Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Diabetes. Jun 15, 2013; 4(3): 70-75
Published online Jun 15, 2013. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v4.i3.70
Published online Jun 15, 2013. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v4.i3.70
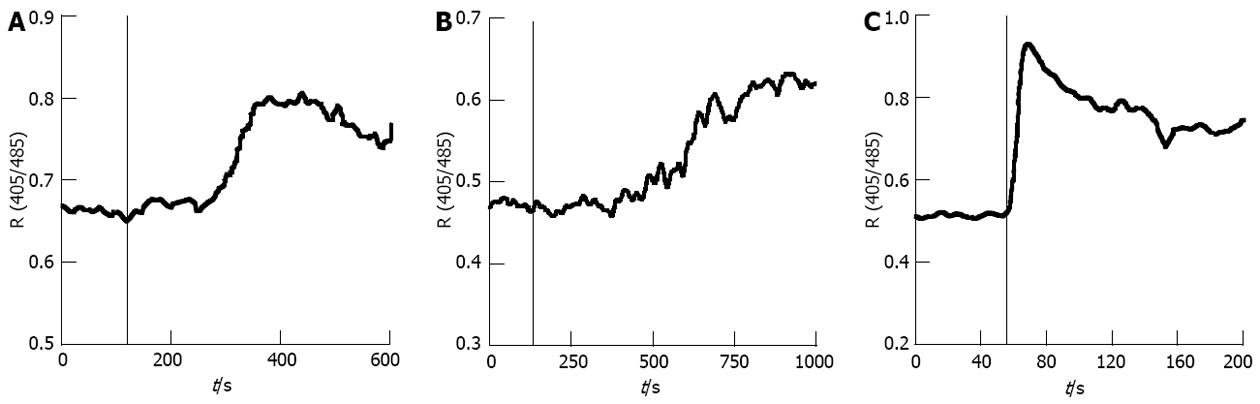
Figure 1 Indo-1 calcium fluorescence measurements of caribbean maitotoxin, pacific maitotoxin and 40 mmol/L of KCl in HIT-T15 cells.
The vertical axis represents relative free intracellular calcium concentration as estimated by the ratio of fluorescent emissions at 405 and 485, respectively. The vertical bars in the figure indicate the time when the toxins or KCl were perfused.
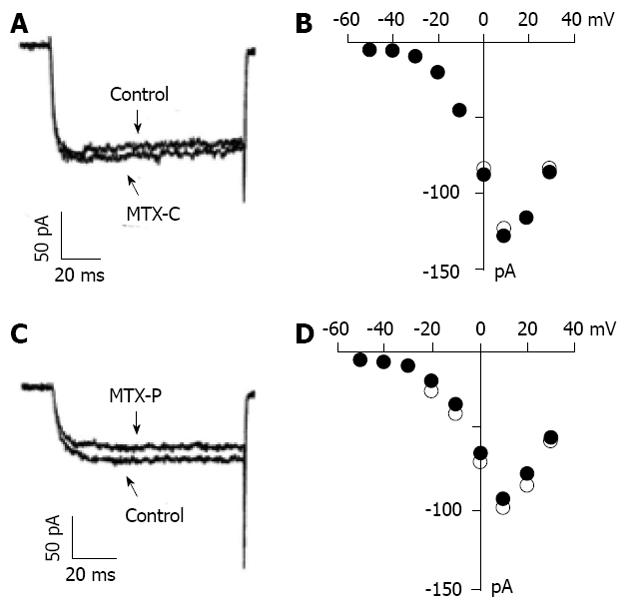
Figure 2 Effect of caribbean maitotoxin (A) and pacific maitotoxin (C) on voltage gated calcium channels in HIT-T15 cells.
Representative barium current traces recorded at 10 mV when held at -70 mV in patch clamp. Extracellular solution contains 40 mmol/L BaCl2. B and D show I-V relationship of voltage gated calcium currents elicited by caribbean maitotoxin (B) and pacific maitotoxin (D), respectively. Open and solid circles represent values of current before and after application of maitotoxins, respectively.
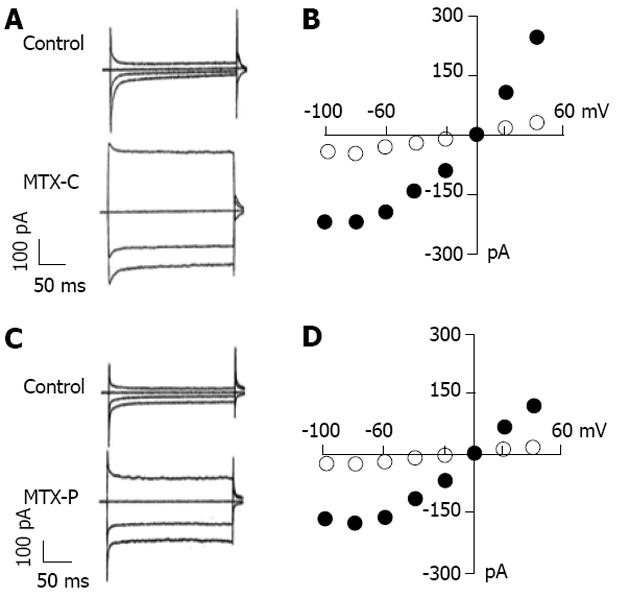
Figure 3 Effect of caribbean maitotoxin and pacific maitotoxin on non-voltage activated cation currents in HIT-T15 cells.
Representative traces of cation current elicited recorded at -80, -40, 0 and 40 mV before and after adding caribbean maitotoxin (MTX-C) (A) or pacific maitotoxin (MTX-P) (C). The holding potential was at 0 mV. I-V relationships of MTX-C- and MTX-P-elicited currents are shown in B and D, respectively. The solid circles represent current amplitudes measured after MTX-C (B) or MTX-P (D) administration. The open circles represent the current recorded under the control condition.
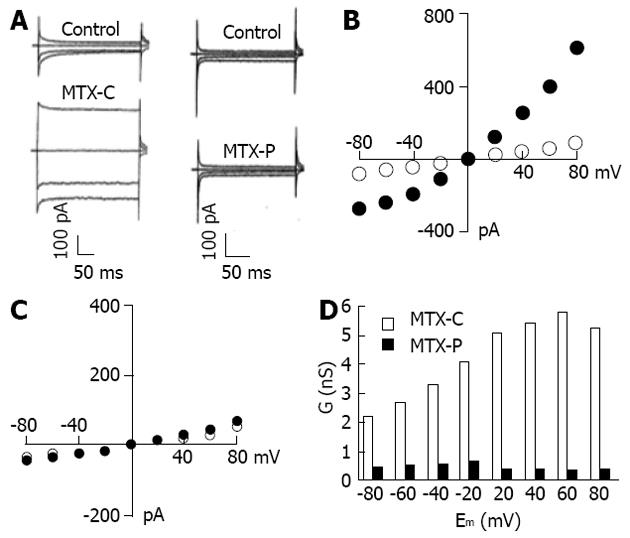
Figure 4 Non-voltage activated cation current induced by caribbean maitotoxin or pacific maitotoxin in the calcium free extracellular solution.
A: Current traces measured before and after caribbean maitotoxin (MTX-C) or pacific maitotoxin (MTX-P) administration at -80, -40, 0 and 40 mV when held at 0 mV; B and C: I-V relationships of MTX-C (B) and MTX-P (C) elicited currents. The solid circles represent current amplitudes measured after MTX-C (B) or MTX-P (C) administration. The open circles represent the current recorded under the control condition; D: Current conductance measured at different test potentials in cells treated with MTX-C or MTX-P.
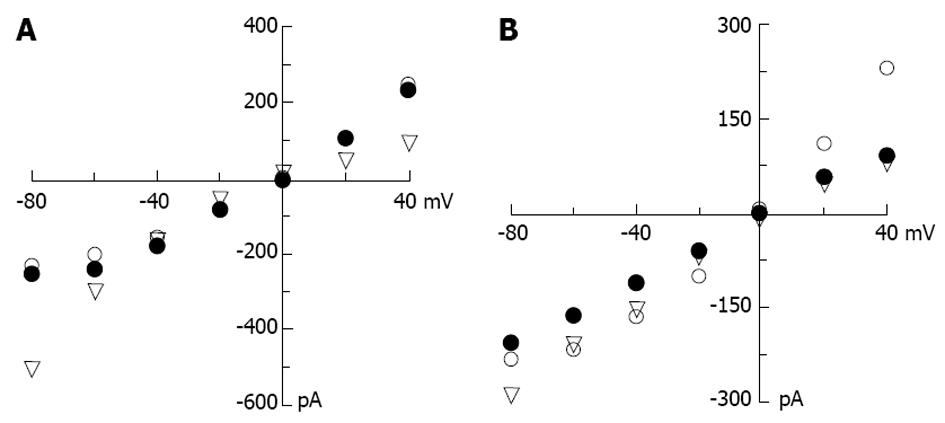
Figure 5 Current and voltage (I-V) relationships of caribbean maitotoxin (A) and pacific maitotoxin (B) opened cation currents.
The pipette solution contains 130 mmol/L CsCl; the bath solutions contain 120 mmol/L of CsCl (open circle), NaCl (solid circle) or KCl (triangle).
- Citation: Lu XZ, Deckey R, Jiao GL, Ren HF, Li M. Caribbean maitotoxin elevates [Ca2+]i and activates non-selective cation channels in HIT-T15 cells. World J Diabetes 2013; 4(3): 70-75
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v4/i3/70.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v4.i3.70