Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2012; 3(12): 186-195
Published online Dec 15, 2012. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v3.i12.186
Published online Dec 15, 2012. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v3.i12.186
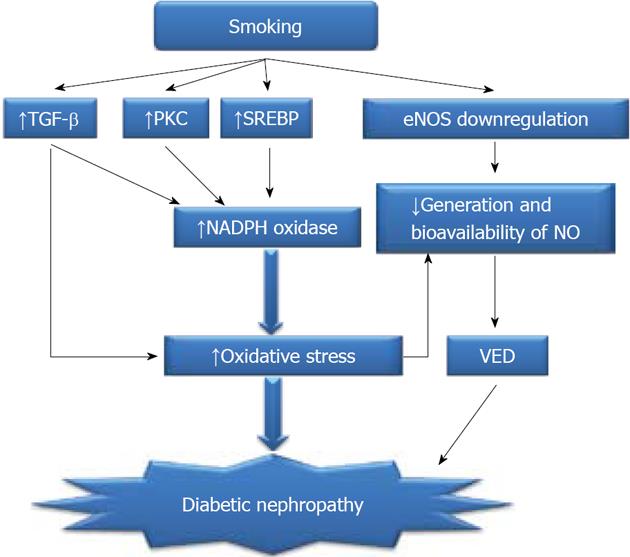
Figure 1 Possible mechanism involved in smoking-induced oxidative stress.
TGF-β: Transforming growth factor β; PKC: Protein kinase C; eNOS: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; NO: Nitric oxide; SREBP: Sterol regulating element binding protein; VED: Vascular endothelial dysfunction.
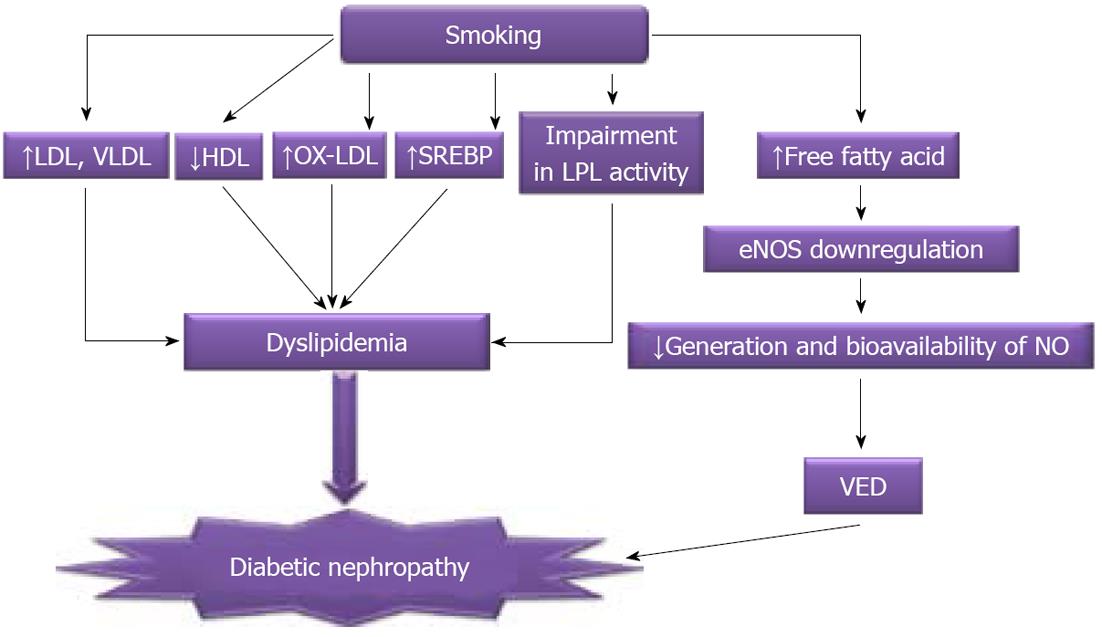
Figure 2 Possible mechanisms involved in smoking-induced dyslipidemia.
eNOS: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; NO: Nitric oxide; SREBP: Sterol regulating element binding protein; VED: Vascular endothelial dysfunction; LDL: Low density lipoprotein; VLDL: Very low density lipoprotein; HDL: High density lipoprotein; LPL: Lipoprotein lipase.
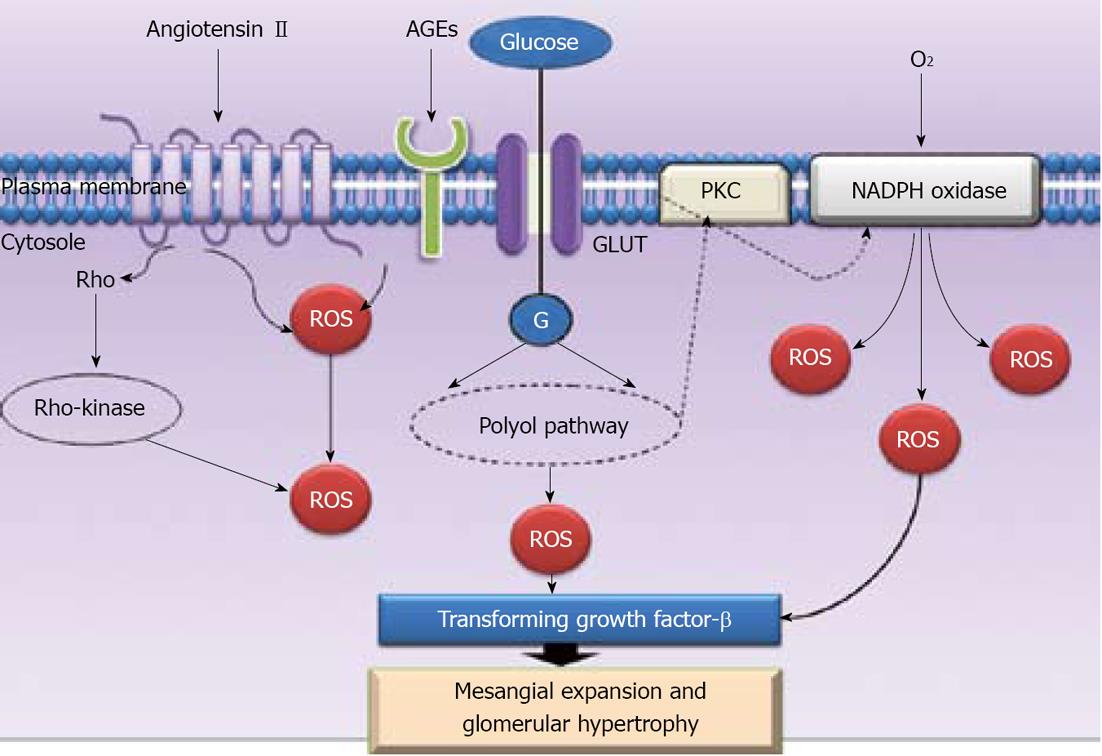
Figure 3 Various endogenous modulators contribute to renal complications.
AGEs: Advance glycation end products; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; GLUT: Glucose transporters; PKC: Protein kinase C; NADPH oxidase: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-oxidase.
- Citation: Chakkarwar VA. Smoking in diabetic nephropathy: sparks in the fuel tank? World J Diabetes 2012; 3(12): 186-195
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v3/i12/186.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v3.i12.186