Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Dec 27, 2020; 12(12): 491-506
Published online Dec 27, 2020. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v12.i12.491
Published online Dec 27, 2020. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v12.i12.491
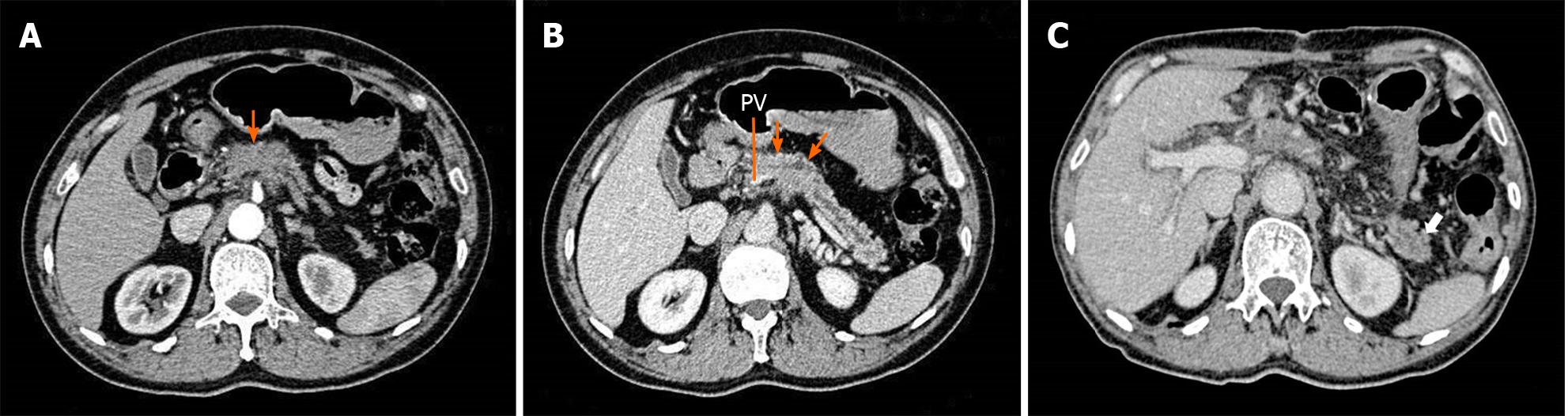
Figure 1 Preoperative and postoperative computed tomography images of a 65-year-old male patient who underwent partial pancreatic tail preserving subtotal pancreatectomy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
The pancreatic cancer involved the pancreatic head and proximal body, which led to the dilatation of the distal pancreatic duct. The length of the preserved pancreatic stump was 31 mm, and the patient was still insulin-independent at the last follow-up. A and B: Preoperative; C: Postoperative. PV: Portal vein.
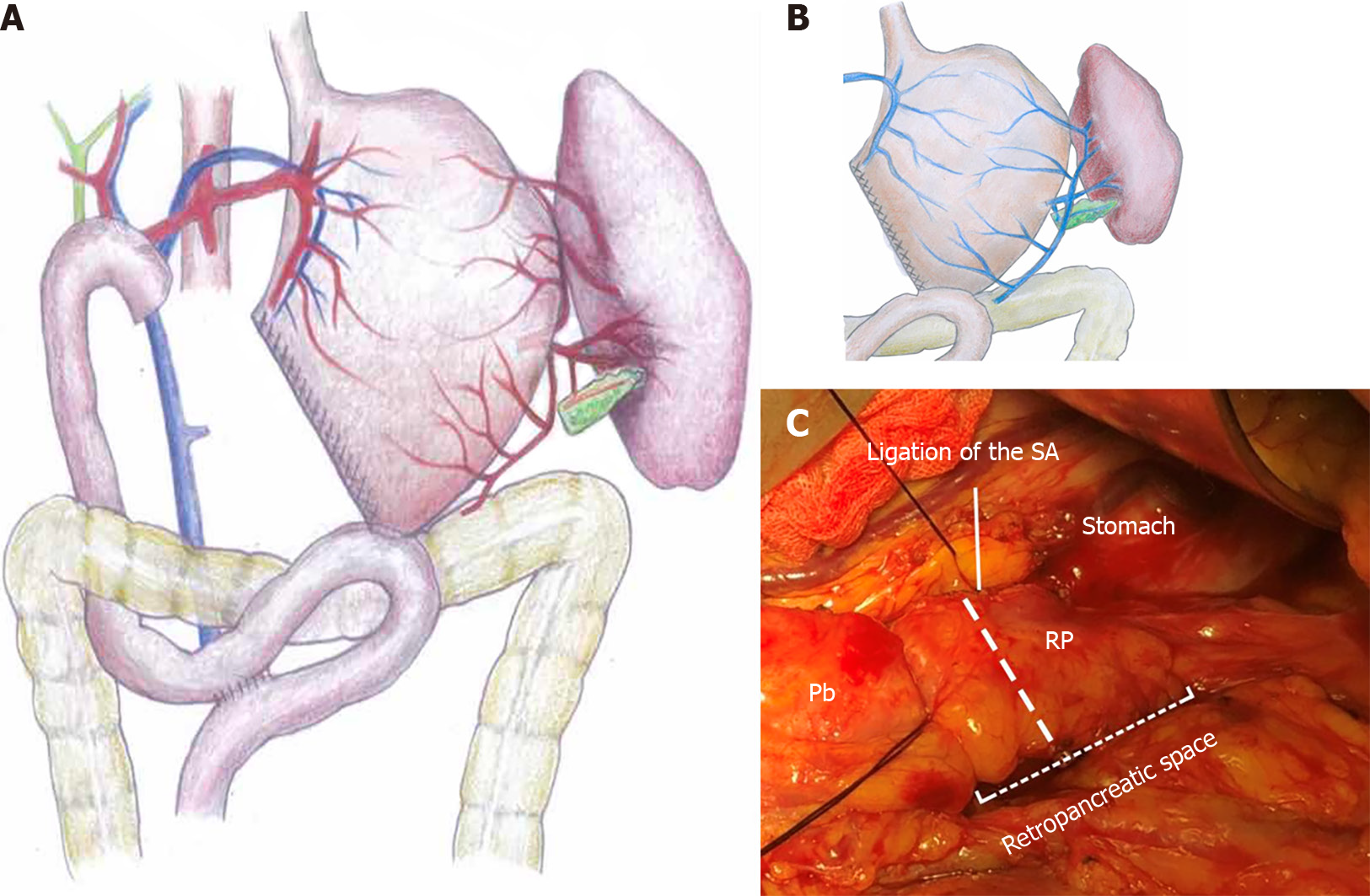
Figure 2 Diagrams and intraoperative image showing the surgical technique.
A and B: Care was taken to ensure the integrity of the left gastroepiploic vessels, the short gastric vessels, and the network of collateral vessels near the splenic hilum. The left gastric vein was preserved as much as possible (B); C: A tunnel was created behind the pancreatic tail, and the pancreas could be transected along the bold dashed line. SA: Splenic artery; Pb: Pancreatic body; RP: Remnant pancreas.
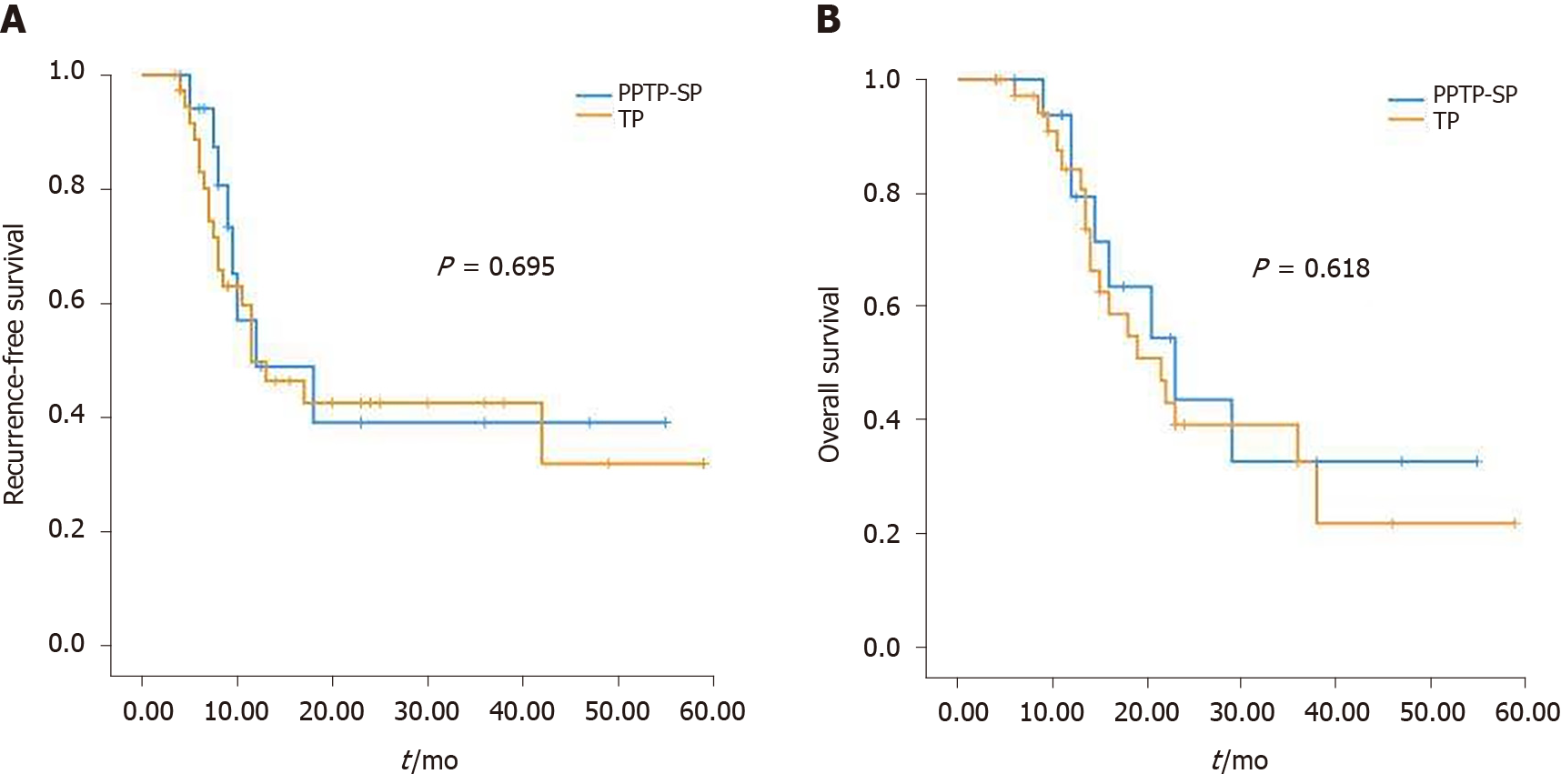
Figure 3 Comparison of recurrence-free survival and overall survival between patients who underwent partial pancreatic tail preserving subtotal pancreatectomy or total pancreatectomy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
A: Recurrence-free survival; B: Overall survival. RFS: Recurrence-free survival; OS: Overall survival.
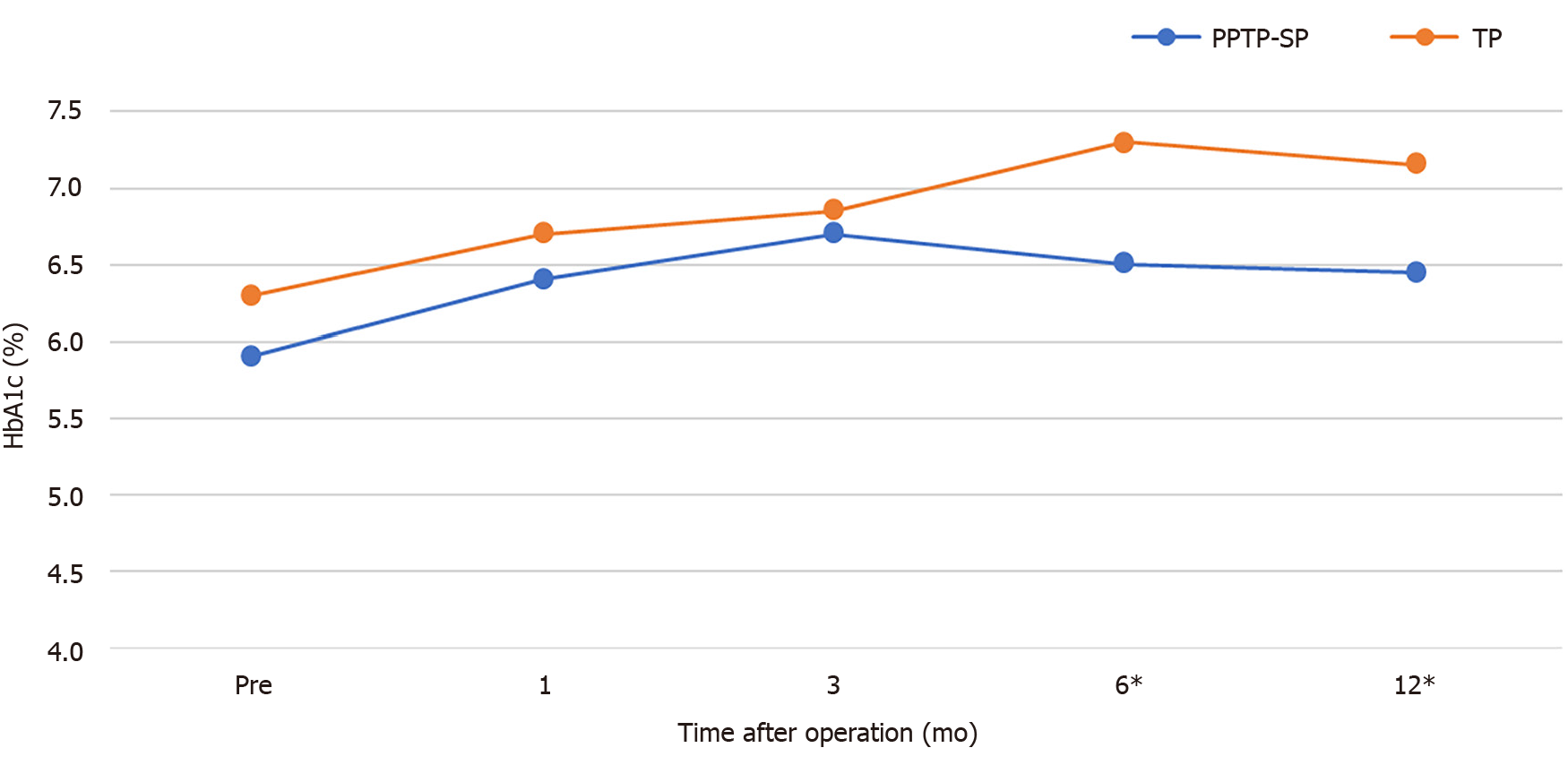
Figure 4 Change of hemoglobin A1c levels after partial pancreatic tail preserving subtotal pancreatectomy or total pancreatectomy.
The asterisk indicates a statistical difference. HbA1c: Hemoglobin A1c; PPTP-SP: Partial pancreatic tail preserving subtotal pancreatectomy; TP: Total pancreatectomy.
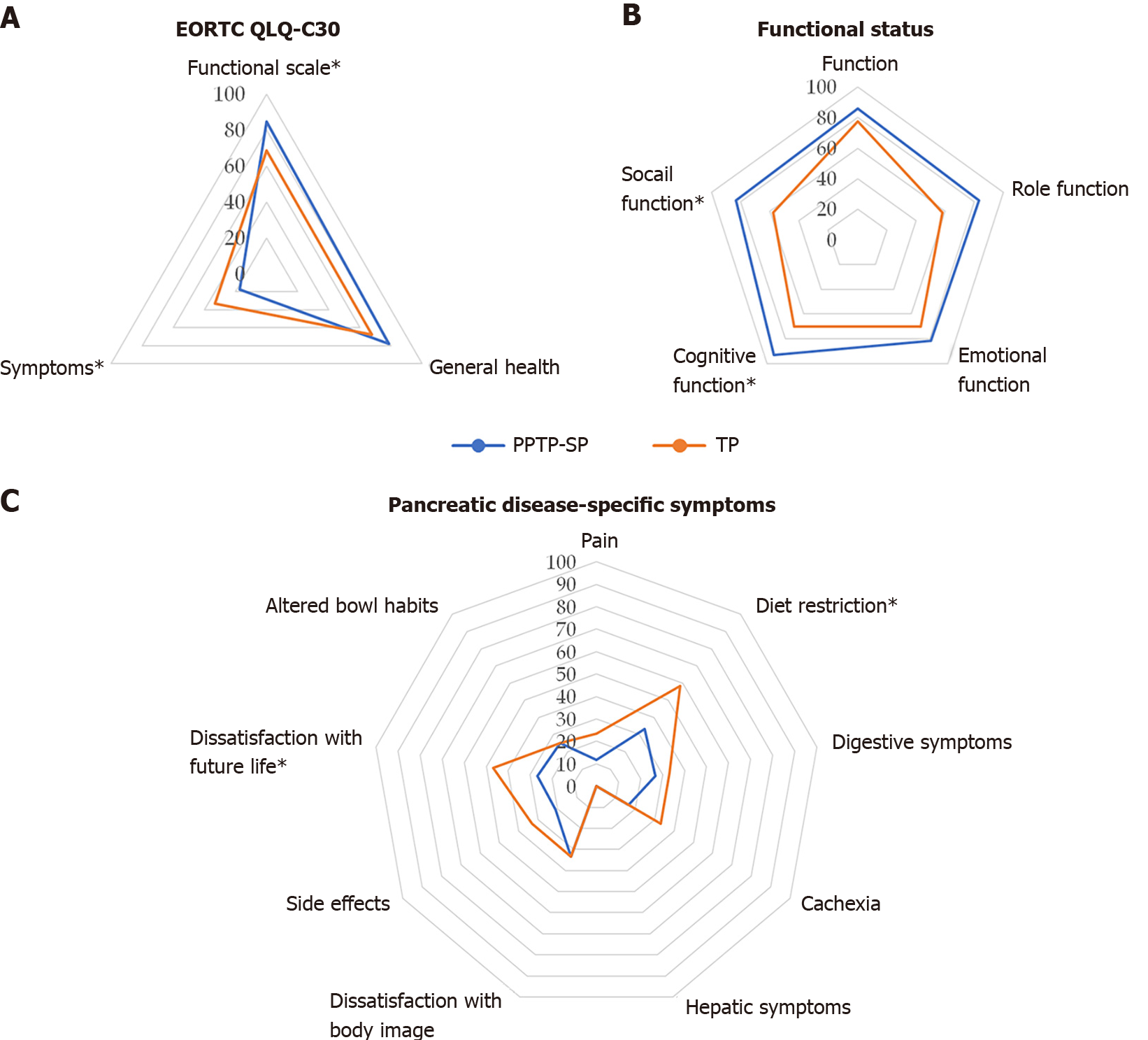
Figure 5 Patients’ quality of life (QoL) after partial pancreatic tail preserving subtotal pancreatectomy or TP.
A: Quality of life (QoL) evaluated using the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire C30; B: Functional status; C: Pancreatic disease-specific symptoms. Patients who underwent partial pancreatic tail preserving subtotal pancreatectomy had better functional status, milder symptoms, less severe diet restriction, and stronger confidence regarding future life. The asterisk indicates a statistical difference. EORTC QLQ-C30: European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire; PPTP-SP: Partial pancreatic tail preserving subtotal pancreatectomy; TP: Total pancreatectomy.
- Citation: You L, Yao L, Mao YS, Zou CF, Jin C, Fu DL. Partial pancreatic tail preserving subtotal pancreatectomy for pancreatic cancer: Improving glycemic control and quality of life without compromising oncological outcomes. World J Gastrointest Surg 2020; 12(12): 491-506
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v12/i12/491.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v12.i12.491