Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Diabetes. Oct 15, 2016; 7(18): 449-461
Published online Oct 15, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i18.449
Published online Oct 15, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i18.449
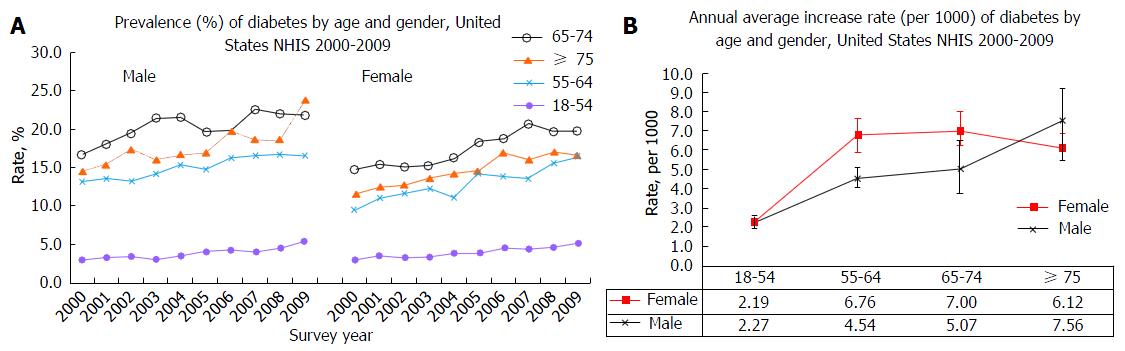
Figure 1 The Burden of diabetes in the United States.
A: Prevalence (%) of diabetes by age and gender, United States NHIS 2000-2009; B: Annual average increase rate (per 1000) of diabetes by age and gender, United States NHIS 2000-2009. NHIS: National Health Interview Surveys.
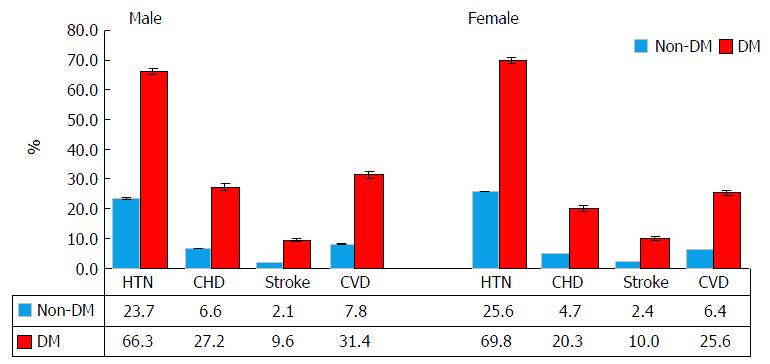
Figure 2 Prevalence (%) of comobid hypertnesion, coronary heart disease, strroke and cardiovascular disease in patients with and without diabetes mellitus, United States National Health Interview Surveys 2000-2009.
HTN: Hypertnesion; CHD: Coronary heart disease; CVD: Cardiovascular disease; DM: Diabetes mellitus; NHIS: National Health Interview Surveys.
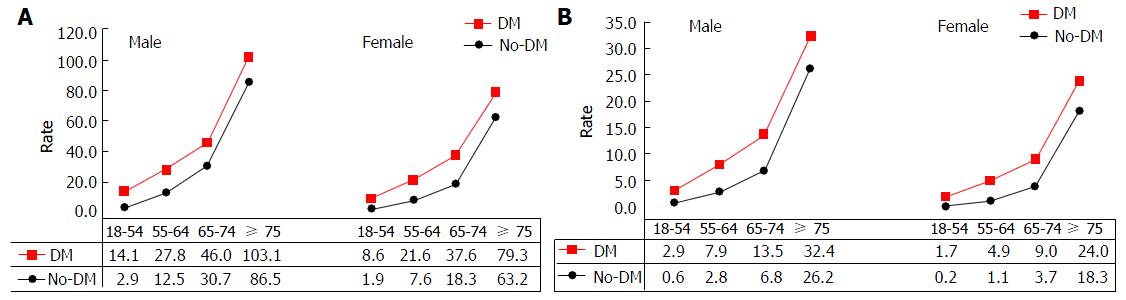
Figure 3 Mortality from all-cause and cardiovascular disease by diabetes status.
A: Mortality (per 1000 person year) from all-cause in patients without and with diabetes, United States NHIS 2000-2009; B: Mortality (per 1000 person year) from CVD in patients with diabetes by age and gender, United States NHIS 2000-2009. CVD: Cardiovascular disease; NHIS: National Health Interview Surveys; DM: Diabetes mellitus.
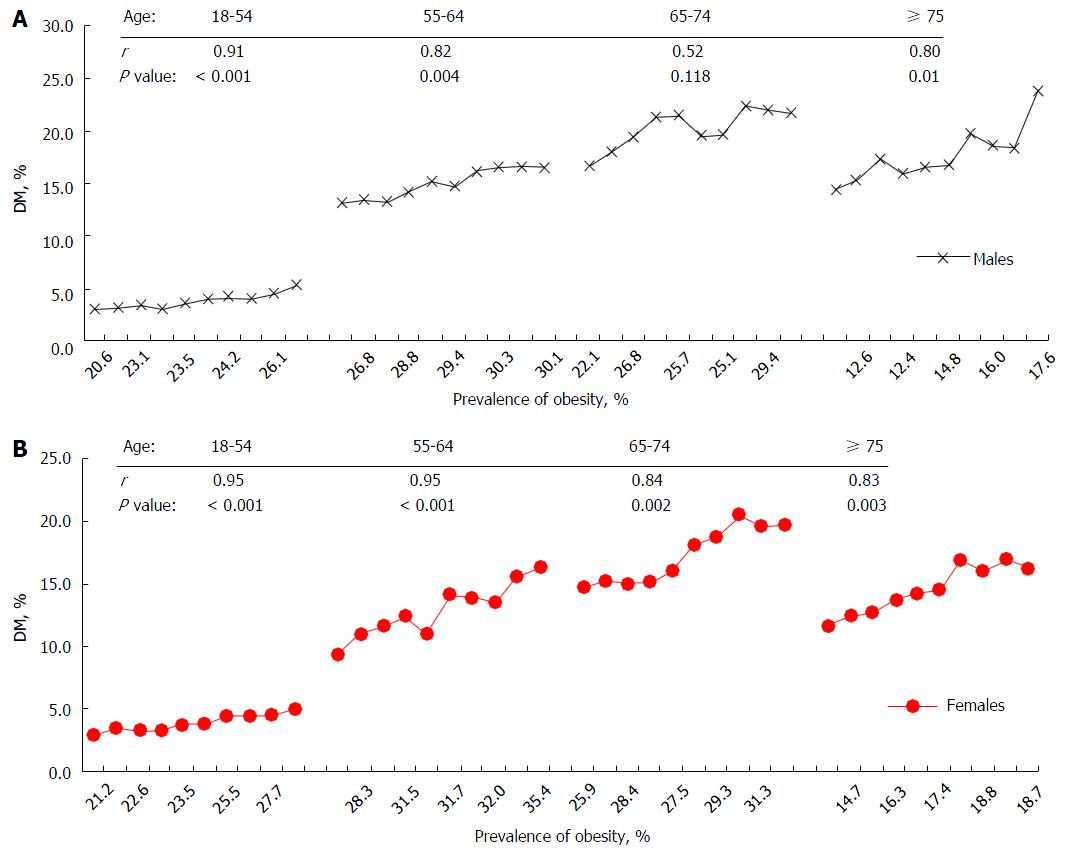
Figure 4 Chnages in obesity rates and its corelation with diabetes rates.
A: Correlation between prevalence of obesity and diabetes by age in males, United States NHIS 2000-2009; B: Correlation between prevalence of obesity and diabetes by age in females, United States NHIS 2000-2009. NHIS: National Health Interview Surveys; DM: Diabetes mellitus.
- Citation: Liu L, Simon B, Shi J, Mallhi AK, Eisen HJ. Impact of diabetes mellitus on risk of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality: Evidence on health outcomes and antidiabetic treatment in United States adults. World J Diabetes 2016; 7(18): 449-461
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v7/i18/449.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v7.i18.449