INTRODUCTION
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a common and serious complication of diabetes, characterized by the accumulation of extracellular matrix in the renal units[1,2]. This process results in the thickening of the glomerular basement membrane, proliferation of mesangial cells (MCs), and ultimately leads to glomerulosclerosis and fibrosis[3]. MCs are primarily responsible for synthesizing the extracellular matrix, which includes fibronectin and collagen, crucial for maintaining kidney tissue structure and function[4,5], and they play a key role in maintaining the tissue structure and physiological function of the kidney. Significant components of the extracellular matrix include fibronectin and collagen[6-8]. In DN, overproduction of tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF)-α and inflammatory responses in the glomerular mesangial membrane are significant indicators of renal fibrosis and dysfunction[9-11]. Therefore, reducing extracellular matrix production and inflammation levels is essential for effective DN treatment.
The exact pathophysiology of DN remains unclear, with various factors such as changes in glucose metabolism, abnormal renal hemodynamics, oxidative stress, inflammation, and aging contributing to its progression[12,13]. The excessive generation of reactive oxygen species due to high hyperglycemia is believed to be a key factor in DN development[12-16]. High glucose levels lead to increased oxidative stress, resulting in decreased production of antioxidant enzymes like catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX) in the extracellular matrix[17-21]. This imbalance also triggers the release of inflammatory factors.
Mizagliflozin (MIZ) is a specific inhibitor of sodium-glucose cotransport protein 1 (SGLT1) found in the small intestinal epithelium. Originally developed as a novel antidiabetic medication, it was hypothesized that reducing glucose absorption in the gut would improve glycemic control[22]. Interestingly, MIZ is more effective at limiting glucose reabsorption in the kidney compared to SGLT2 inhibitors like dagliflozin, which can reduce complications associated with DN[23]. Prior studies have demonstrated MIZ’s high efficacy and safety in individuals with functional constipation, leading to a decreased risk of hypoglycemia[23]. MIZ significantly reduces glucose absorption in the intestinal tract[24]. However, there is a lack of research on MIZ’s involvement in DN[25]. Therefore, the objective of this study is to assess MIZ’s potential impact on DN and its influence on the synthesis of extracellular matrix by MCs and diabetic mice.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
All animal experiments must adhere to the guidelines outlined by the Canadian Council on Animal Care or the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Our study received approval from the ethics committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University for both consent and implementation, as well as the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (No. FJSS20111511). Upon completion of treatment, all mice were anesthetized and euthanized using 4.0% isoflurane (Isoflurane, Piramal Critical Care, Bethlehem, PA, United States).
Drugs
MIZ is a selective blocker of SGLT1, generously provided by Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Animals
We utilized ten-week-old male db/db mice along with their age-matched non-diabetic lean controls, which were littermates (db/+). These animals were raised in a pathogen-free environment at the Biomedical Research Center, Human Disease Modeling Research Center, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyushu University (Fukuoka, Japan). They had ad libitum access to tap water and were fed a standard diet comprising 50.1% carbohydrates, 25.1% protein, 7.1% minerals, 4.5% fat, and 4.3% fiber.
The mice were housed in a facility with a 12-hour light-dark cycle at a temperature of 22 °C. Following a two-week acclimation period, the mice were randomly assigned to one of four groups (n = 10): db/+, db/db, db/db + MIZ 0.5 mg/kg, and db/db + MIZ 1.0 mg/kg. They were then administered either 0.5 or 1.0 mg/kg of MIZ via oral gavage. The MIZ was suspended in a 0.5% methylcellulose solution for administration. To assess the effects of MIZ treatment on blood glucose levels in diabetic mice, high (1.0 mg/kg/day) or low (0.5 mg/kg/day) doses of MIZ were administered via oral gavage to diabetic mice at 12 weeks of age for a duration of 2 weeks, as previously reported[26].
Additionally, to examine the impact of MIZ treatment on renal damage in diabetic mice, MIZ (0.5 or 1.0 mg/kg/day) was administered to db/db mice for a period of 8 weeks, starting at 12 weeks of age. Control db/db mice and db/db + mice received a 0.5% methylcellulose solution alone for the same duration. Blood samples were collected at each time point, and during the final 2 days of the 4-week or 8-week treatment, 24-hour urine samples were collected using metabolic cages (one mouse per cage). The urine samples were centrifuged at 7500 × g for 5 minutes, purged of air with nitrogen to prevent artificial formation of 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine, and then stored at -80 °C until analysis[27,28]. At the conclusion of the study, all mice were anesthetized and euthanized with 4.0% isoflurane (Isoflurane, Piramal Critical Care, Bethlehem, PA, United States), and blood samples were obtained via heart puncture to assess glucose levels[29]. The kidneys were promptly excised and preserved in formalin for subsequent analyses.
Blood and urine analysis
Plasma glucose and urine albumin concentrations were assessed following established protocols outlined in previous studies[27]. Urinary excretions were calculated over a 24-hour period by multiplying the analyte concentration with urine volume and then adjusting for a 24-hour timeframe. Blood pressure was monitored using the tail-cuff technique (MK-2000; Muromachi Kikai, Tokyo, Japan). Prior to the trial’s commencement, all mice underwent a three-day acclimation period during which they were familiarized with restraint and tail-cuff inflation[27].
Morphological studies
For morphological analysis, kidneys were fixed in paraffin, sectioned (3 μm thickness), and stained with periodic acid Schiff (PAS). The kidney tissue was identified by the presence of PAS-positive regions devoid of nuclei. Glomerular area measurements and corrections were performed using image analysis software (Keyence, Osaka, Japan), as previously described[28].
Oxidative stress indicators
Oxidative stress indicators were assessed using a full-wavelength microarray chip (BioTek Power Wave XS) to evaluate antioxidants and oxidative stress levels in kidney tissue lysates, serum, and cell supernatants of mice. Assays for SOD, GSH-PX, CAT, and malondialdehyde were conducted using assay kits (A001-3, A007-1-1, A005, A003-1, Nanjing Jiancheng Institute of Biological Engineering, Nanjing, China) on the BioTek Power Wave XS platform. Each sample was analyzed in triplicate, following previously established procedures[21]. Experiments were replicated three times to ensure consistency.
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
Total RNA was extracted from MCs using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States) and reverse transcribed with the PrimeScript Reverse Transcription Kit (Takara Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan). Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed using the SYBR premixed Ex Taq kit (Takara Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan) on an ABI 7300 RT-PCR detection system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, United States). The primer sequences used were as follows: SGLT1 forward 5’-GGACAGTAGCACCTTGAGC-3’ and reverse 5’-CCAACAGTCCCACGAATTAG-3’; interleukin (IL)-1β forward 5’-TCCAGGATGAGGACATGAGCAC-3’ and reverse 5’-GAACGTCACACACCAGCAGGTTA-3’; TNF-α forward 5’-AAGCCTGTAGCCCACGTCGTA-3’ and reverse 5’-GGCACCACTAGTTGGTTGTCTT-3’; collagen type 1 alpha 1 (COL1A1) forward 5’-GTATGCTTGATCTGTATCTG-3’ and reverse 5’-CGACTCCTACATCTTCTG-3’; COL1A2 forward 5’-CCGTGCTTCTCAGAAGACAG-3’ and reverse 5’-CTTGCCCCATTCATTCATCA-3’; transforming growth factor (TGF)-β forward 5’-GACTCTCCACCTGCAAGACCAT-3’ and reverse 5’-GGGACTGGCGAGCCTTAGTT-3’; NF-E2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) forward 5’-GTGGTTTAGGGCAGAAGG-3’ and reverse 5’-TCTTTCTTACTCTGCCTCTA-3’. Each set of samples was analyzed in triplicate, and the experiments were repeated three times. mRNA expression levels were normalized to the expression of the housekeeping gene β-actin.
Cell culture
MCs were isolated from the kidneys of 12-week-old db/+ mice, following previously established methods[30,31]. These cells were cultured on gelatin-coated plates in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM) supplemented with 20% fetal bovine serum (FBS), penicillin (100 U/mL) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, United States), and streptomycin (100 μg/mL) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, United States). MCs from generations 3-8 were used for subsequent investigations after reaching > 80%-90% confluence, as SGLT expression was known to diminish beyond generation[32]. Proximal renal tubular cells from the same animals were prepared as previously described[33]. For experiments, cells were allowed to reach 60%-70% confluence in multi-well plates before changing the medium to 0.5% FBS DMEM containing either 5.5 mmol/L glucose plus 19.5 mmol/L mannitol (to ensure equal osmolarity) or 25 mmol/L glucose. MIZ was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, CAS No: 67-68-5) to achieve the required final concentration, with DMSO serving as a control. The medium was changed daily to maintain optimal glucose and MIZ levels. All tests were conducted in triplicate and repeated at least three times.
Cell viability
Cell viability was determined using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay kit (CCK-8, Kumamoto Tongindo Molecular Technology, Japan CCK-8) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, cells were seeded into 96-well plates, and 10 μL of CCK-8 solution was added to each well. Cell viability was assessed as previously described[34]. All experiments were replicated three times.
Glucose consumption
Inoculate MCs in 24-well plates at a density of 1 × 104 cells/well and incubate to 70%-80% confluence. Aliquots of medium were withdrawn at incubation time 0 and 72 hours, and glucose concentration was measured by the glucose oxidase test. Glucose intake was determined by the difference between the glucose content of the aliquots obtained after the incubation period of 0 and 72 hours, which has been reported previously[3]. All experiments were repeated three times.
Lactate dehydrogenase activity assay
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity in cell lysates was determined following the protocol outlined in the LDH Cytotoxicity Assay Kit by BioVision. Briefly, 2 × 105 cells were infected in 24-well plates one day prior to the experiment, and all samples were assessed in triplicate. Subsequently, cells were harvested, washed, and protein extracts were obtained for LDH activity assessment. Results were normalized to the total protein quantity relative to control cells[34].
Western blot analysis
Proteins were separated discontinuously on a polyacrylamide gel containing 7.5% sodium dodecyl sulfate and transferred onto a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, United States). Following nonspecific binding blocking, membranes were incubated at 4 °C with rabbit anti-SGLT1 (1:500; Abcam), anti-TGF-β (1:500; Cell Signaling Technology), or anti-IL-1β (1:5000; Cell Signaling Technology) antibodies, succeeded by secondary antibodies of HRP-coupled donkey anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G (1:10000; Amersham). Antibody binding was visualized using the ECL Plus method (Amersham), as previously described[28].
Statistical analysis
Results were expressed as mean ± SD. Group comparisons were conducted using one-way ANOVA. A significance level of P < 0.05 was deemed statistically significant. Data analysis was performed using SPSS version 19.0 software.
RESULTS
Effect of MIZ treatment on renal damage in diabetic mice
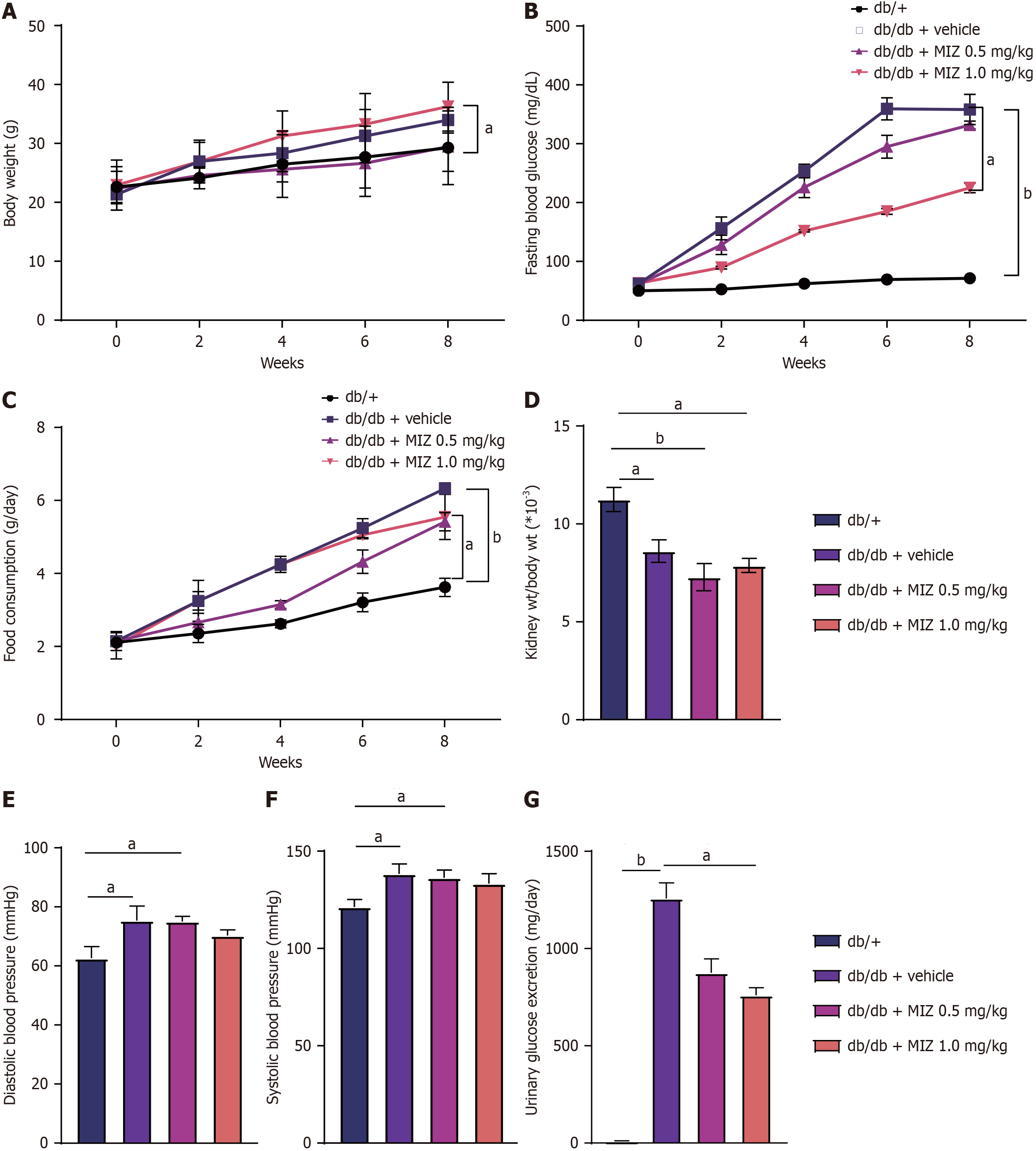
Our study investigated the effects of MIZ on renal damage in diabetic mice. As illustrated in Figure 1, the db/db + MIZ 1 mg/kg group exhibited a significant increase in body weight compared to the db/db + MIZ 0.5 mg/kg group, despite a decrease in blood glucose levels and food intake. Additionally, the db/db + MIZ 0.5 mg/kg group showed no significant changes in body weight, food intake, or blood glucose levels compared to the db/db mice.
Figure 1 Effect of mizagliflozin treatment on renal damage in diabetic mice.
A: Body weight; B: Fasting blood glucose; C: Food consumption; D: Kidney weight/body weight; E: Diastolic blood pressure; F: Systolic blood pressure; G: Urinary glucose excretion. The values are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. MIZ: Mizagliflozin.
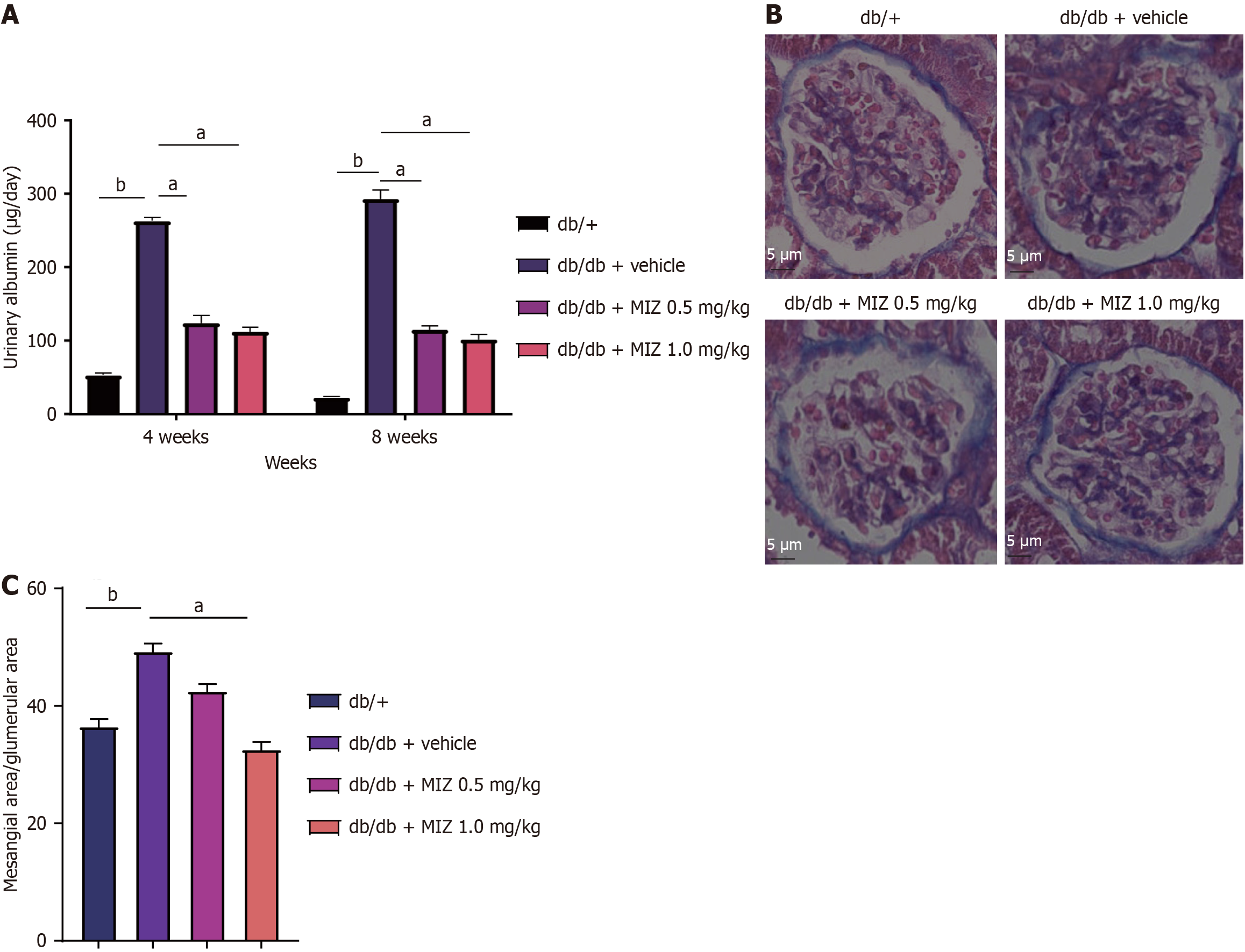
We also studied the findings of kidney weight to body weight ratio, diastolic blood pressure, and systolic blood pressure and discovered that neither low nor db/db + MIZ 1 mg/kg group had a significant influence on these outcomes. As for the glucose clearance in the urine, db/db + MIZ 1 mg/kg group exhibited a significantly reduction comparing to the db/db mice. As demonstrated in Figure 2, db/db + MIZ 0.5 mg/kg group considerably alleviated albuminuria compare to db/db + MIZ 1 mg/kg group. We then evaluated the impact of glomeruli utilizing histology and discovered that db/db + MIZ 1 mg/kg group considerably increased renal mesangial expansion, whereas db/db + MIZ 0.5 mg/kg group had no significant effect on renal mesangial expansion. Therefore, this partial finding supports an ameliorative impact of MIZ on DN.
Figure 2 Effect of mizagliflozin treatment on renal histological change in diabetic mice.
A: Urinary albumin; B: Periodic acid Schiff staining of kidney tissue; C: Mesangial area/glumerular area. The values are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. MIZ: Mizagliflozin.
MIZ decreases extracellular matrix and inflammation-related gene expression in diabetic mice
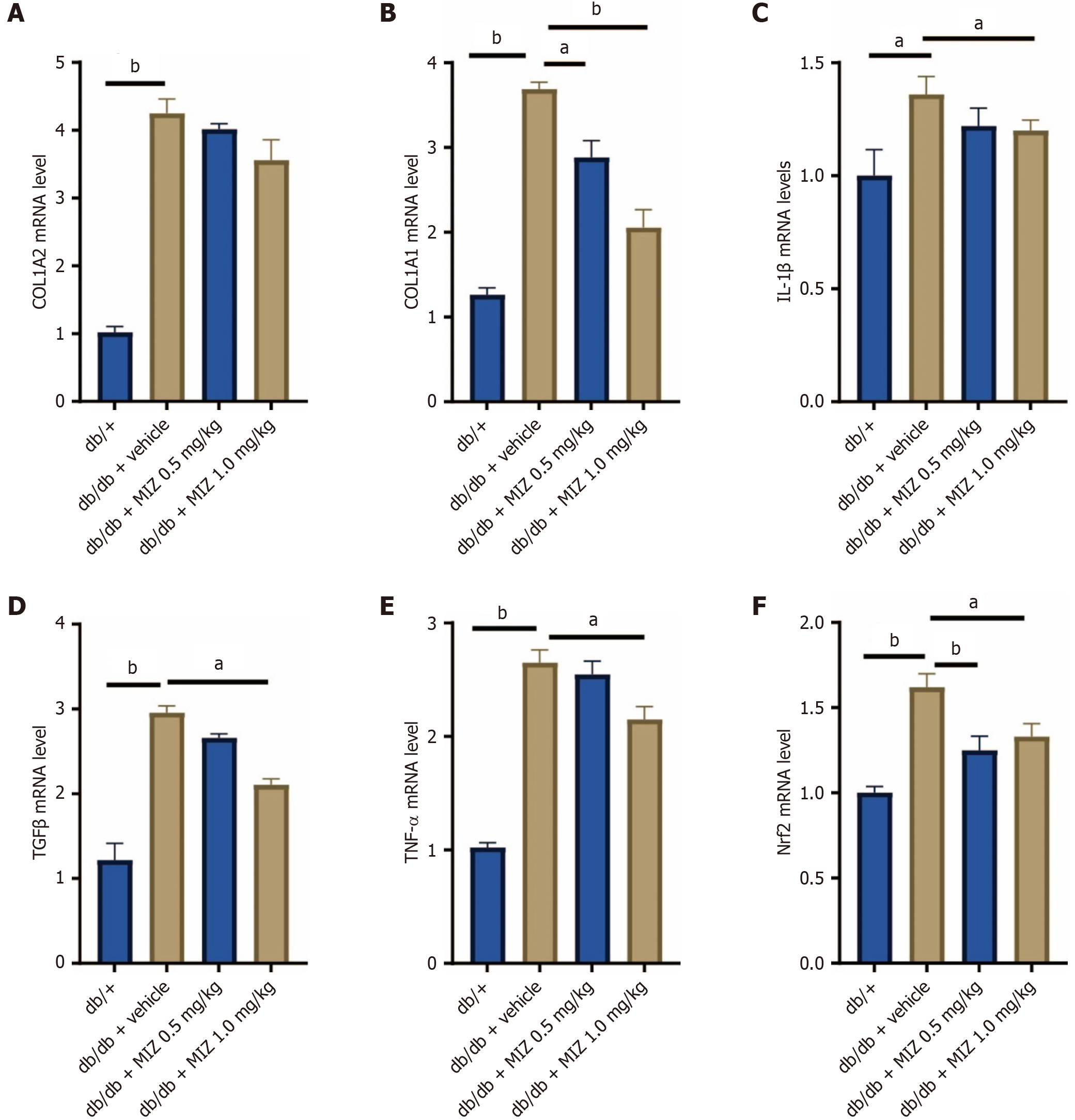
We investigated the effects of MIZ on extracellular matrix and inflammatory-related mRNA in kidney tissue of db/db mice. Compared to control animals, diabetic mice had significantly higher levels of COL1A2, COL1A1, IL-1β, TGF-β, and TNF-α mRNA. The db/db + MIZ 1 mg/kg group intervention significantly decreased COL1A1 levels, while db/db + MIZ 0.5 mg/kg group had no significant impact on COL1A2, COL1A1, IL-1β, TGF-β, and TNF-α mRNA levels. Additionally, Nrf2 was greatly enhanced in DN mice, but both db/db + MIZ 1 mg/kg group and db/db + MIZ 0.5 mg/kg group effectively lowered Nrf2 mRNA levels (Figure 3). Thus, at the animal level, we discovered that MIZ reduced extracellular matrix and inflammation levels.
Figure 3 Mizagliflozin decreases extracellular matrix and inflammation-related gene expression in diabetic mice.
A: Collagen type 1 alpha 2 (COL1A2) mRNA level; B: COL1A1 mRNA level; C: Interleukin 1 beta mRNA level; D: Transforming growth factor beta mRNA level; E: Tumour necrosis factor alpha mRNA level; F: NF-E2-related factor-2 mRNA level. The values are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. MIZ: Mizagliflozin; COL1A2: Collagen type 1 alpha 2; IL: Interleukin; TGF: Transforming growth factor; TNF: Tumour necrosis factor; Nrf2: NF-E2-related factor-2.
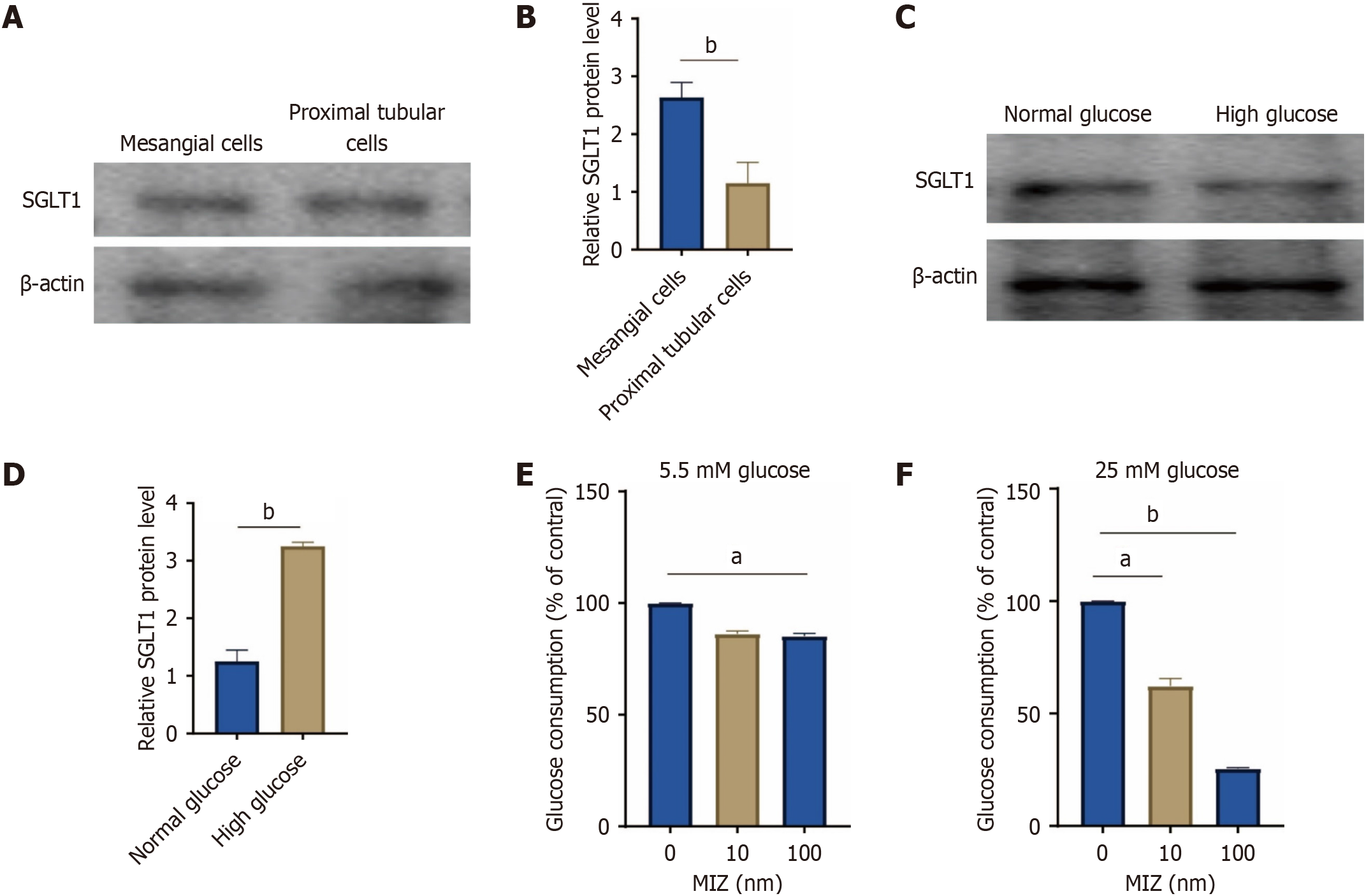
Expression of SGLT1 increased after treatment with high glucose
Figure 4 illustrates the ameliorative impact of MIZ on DN. We proceeded to examine the expression of SGLT1 in MCs of mice considering this effect. Western blot analysis revealed the presence of SGLT1 bands in both MCs and proximal renal tubules of mice. Notably, MCs exhibited higher levels of SGLT1 protein compared to proximal renal tubules. Additionally, we explored the SGLT1 protein concentration across varying glucose concentrations. The results indicated a significant increase in SGLT1 protein levels following high glucose intervention, suggesting its correlation with glucose levels.
Figure 4 High glucose intervention resulted in a considerable rise in sodium-glucose cotransport protein 1 protein levels.
A and B: Western blot of sodium-glucose cotransport protein 1 (SGLT1) expression in mesangial cells and proximal tubular cells; C and D: Western blot of SGLT1 expression in normal glucose and high glucose treatment with mesangial cells; E: Glucose consumption in 5.5 mmol/L glucose; F: Glucose consumption in 25 mmol/L glucose. The values are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. MIZ: Mizagliflozin; SGLT1: Sodium-glucose cotransport protein 1.
The expression of SGLT1 was decreased after treatment with MIZ
To investigate the function of SGLT2 in MCs, we assessed the rate of glucose intake in the culture medium. Cells were grown in media containing 5.5 mmol/L glucose (normal glucose level) or 25 mmol/L glucose (high glucose level) for 3 days. When incubated in media containing 5.5 mmol/L glucose, glucose intake in the medium was suppressed by 100 nmol/L MIZ. Conversely, when incubated in media containing 25 mmol/L glucose, the glucose depletion was greatly reduced by MIZ in a dose-dependent manner of 10 and 100 nmol/L. This section of the research reveals that high glucose not only raises SGLT1 protein levels but also lowers the level of SGLT1 treated with MIZ intervention.
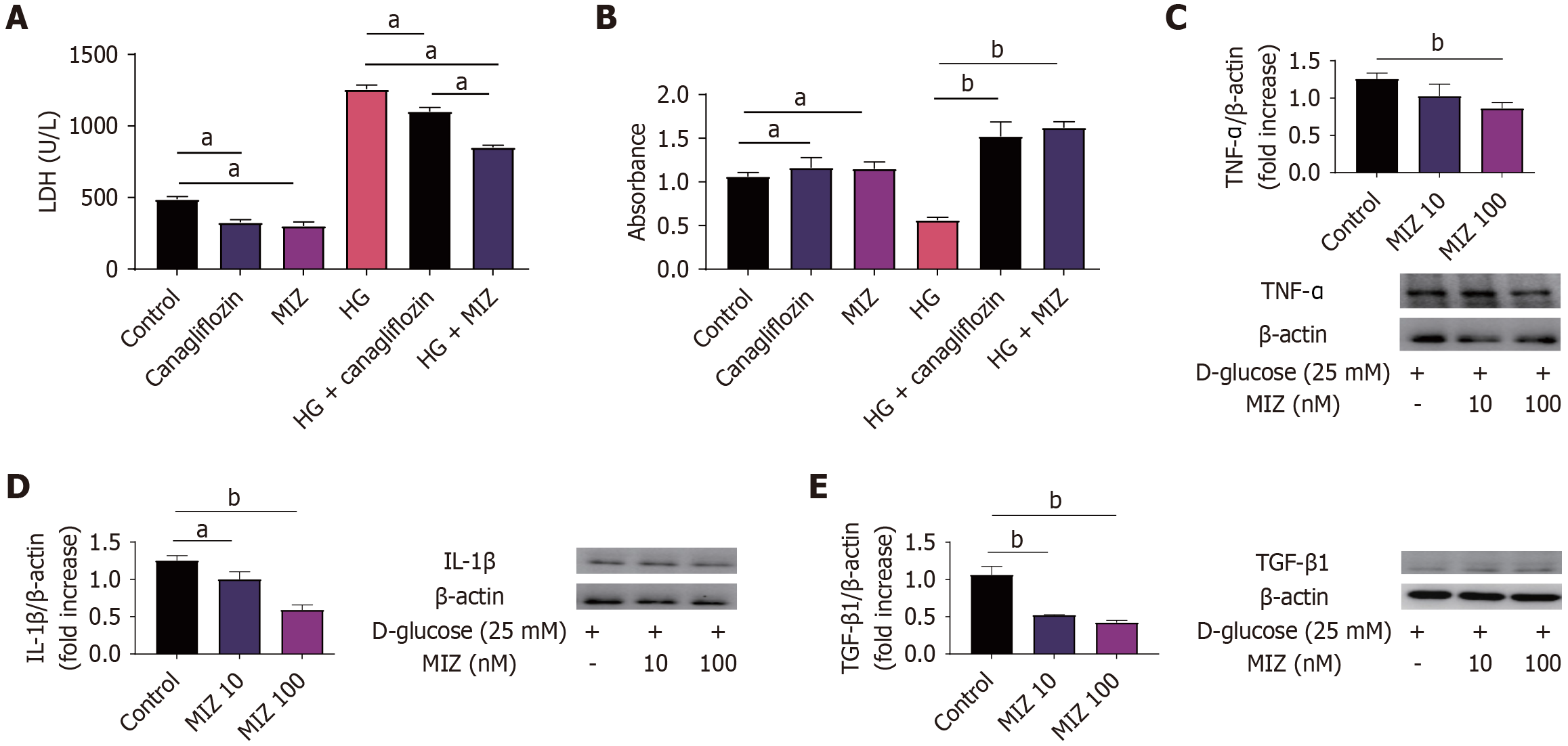
MIZ intervention improved the LDH levels of MCs caused by high glucose better than canagliflozin
To further examine the efficacy of MIZ in treating DN, we compared the effect of MIZ and canagliflozin on MCs. It was discovered that MIZ significantly lowered LDH levels compared to canagliflozin in MCs with high glucose intervention. Meanwhile, MIZ was not substantially different from canagliflozin in enhancing the cellular activity of MCs. We also studied the effects of various concentrations of MIZ on IL-1β, TNF-α, and TGF-β in MCs, and the findings revealed that high concentrations of MIZ substantially decreased IL-1β, TNF-α, and TGF-β protein levels in MCs, whereas low concentrations of MIZ reduced IL-1β and TGF-β protein levels. Thus, our data suggest that MIZ may be better than canagliflozin in decreasing LDH levels (Figure 5).
Figure 5 Mizagliflozin intervention improved the lactate dehydrogenase levels of mesangial cells caused by high glucose better than canagliflozin.
A: Lactate dehydrogenase levels; B: Cell Counting Kit-8 test; C: Western blot of tumour necrosis factor-α in high glucose with varying levels of mizagliflozin (MIZ); D: Western blot of interleukin-1β in high glucose with varying levels of MIZ; E: Western blot of transforming growth factor β in high glucose with varying levels of MIZ. The values are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. MIZ: Mizagliflozin; IL: Interleukin; TGF: Transforming growth factor; TNF: Tumour necrosis factor; HG: High glucose.
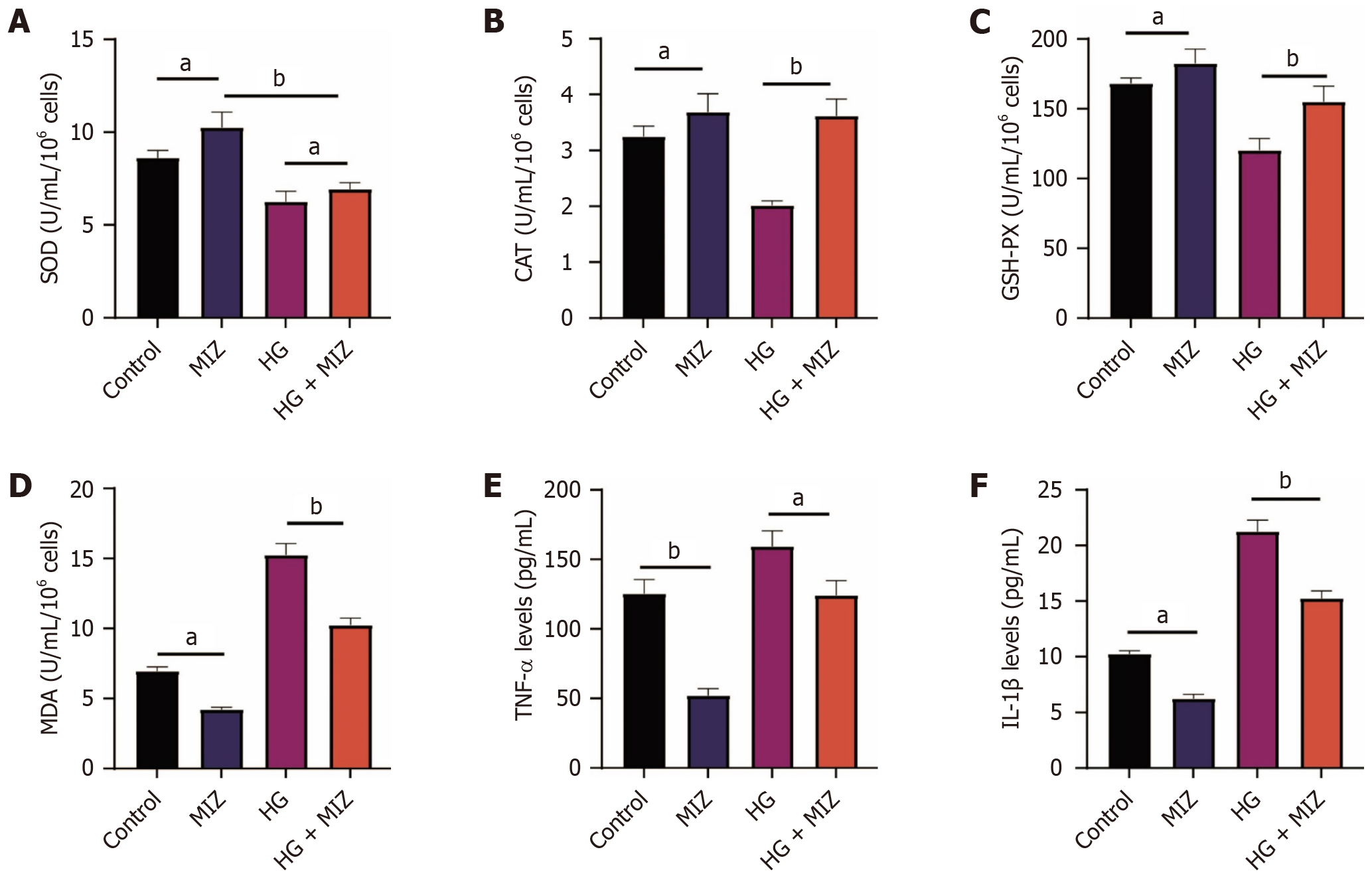
MIZ controls oxidative stress and inflammatory factors in response to high hyperglycemia treatment
Oxidative stress plays a pivotal role in the progression of DN. Thus, we investigated the impact of MIZ on oxidative stress levels. Our findings demonstrated a notable elevation in SOD, CAT, and GSH levels alongside a reduction in malondialdehyde levels upon MIZ treatment. This pattern persisted even after exposure to high glucose levels. Furthermore, we analyzed the levels of TNF-α and IL-1β. Remarkably, MIZ exhibited a significant downregulation effect on their expression in both normal MCs and MCs induced by high glucose, indicating its potential as an inhibitor of inflammatory factors. Collectively, these results suggest that MIZ holds promise in improving DN by mitigating oxidative stress and suppressing inflammatory factors (refer to Figure 6).
Figure 6 Mizagliflozin regulates oxidative stress and inflammatory factors in mesangial cells exposed to high hyperglycemia.
A: Superoxide dismutase levels; B: Catalase levels; C: Glutathione peroxidase levels; D: Malondialdehyde levels; E: Tumour necrosis factor-α levels; F: Interleukin-1β levels. The data are presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. n = 8, experiment duration = 3 days. MIZ: Mizagliflozin; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumour necrosis factor; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; CAT: Catalase; GSH-PX: Glutathione peroxidase; MDA: Malondialdehyde.
DISCUSSION
MIZ has been widely used as an anti-diabetic drug to lower blood glucose levels and improve small vascular disease. However, there is a lack of studies related to DN[23,26]. The current investigation demonstrated that MIZ reduced renal damage in mice with DN by lowering the amounts of extracellular matrix and inflammatory factors. At the cellular level, MIZ also lowered glucose intake in db/db mice and substantially decreased LDH levels in MCs with high glucose intervention. Ultimately, MIZ reduced oxidative stress levels and inflammatory factor levels in MCs with high glucose intervention. This study may provide a new treatment strategy for DN using MIZ.
Damage to tubular cells results in interstitial fibrosis and dissociation from the glomerulus[35,36]. A previous study identified that proximal tubule cells, expressing the SGLT2, and MCs, expressing SGLT1, play a role in SGLT-dependent glucose uptake, which is a risk factor for diabetic complications[37]. This underscores the importance of therapeutic strategies targeting specific cell types in diabetic kidney disease. Therefore, our study primarily investigates the impact of SGLT1 function and inhibitors, leading us to choose MCs over the S3 segment of renal tubules.
The primary focus in treating DN is to manage patient glycemia effectively while halting the progression of the disease and reducing albuminuria. However, selecting drugs that can simultaneously improve glycemic control and nephropathy in clinical practice is challenging[38,39]. Most existing treatments only slow down the onset of the disease without being able to halt or reverse its progression[40]. Hence, optimizing the glycemic environment is crucial. Our research revealed that MIZ significantly enhanced glycemic control in mice with DN, potentially leading to an amelioration of the condition.
Renal fibrosis serves as both a diagnostic hallmark and a common endpoint of DN. It is characterized by the accumulation of extracellular matrix in the glomerulus, glomerular hypertrophy, and fibrotic alterations in the glomerular basement membrane and tubular interstitium[41]. These changes are marked by an upregulation of growth factors, including TGF-β1, which induces the production of α-smooth muscle actin and fibronectin[42]. Our study revealed that MIZ significantly reduces extracellular matrix synthesis, leading to an improvement in DN. In db/db mice treated with MIZ, there was a decrease in mesangial area, suggesting a potential beneficial effect of MIZ in reducing mesangial expansion commonly seen in DN. This reduction in mesangial area may be linked to the inhibition of abnormal MC proliferation. Interestingly, MIZ resulted in increased proliferation of MCs isolated from the kidneys of db/+ mice, indicating a potential stimulatory effect on MC growth in non-diabetic conditions. However, it is essential to note that this stimulatory effect may not necessarily lead to increased mesangial expansion or pathological changes in the kidneys. These findings suggest that MIZ may exert varying effects on MCs depending on the underlying condition. Further research is required to fully elucidate the mechanisms underlying these contrasting effects and to determine their clinical implications[43-46].
In DN, inflammation plays a significant role as a key mechanism. Inflammation is a biological process that responds to adverse conditions to maintain tissue balance and integrity[47]. However, prolonged activation of the inflammatory response can lead to detrimental effects. While hyperglycemia, oxidative stress, and RAAS activation are known causes of kidney damage in diabetes, substantial evidence points to the crucial involvement of inflammation in the development and progression of diabetic complications[14,48-51]. In DN, high blood sugar levels trigger the production of inflammatory mediators (such as chemokines and cytokines) by damaged glomerular and tubular cells, resulting in kidney injury through various pathways like thylakoid proliferation, podocyte/tubular damage, and leukocyte infiltration[52,53]. These pro-inflammatory substances also promote the deposition of extracellular matrix and the differentiation/proliferation of myofibroblasts through multiple signaling pathways (e.g., nuclear factor-kappaB, JAK/STAT, TGFβ/Smad). The inflammatory mediators contribute to vascular remodeling, endothelial dysfunction, extracellular matrix accumulation, thylakoid proliferation, podocyte and tubular cell death, thickening of the glomerular basement membrane, and glomerulosclerosis, all of which are hallmark features of DN[54]. Ishida et al[26] explored the role of MIZ in vascular cognitive impairment associated with small vessel disease and discovered that MIZ reduced the expression of proinflammatory cytokine genes like IL-1β. Furthermore, MIZ enhanced the survival rates of IL-1β-treated PC12HS cells. Consistent with previous findings, our investigation also demonstrated that high glucose treatment significantly increased inflammatory factor levels in MCs, while MIZ treatment substantially decreased inflammatory levels.
Inflammatory markers have been directly linked to oxidative stress levels in DN[55]. Studies using experimental models of DN suggest that hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress partially drives cytokine production[56]. Research on patients has revealed that glucose treatment raises plasma concentrations of IL-6 or IL-18, and that the antioxidant glutathione diminishes this effect[57]. Oxidative stress can stimulate pro-inflammatory factor production via activation of nuclear factor-kappaB and activator protein-1, two key transcription factors that regulate the inflammatory response in DN[58-60]. While a review of literature did not uncover prior studies examining how MIZ mitigates oxidative stress, it is important as an SGLT inhibitor in reducing oxidative stress. Trnovska et al[61] found that empagliflozin, a SGLT-2 inhibitor, decreases markers of inflammation, oxidative stress, and cell senescence in hereditary hypertriglyceridemic rats. Additionally, increased production of ketone bodies, which serve as an alternative fuel for adenosine triphosphate generation in mitochondria, helps attenuate inflammation and protect against hypoxia, oxidative stress, and fibrosis, as demonstrated in previous research[62]. Our study showed that MIZ substantially decreases oxidative stress levels.
SGLT1 and SGLT2 are the most extensively studied and highly expressed SGLT isoforms. SGLT1 is mainly expressed in the small intestine and plays a crucial role in intestinal glucose absorption[63,64]. In contrast, SGLT2 is the primary transporter protein responsible for reabsorbing glucose filtered via the glomerulus[65,66]. Recent research has revealed SGLTs as promising therapeutic targets. Inhibiting SGLT2 is believed to improve renal glucose excretion and lower plasma glucose levels; currently, numerous SGLT2 inhibitors are clinically used as antidiabetic agents[67]. Selective inhibition of SGLT1 reduces glucose uptake in the small intestine and alters postprandial glucose excursions[68]. Furthermore, sodium-glucose cotransport by SGLT1 on macula densa cells triggers nitric oxide production, which also contributes to glomerular hyperfiltration[69]. SGLT1-specific inhibition improves renal failure and alters the gut microbial community in mice with adenine-induced renal failure[70]. However, there is a lack of clinical trials on SGLT1 inhibitors for DN. In this study, we investigated the impact of MIZ on DN and found that MIZ significantly ameliorated renal damage induced by DN.
Limitation of the study
Our study had some limitations. Firstly, we only used db/db mice to establish a diabetic kidney injury model and did not verify it in other animal models. Secondly, as the reviewers noted, we used only MCs cells without validating in other cell lines, so we will further add relevant cell lines for future validation experiments. DN is characterized by scarring of both the renal glomerulus and tubulointerstitial region. While we performed histochemical analysis of collagen deposition in the glomerulus, it would be valuable to analyze the effect of MIZ on extracellular matrix deposition in the tubulointerstitial region as well[38,71]. Finally in our study there were no clinical studies for validation, our study preliminarily demonstrated the function of MIZ in in vivo and in vitro experiments, and the results of clinical studies will be added in future studies.