Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Diabetes. Oct 15, 2014; 5(5): 678-688
Published online Oct 15, 2014. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i5.678
Published online Oct 15, 2014. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i5.678
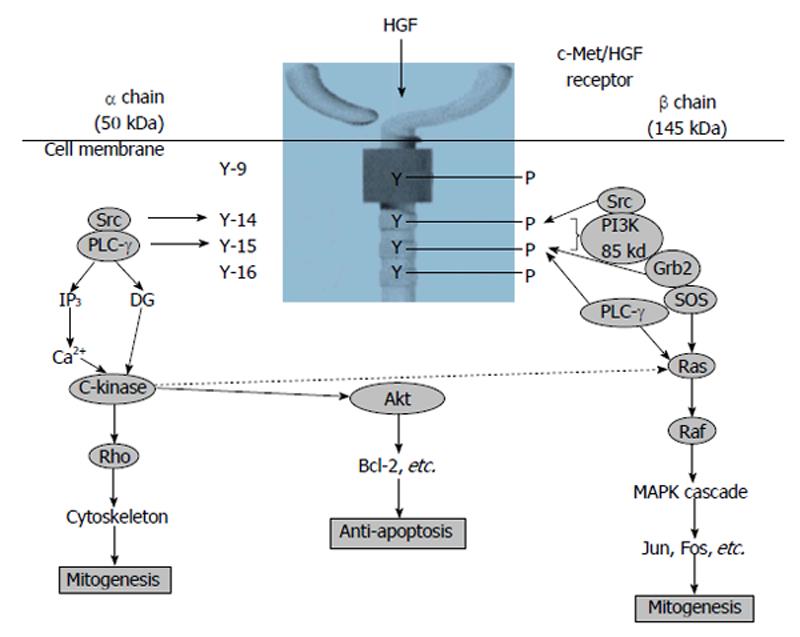
Figure 1 Signal transduction system of hepatocyte growth factor[20].
HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PLC-γ: Phospholipase C-γ; Grb2: Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; SOS: Son of sevenless.
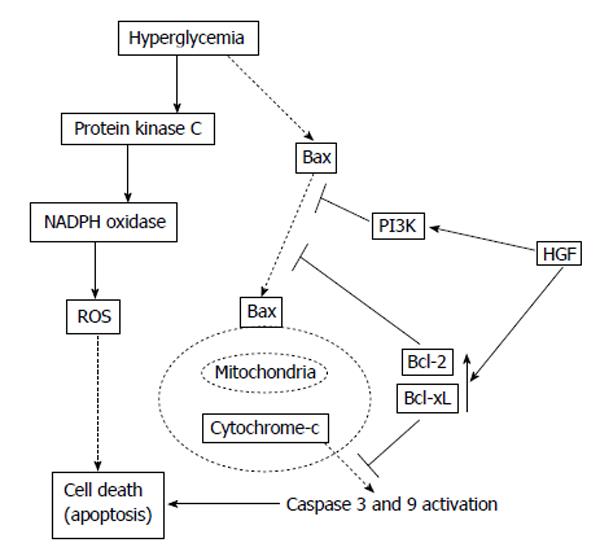
Figure 2 Potential mechanisms of anti-apoptotic effect of hepatocyte growth factor[33].
HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
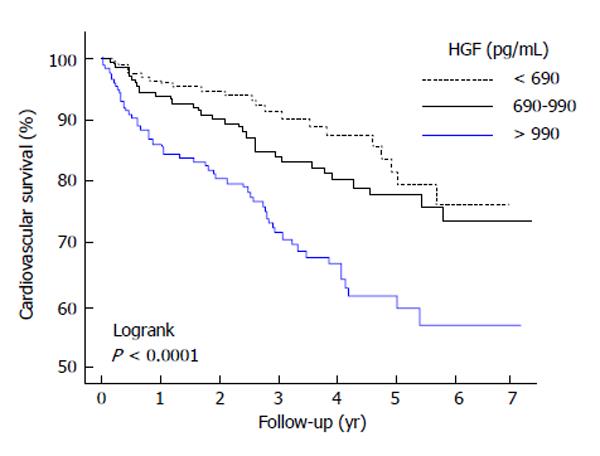
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier survival curves in accordance with the tertiles of hepatocyte growth factor.
The survival curves shows a worsened result for subjects with elevated hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) concentrations[45].
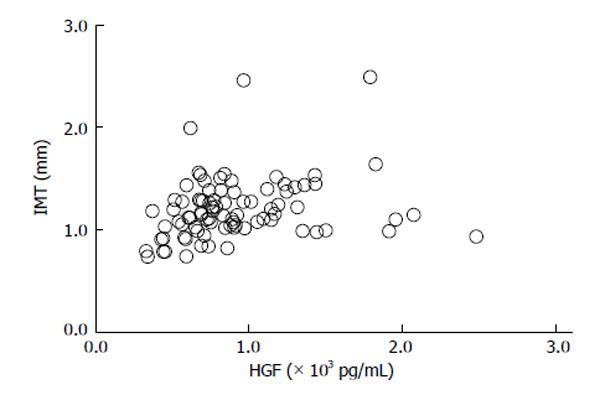
Figure 4 Relationship between serum hepatocyte growth factor and intimal-media thickness in type 2 diabetes mellitus subjects (r = 0.
24, P = 0.0248)[69]. HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor.
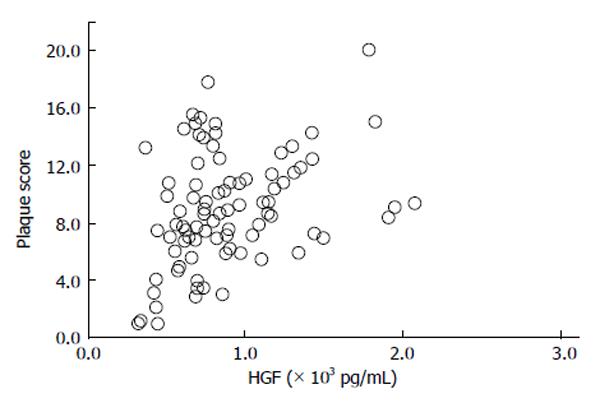
Figure 5 Relationship between serum hepatocyte growth factor and plaque score in type 2 diabetes mellitus subjects (r = 0.
27, P = 0.0126)[69]. HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor.
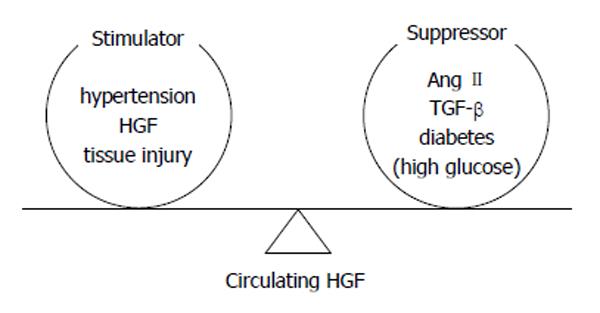
Figure 6 Determination of circulating hepatocyte growth factor level by the balance between stimulators and suppressors[19].
HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; TGF: Transforming growth factor.
- Citation: Konya H, Miuchi M, Satani K, Matsutani S, Tsunoda T, Yano Y, Katsuno T, Hamaguchi T, Miyagawa JI, Namba M. Hepatocyte growth factor, a biomarker of macroangiopathy in diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 2014; 5(5): 678-688
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v5/i5/678.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v5.i5.678