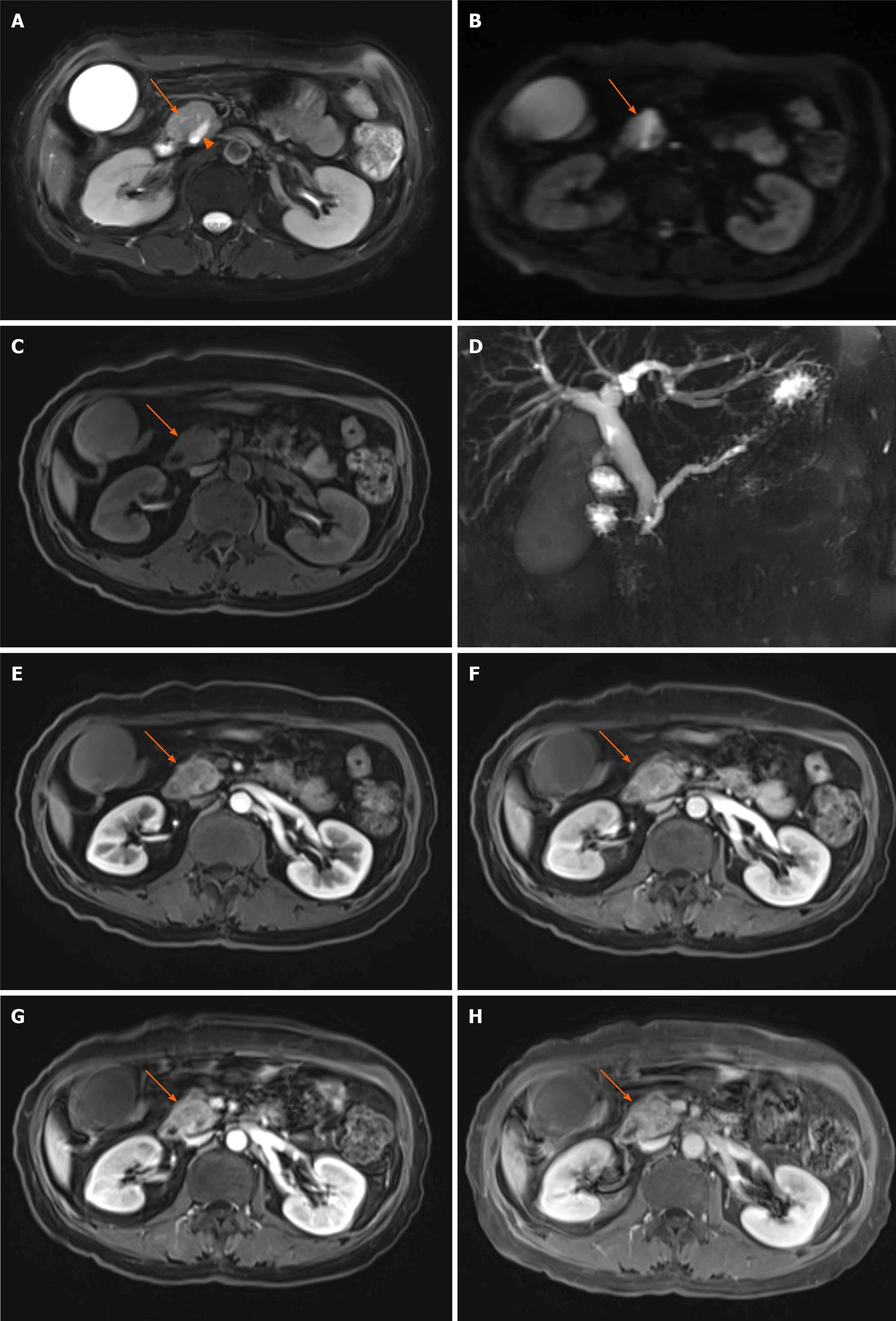
Figure 4 Typical magnetic resonance features of pancreatic head carcinoma in a 57-year-old female patient.
A–C: Swollen pancreatic head (arrow) with slightly higher signal on T2-weighted imaging (WI) (A) and diffusion-weighted imaging (B), and low signal on T1WI (C) was detected; D: Notes that the dilation of pancreatic duct (arow head) and double duct sign on magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography; E–H: After administration of contrast agent, the tumor shows a progressive enhancement pattern similar to computed tomography on early arterial phase (E), late arterial phase (F), venous phase (G), and delay phase (H).
- Citation: Feng P, Cheng B, Wang ZD, Liu JG, Fan W, Liu H, Qi CY, Pan JJ. Application and progress of medical imaging in total mesopancreas excision for pancreatic head carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Surg 2021; 13(11): 1315-1326
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v13/i11/1315.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v13.i11.1315