Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Diabetes. Oct 15, 2019; 10(10): 490-510
Published online Oct 15, 2019. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v10.i10.490
Published online Oct 15, 2019. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v10.i10.490
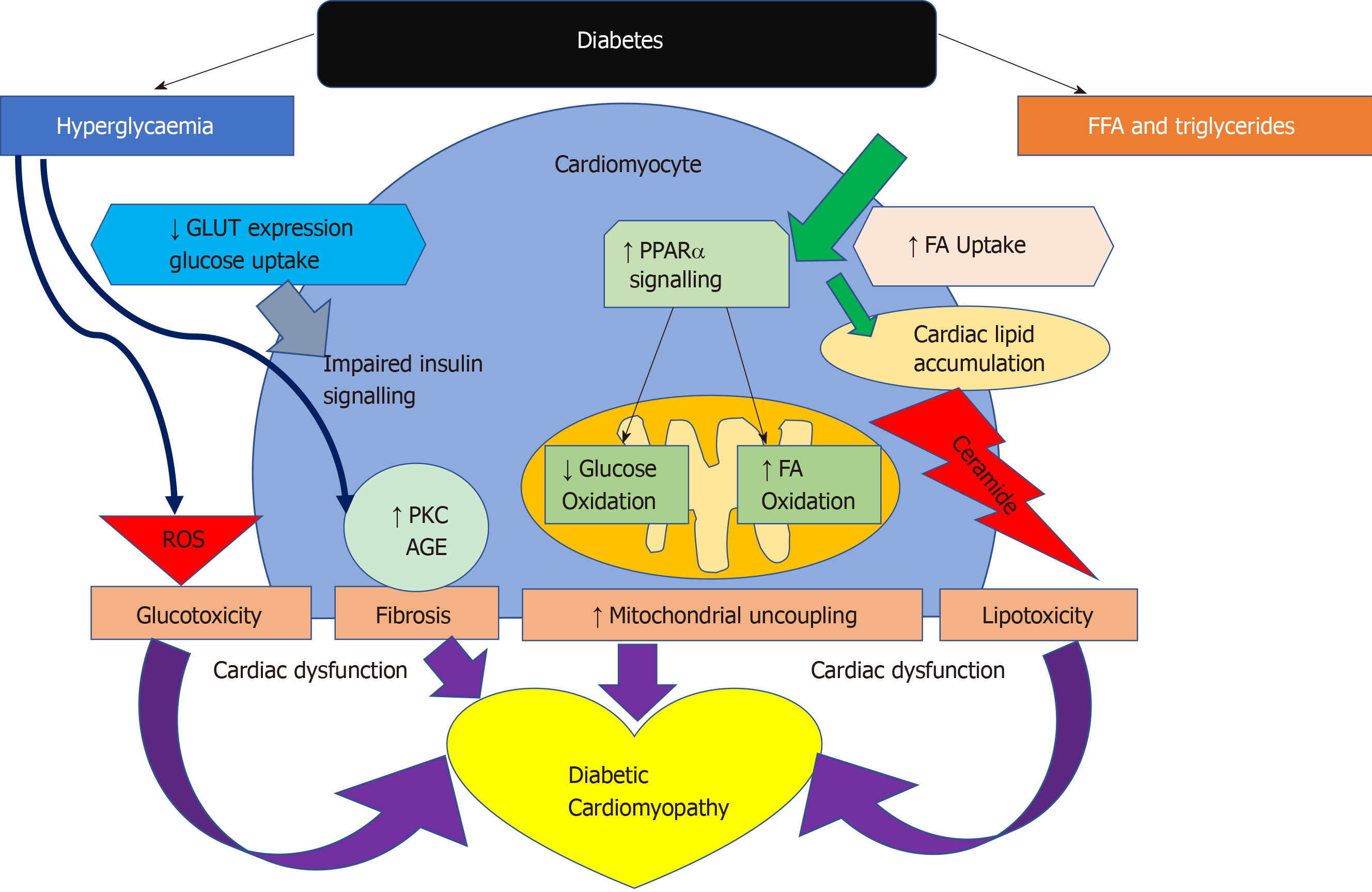
Figure 4 Pathways of cardiac dysfunction leading to diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Pathways leading to the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy[154]. AGE: Advanced glycation end products; FA: Fatty acids; FFA: Free fatty acids; GLUT: Glucose transporters; PKC: Protein kinase C; PPARα: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: Athithan L, Gulsin GS, McCann GP, Levelt E. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Pathophysiology, theories and evidence to date. World J Diabetes 2019; 10(10): 490-510
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v10/i10/490.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v10.i10.490