Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Diabetes. Jul 25, 2015; 6(8): 1045-1056
Published online Jul 25, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i8.1045
Published online Jul 25, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i8.1045
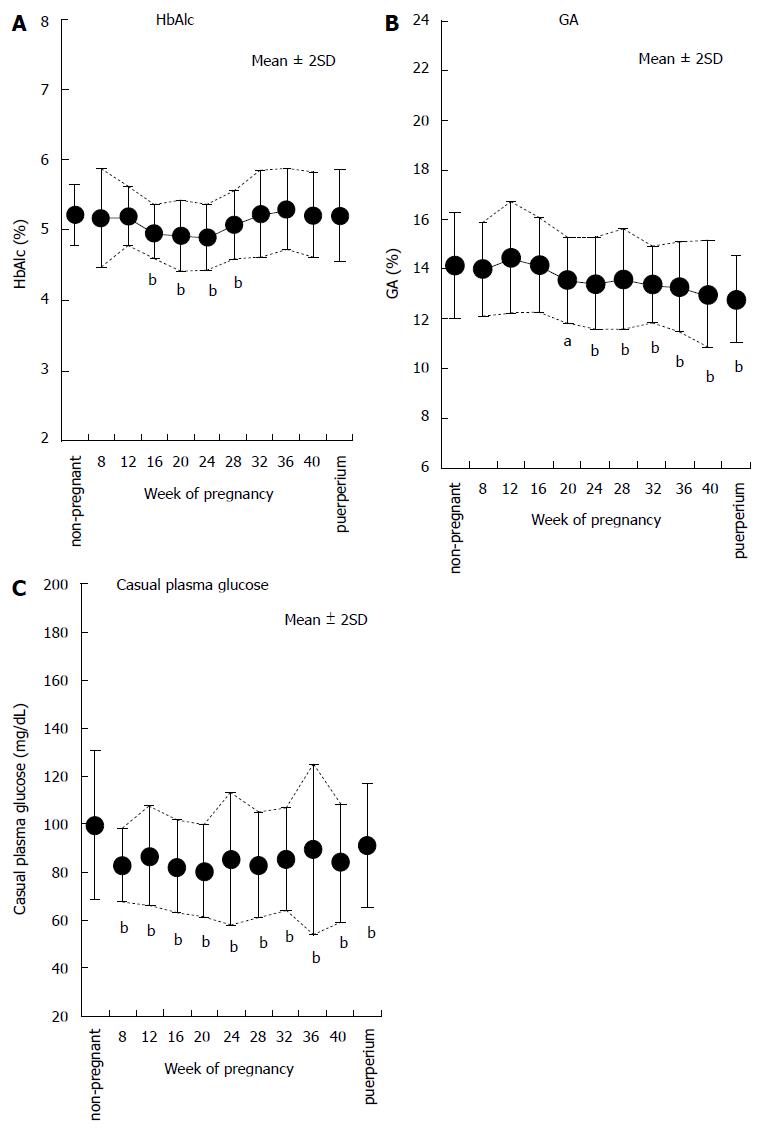
Figure 1 Time courses of indicators of glycemic control in normal pregnant women.
The time courses of HbA1c (A), GA (B), and casual plasma glucose (C) in normal pregnant women are shown (modified from Ref.[73]). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs non-pregnant women. HbA1c: Hemoglobin A1c; GA: Glycated albumin.
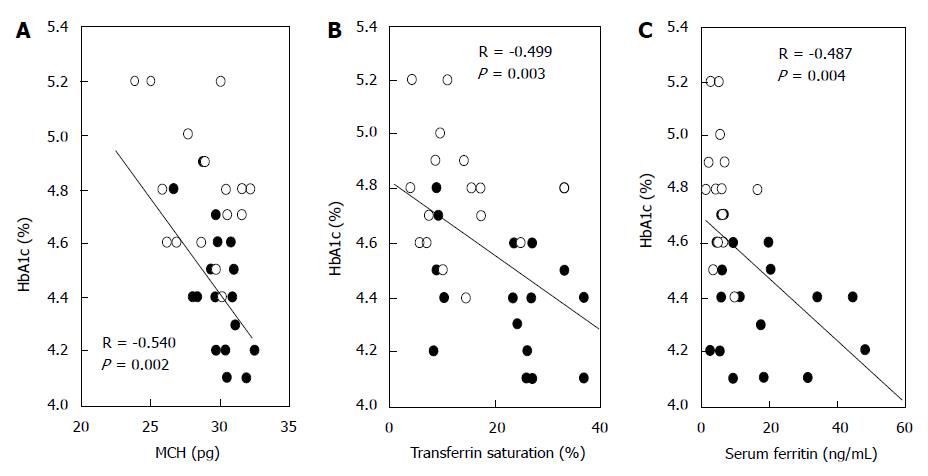
Figure 2 Correlations between hemoglobin A1c and indicators of iron deficiency in normal pregnant women.
The correlations between HbA1c and mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) (A), transferrin saturation (B), and serum ferritin (C) in normal pregnant women are shown (modified from Reference[74]). ●: Middle stage of pregnancy (wk: 20-23); ○: End stage of pregnancy (wk: 32-33); HbA1c: Hemoglobin A1c.
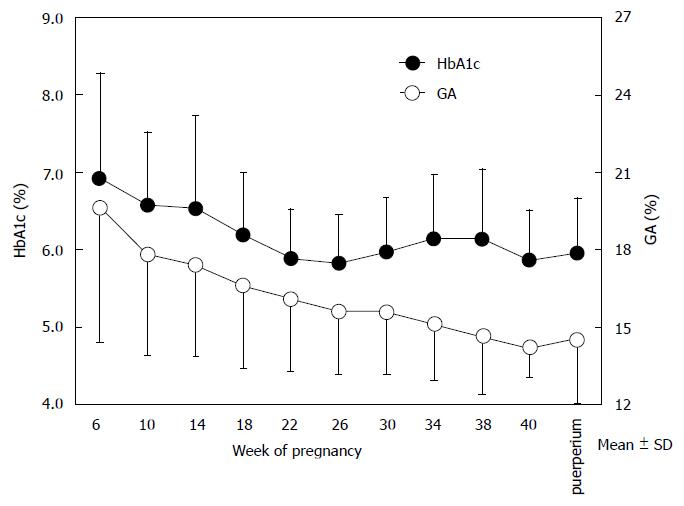
Figure 3 Time courses of hemoglobin A1c and glycated albumin in pregnant women with diabetes mellitus and patients with gestational diabetes mellitus.
The time courses of HbA1c (closed circles) and GA (open circles) in pregnant women with diabetes mellitus and patients with gestational diabetes mellitus are shown (modified from Hiramatsu et al[73]). HbA1c: Hemoglobin A1c. GA: Glycated albumin.
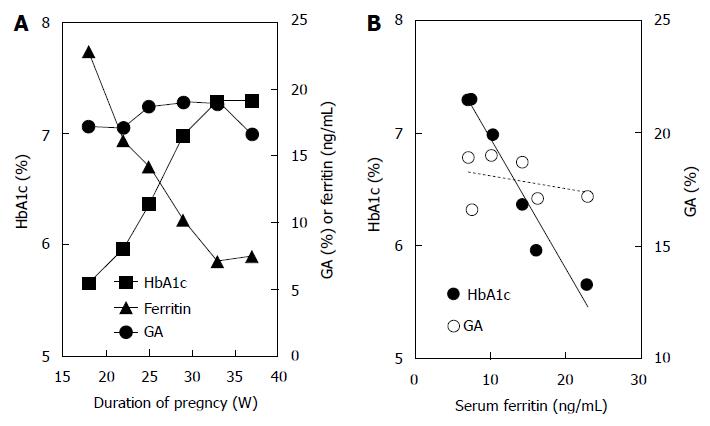
Figure 4 Time courses of hemoglobin A1c and glycated albumin and correlations between serum ferritin and hemoglobin A1c or glycated albumin in a pregnant woman with diabetes mellitus.
A: The time courses of HbA1c (closed squares), GA (closed circles), and serum ferritin (closed triangles) in a pregnant woman with diabetes mellitus (a 36-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving insulin therapy), are shown; B: Correlations between serum ferritin and HbA1c (R = -0.975, P < 0.001) or GA (R = 0.322, P = 0.534) in a pregnant woman with diabetes mellitus are shown. HbA1c: Hemoglobin A1c; GA: Glycated albumin.
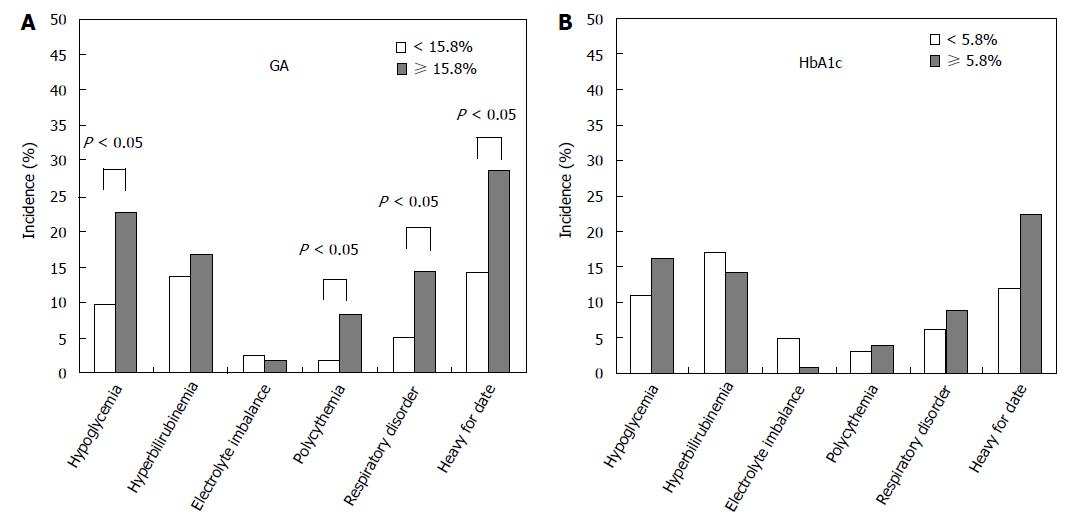
Figure 5 Comparison between glycated albumin and hemoglobin A1c during pregnancy and the incidence of neonatal complications.
For GA (A) and HbA1c (B) measured during the end stage of pregnancy, the incidence of neonatal complications was compared between the group of women whose GA or HbA1c was within the reference range (GA < 15.8%; HbA1c < 5.8%) and the group of women whose GA or HbA1c exceeded the reference range (GA ≥ 15.8%; HbA1c ≥ 5.8%) (modified from Shimizu et al[75]). HbA1c: Hemoglobin A1c; GA: Glycated albumin.
- Citation: Hashimoto K, Koga M. Indicators of glycemic control in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus and pregnant women with diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 2015; 6(8): 1045-1056
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v6/i8/1045.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i8.1045