Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Diabetes. May 10, 2016; 7(9): 189-197
Published online May 10, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i9.189
Published online May 10, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i9.189
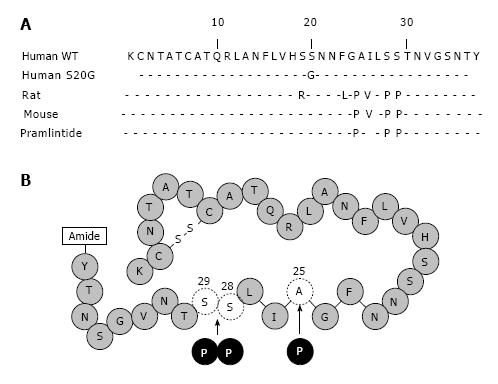
Figure 2 Amino acid sequence and diagrammatic representations of human amylin and pramlintide.
A: Amino acid sequence alignment of human (WT, S20G), rat, mouse amylin and pramlintide. Only the amino acids that differ are shown. The sequence between amino acids 20 to 29 represents the amyloidogenic domain; B: The synthetic amylin analog pramlintide differs from human amylin at three amino acid sites (proline at 25, 28, and 29) and this molecule overcomes these disadvantages of human amylin.
- Citation: Zhang XX, Pan YH, Huang YM, Zhao HL. Neuroendocrine hormone amylin in diabetes. World J Diabetes 2016; 7(9): 189-197
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v7/i9/189.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v7.i9.189