Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Feb 15, 2023; 14(2): 76-91
Published online Feb 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i2.76
Published online Feb 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i2.76
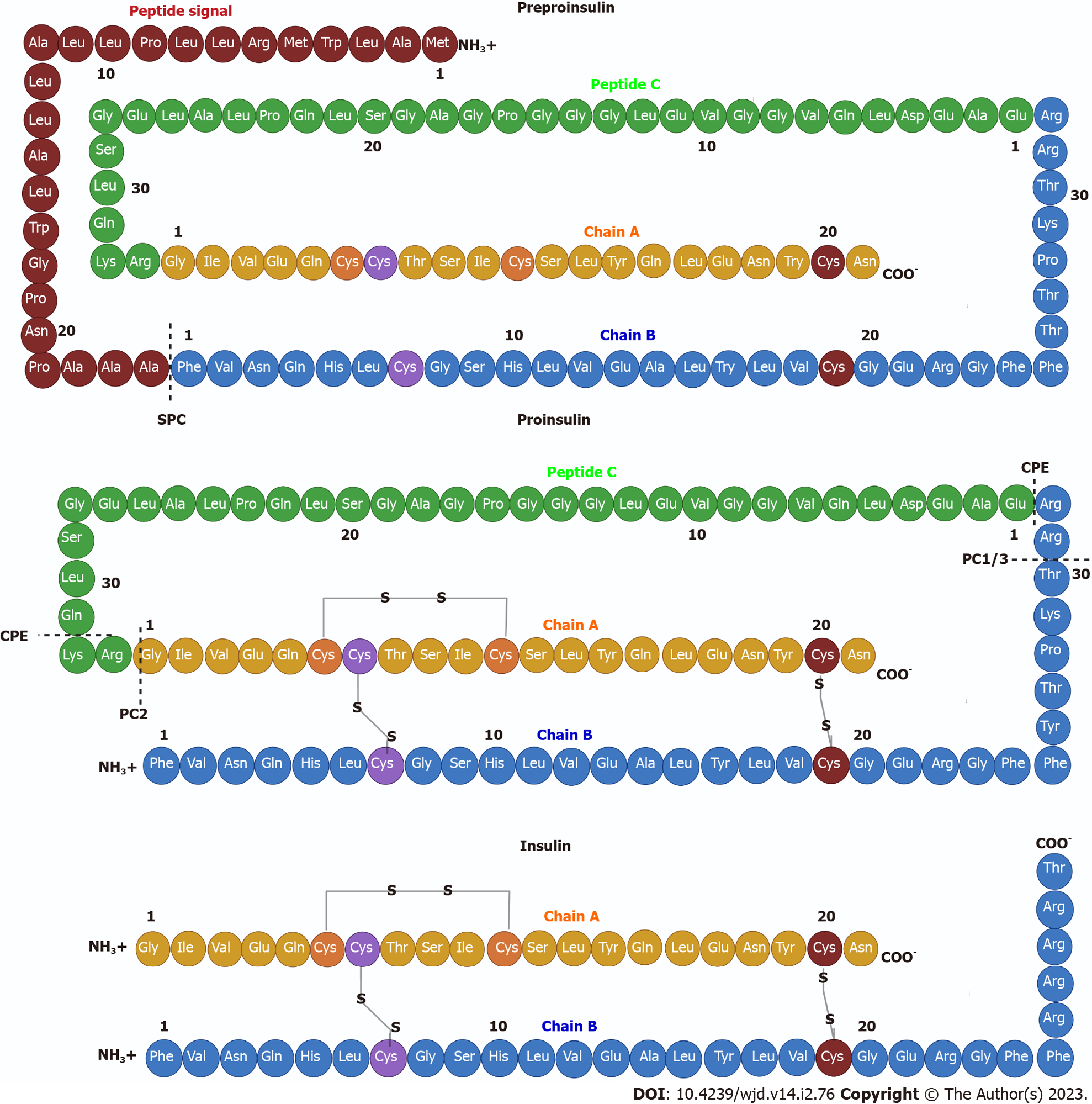
Figure 2 Insulin structure.
Pre-proinsulin is secreted as a polypeptide chain of 110 amino acids (aa), composed of a signal peptide (24 aa), chain A (21 aa), peptide C (33 aa) and a chain B (32 aa). The signal peptide is cleaved by signal peptidase generating pro-insulin, a chain of 86 aa that folds and stabilizes in its three-dimensional configuration by three disulfide bonds between both chains: CysA7-CysB7; CysA20-CysB19; and CysA7-CysA11. Finally, two endoproteases, prohormone convertase 2 and prohormone convertase 1/3, hydrolyze between the basic aa Arg33-Gly1 at the C-peptide and A-chain junction and between the dipeptide Thr30-Arg31 at the B-chain and C-peptide junction, respectively. Subsequently, carboxypeptidase E hydrolyzes between the Gln31-Lys32 aa as well as between Arg32 and Glu1 basic C-termini of the resulting peptide chains, producing a mature insulin protein of 51 aa.
- Citation: De la Cruz-Concepción B, Flores-Cortez YA, Barragán-Bonilla MI, Mendoza-Bello JM, Espinoza-Rojo M. Insulin: A connection between pancreatic β cells and the hypothalamus. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(2): 76-91
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i2/76.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i2.76