Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Surg. May 27, 2020; 12(5): 226-235
Published online May 27, 2020. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v12.i5.226
Published online May 27, 2020. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v12.i5.226
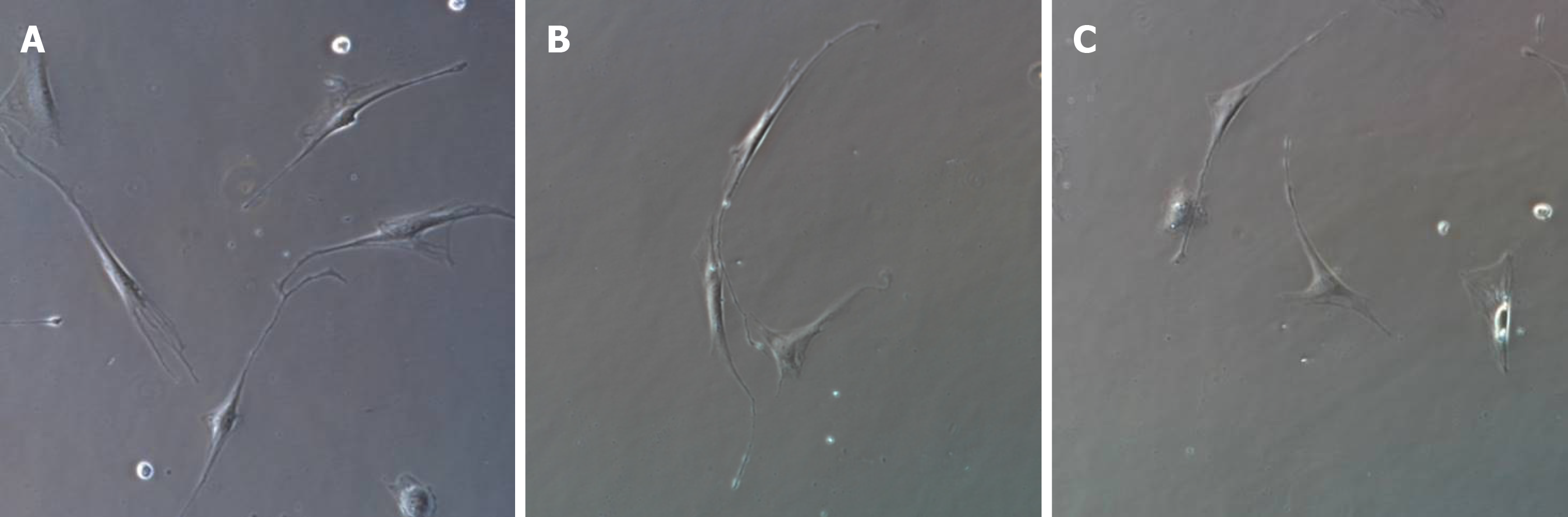
Figure 1 Inverted microscopic images of interstitial Cajal-like cell culture after 1 wk (× 400).
A: The cells were spindle-shaped, round, or oval, with connections between processes; B: The cells were spindle-shaped, with connections between processes; C: The cells were triangular.
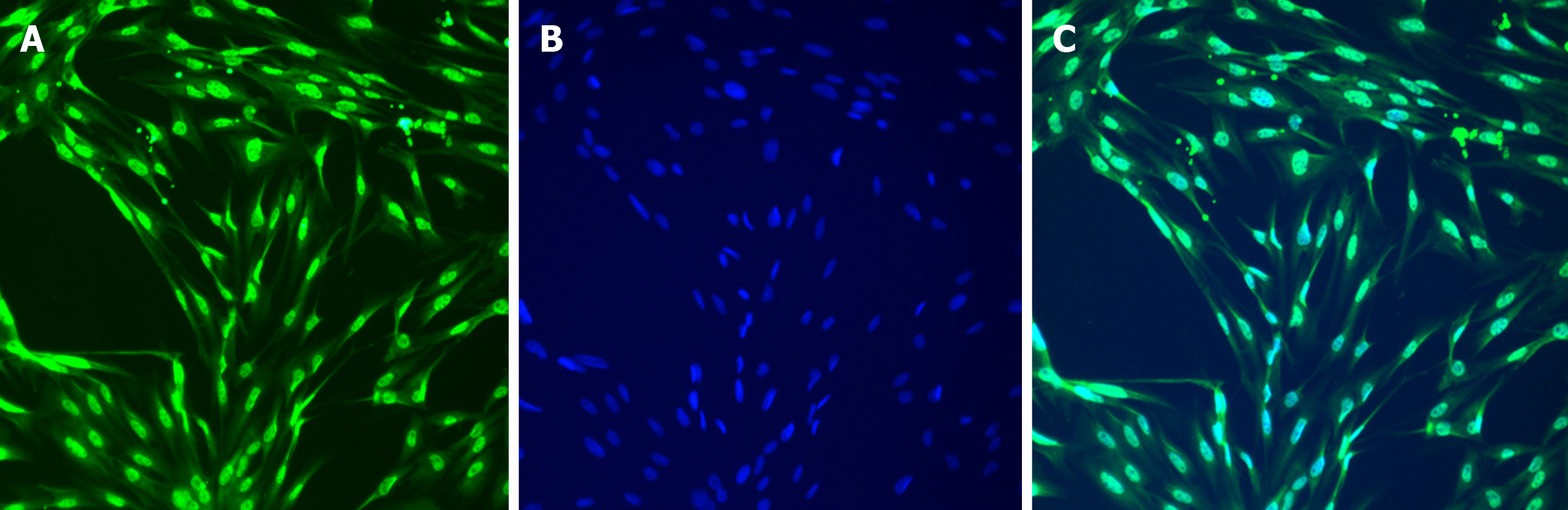
Figure 2 Immunofluorescence staining of third generation interstitial Cajal-like cells (× 200).
A: c-Kit fluorescent antibody staining; B: DAPI staining; C: Merged image.
Figure 3 Immunofluorescence staining of third generation interstitial Cajal-like cells (× 400).
A: c-Kit fluorescent antibody staining; B: DAPI staining; C: Merged image.
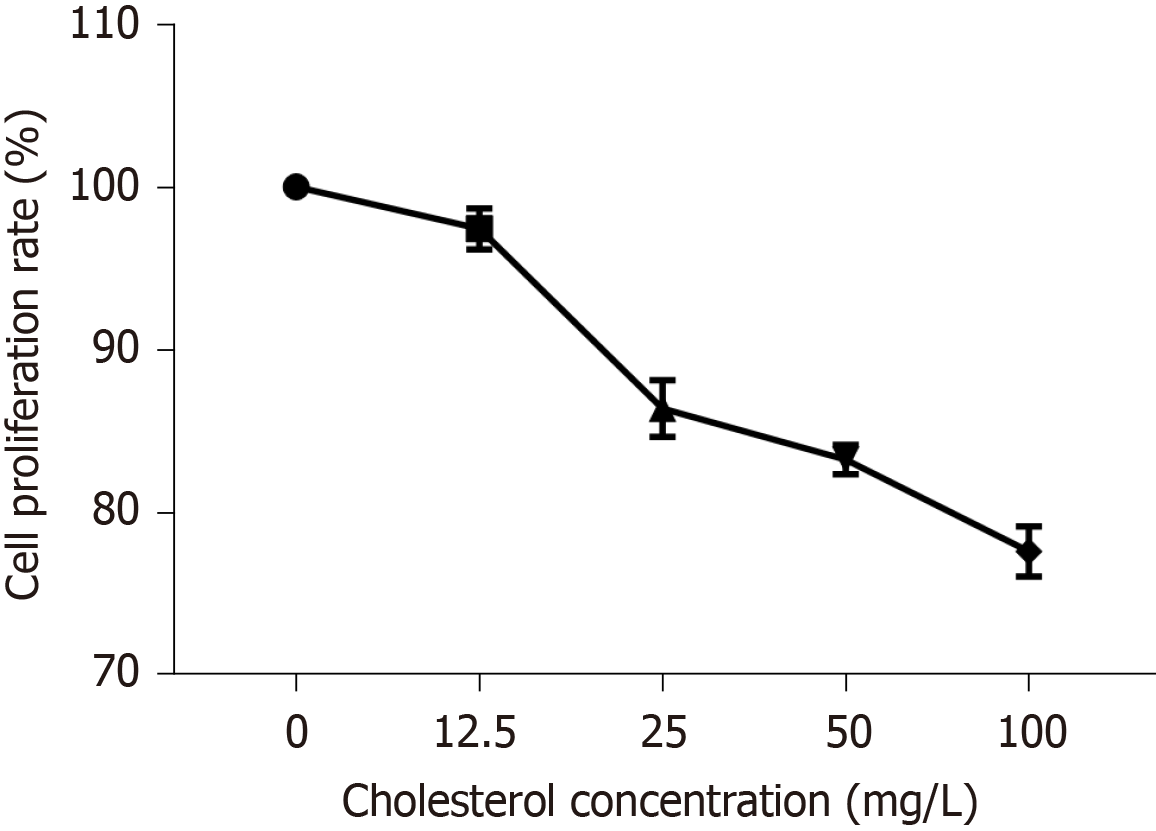
Figure 4 Effect of different concentrations of cholesterol on interstitial Cajal-like cell proliferation.
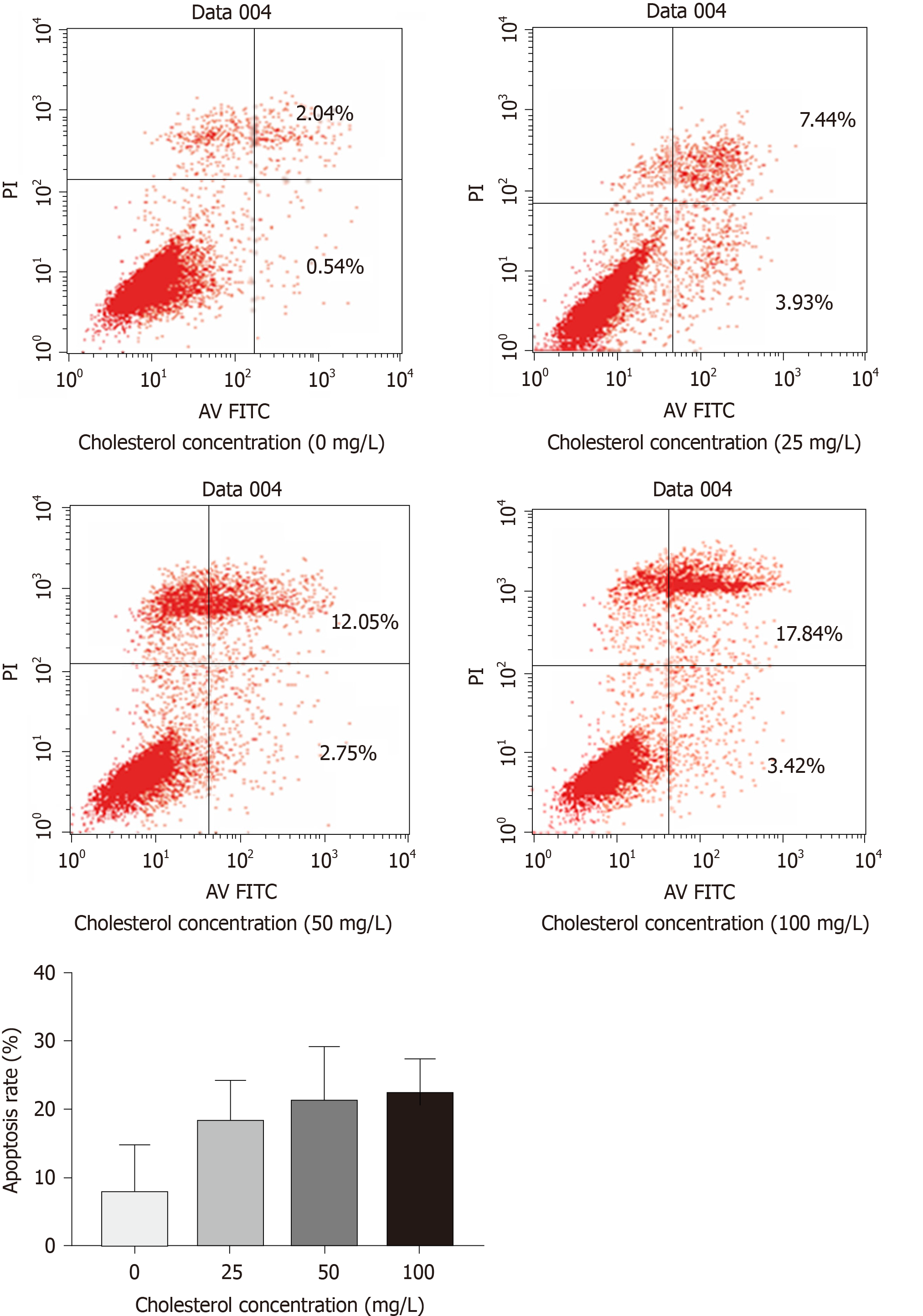
Figure 5 Effect of different concentrations of cholesterol on the rate of apoptosis in interstitial Cajal-like cells.
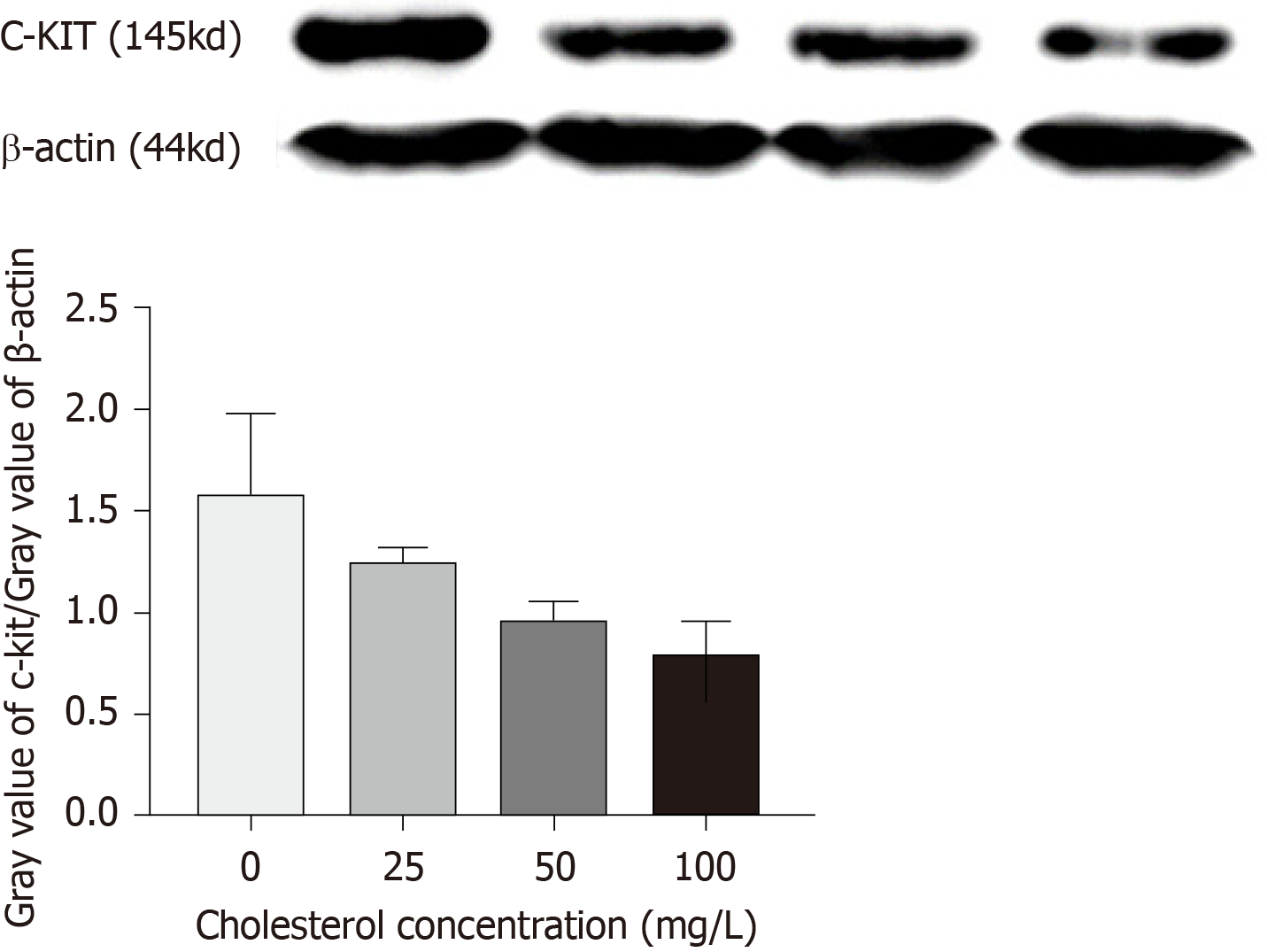
Figure 6 Expression of c-Kit protein in interstitial Cajal-like cells of each group.
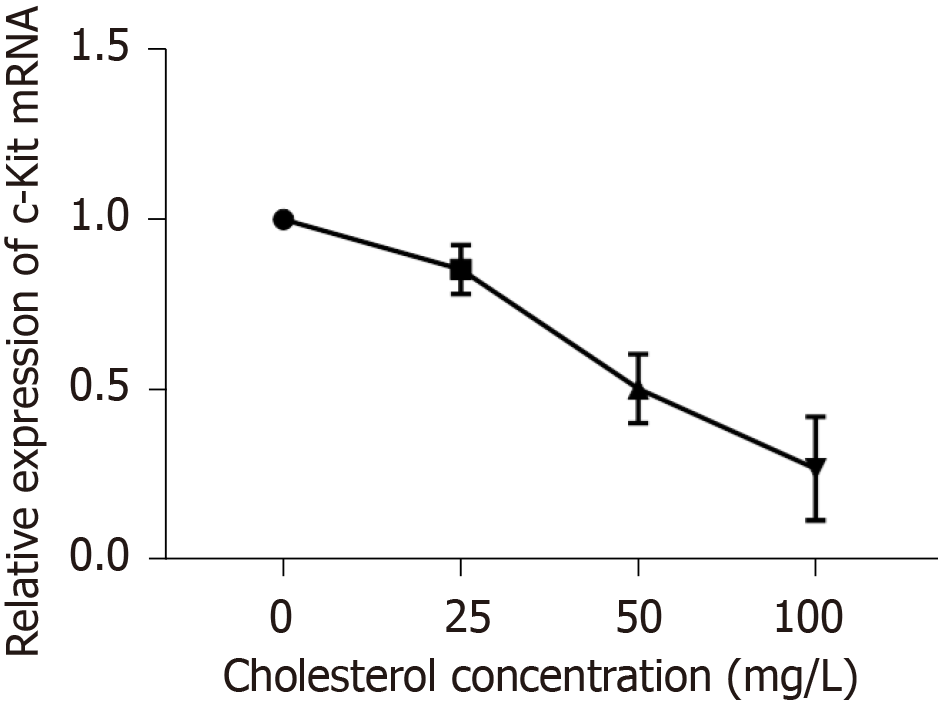
Figure 7 Statistical analysis of effect of cholesterol on the expression of c-Kit mRNA in interstitial Cajal-like cells.
- Citation: Fu BB, Xu JH, Wu SD, Fan Y. Effect of cholesterol on in vitro cultured interstitial Cajal-like cells isolated from guinea pig gallbladders. World J Gastrointest Surg 2020; 12(5): 226-235
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v12/i5/226.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v12.i5.226