Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Diabetes. Aug 10, 2016; 7(15): 316-320
Published online Aug 10, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i15.316
Published online Aug 10, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i15.316
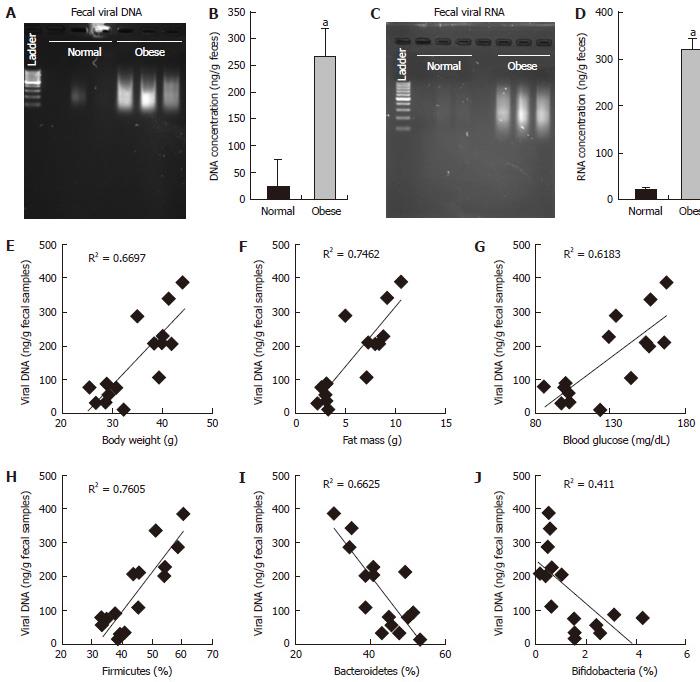
Figure 1 Fecal viral DNA and RNA content was significantly increased in obese mice and shown strong correlations with obesity associated measures and gut bacterial microbiome.
A-D: Fecal viral DNA (A and B) and fecal viral RNA (C and D) content was found to be dramatically increased in obese animals; E-J: Viral DNA was positively correlated with body weight (E), fat mass (F), blood glucose (G) and firmicutes (H), whilst negatively correlated with bacteroidetes (I) and bifidobacteria (J). Values presented here are means (n = 7) and standard error of means. Values indicated with “a“ are significantly different at the level of P < 0.001.
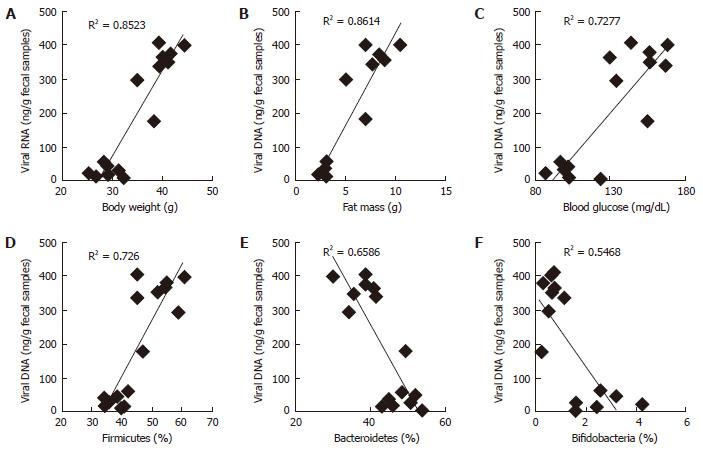
Figure 2 Fecal viral RNA content was significantly correlated with obesity associated measures and gut bacterial microbiome.
A-F: Fecal viral RNA content was positively correlated with body weight (A), fat mass (B), blood glucose (C) and firmicutes (D), whilst negatively correlated with bacteroidetes (E) and bifidobacteria (F). Values presented here are means (n = 7) and standard error of means.
- Citation: Yadav H, Jain S, Nagpal R, Marotta F. Increased fecal viral content associated with obesity in mice. World J Diabetes 2016; 7(15): 316-320
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v7/i15/316.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v7.i15.316