Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Apr 27, 2020; 12(4): 138-148
Published online Apr 27, 2020. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v12.i4.138
Published online Apr 27, 2020. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v12.i4.138
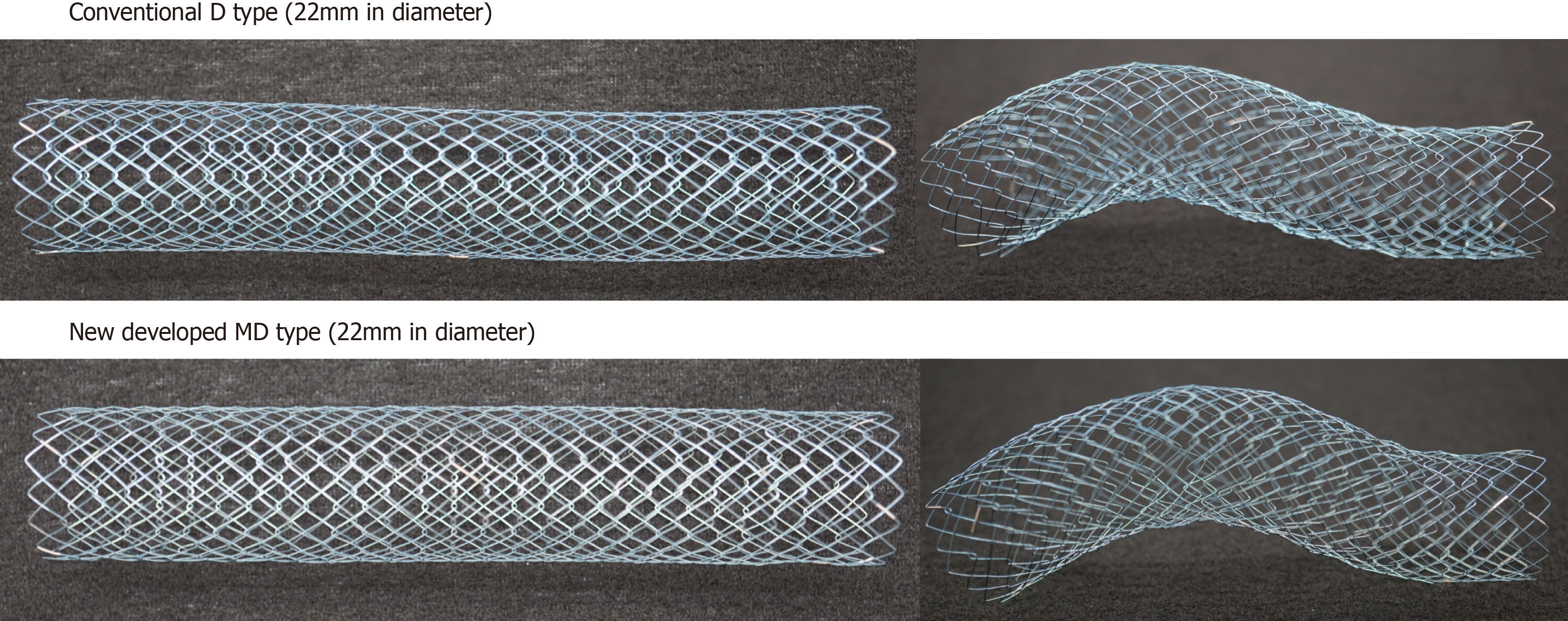
Figure 1 The newly developed Niti-S MD type stent (22 mm in diameter).
The newly developed stent, “Niti-S MD type,” has a diameter of 22 mm, that can be introduced into a 9-Fr delivery system while maintaining the Niti-S D type structure.
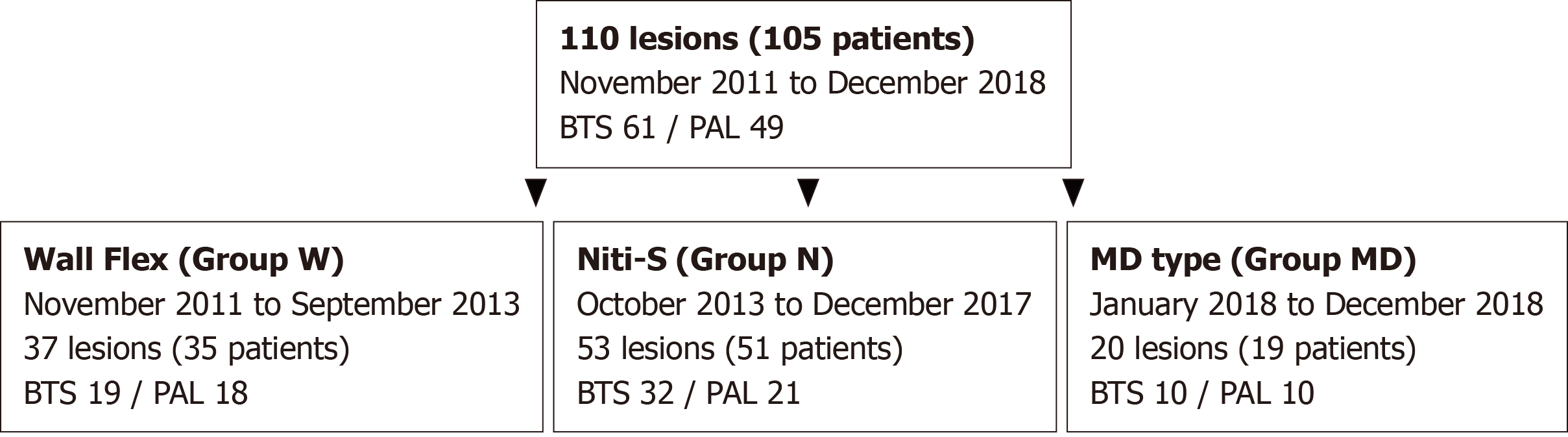
Figure 2 Flow chart of patient allocation.
Of the 105 patients (110 lesions) who were enrolled in the study, 35 patients (37 lesions) were treated with WallFlex stents (Group W), 51 patients (53 lesions) with Niti-S stents (Group N), and 19 patients (20 lesions) with the newly developed Niti-S MD type stent (Group MD). BTS: Bridge-to-surgery; PAL: Palliative.
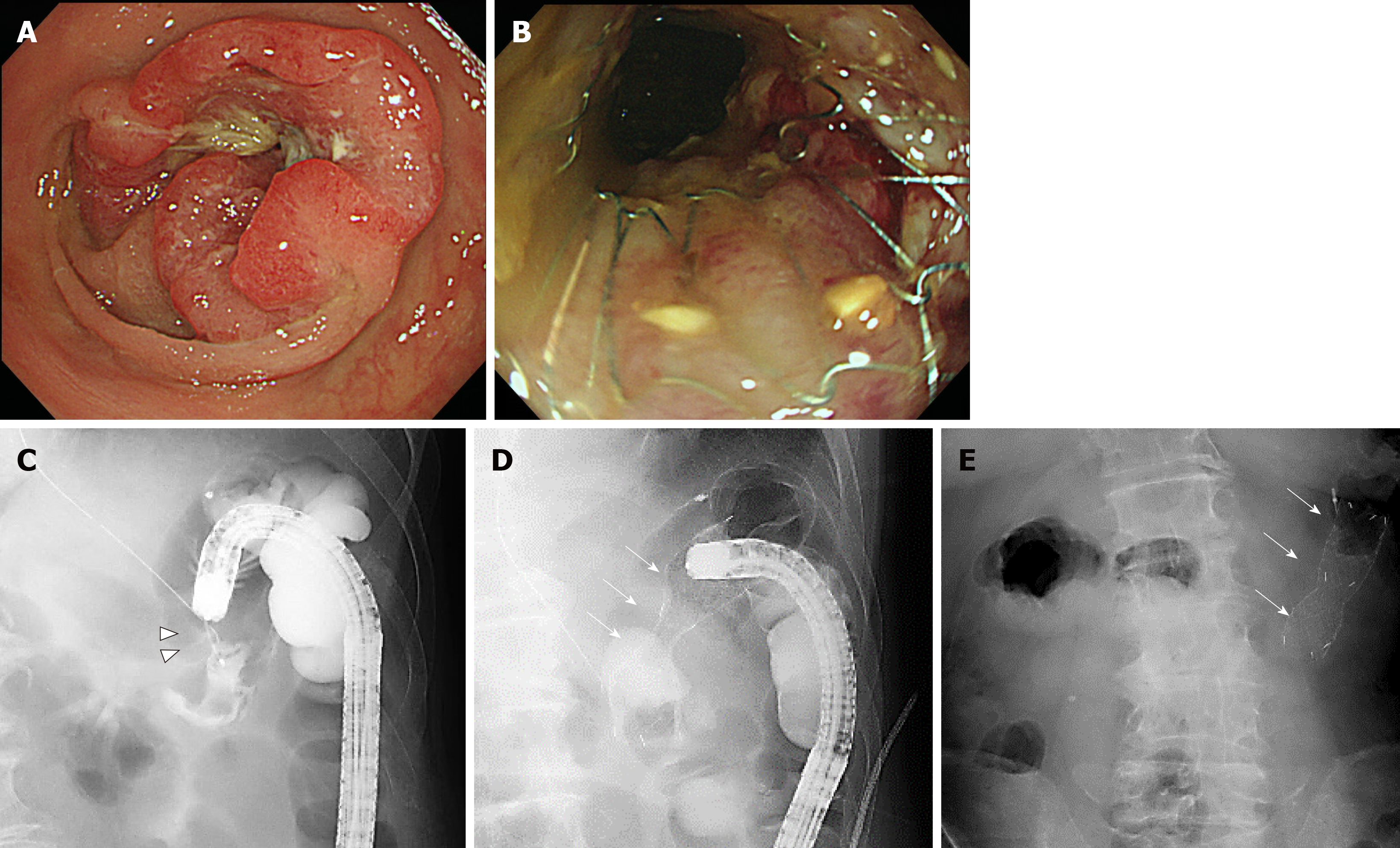
Figure 3 One of the bridge-to-surgery cases using the newly developed Niti-S MD type stent.
A and C: The patient was an 83-year-old man with peritoneal type 2 advanced colorectal cancer (arrowhead) in the transverse colon; B and D: Using a smaller caliber colonoscope, we placed a 22 mm × 8 cm stent (arrow); E: Abdominal radiograph 2 d later shows firmly expanded stent successfully decompressing the acute obstruction. Tight stenosis is seen, and the enhanced expansible force of this stent enables successful decompression.
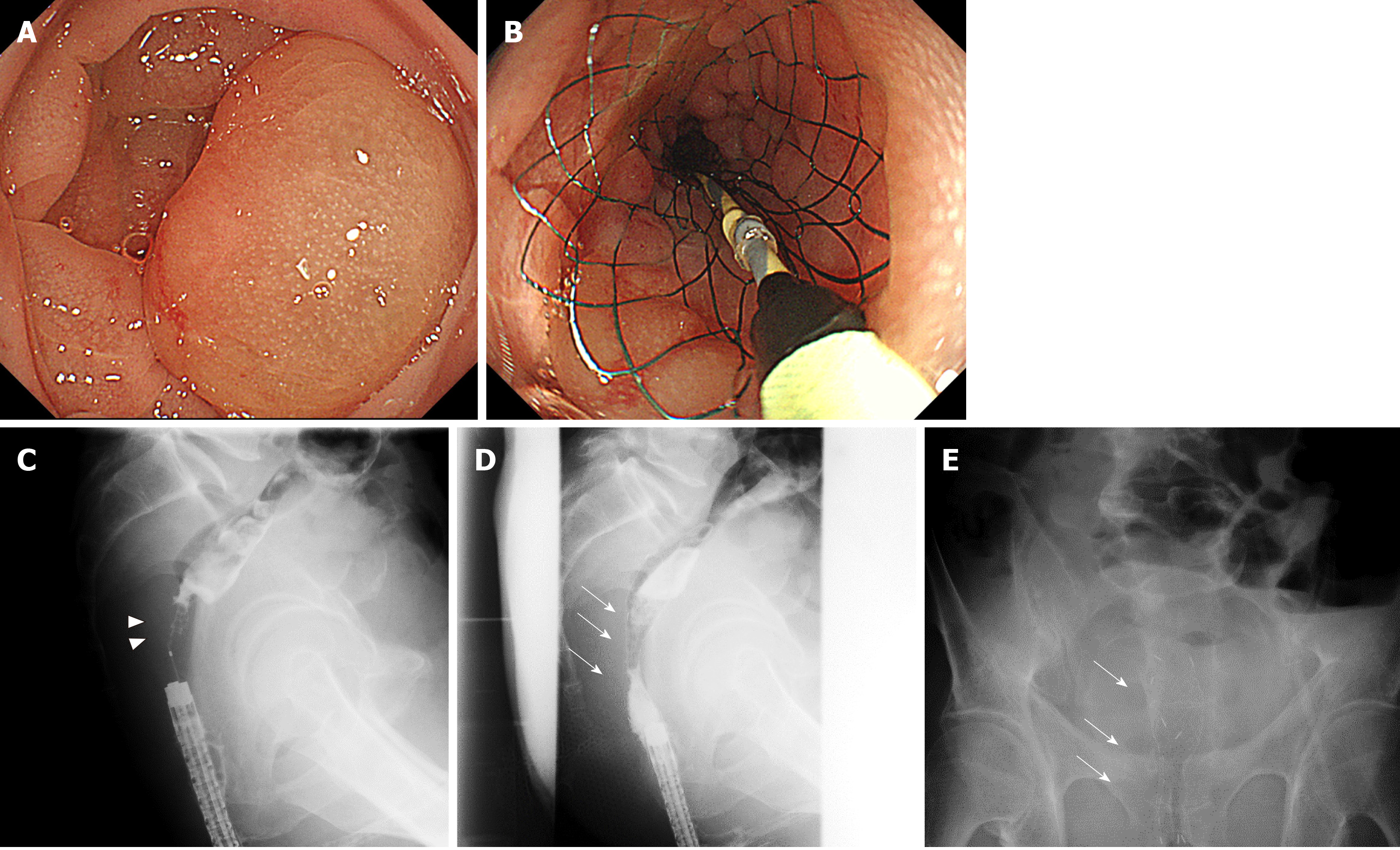
Figure 4 Palliative care using the newly developed Niti-S MD type colonic stent.
A and C: The patient was a 65-year-old man who presented with obstructive lesion (arrowhead) in the rectum (Rb); B and D: The patient had rectal stenosis caused by peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancer. Using a smaller caliber colonoscope, we placed a 22 mm×8 cm stent (arrow) while paying attention not to cover the stent on the pectinate line; E: On the second day, the stent was fully expanded, decompressing the acute obstruction.
- Citation: Miyasako Y, Kuwai T, Ishaq S, Tao K, Konishi H, Miura R, Sumida Y, Kuroki K, Tamaru Y, Kusunoki R, Yamaguchi A, Kouno H, Kohno H. Newly developed self-expandable Niti-S MD colonic metal stent for malignant colonic obstruction. World J Gastrointest Surg 2020; 12(4): 138-148
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v12/i4/138.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v12.i4.138