Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Aug 15, 2025; 16(8): 105228
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i8.105228
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i8.105228
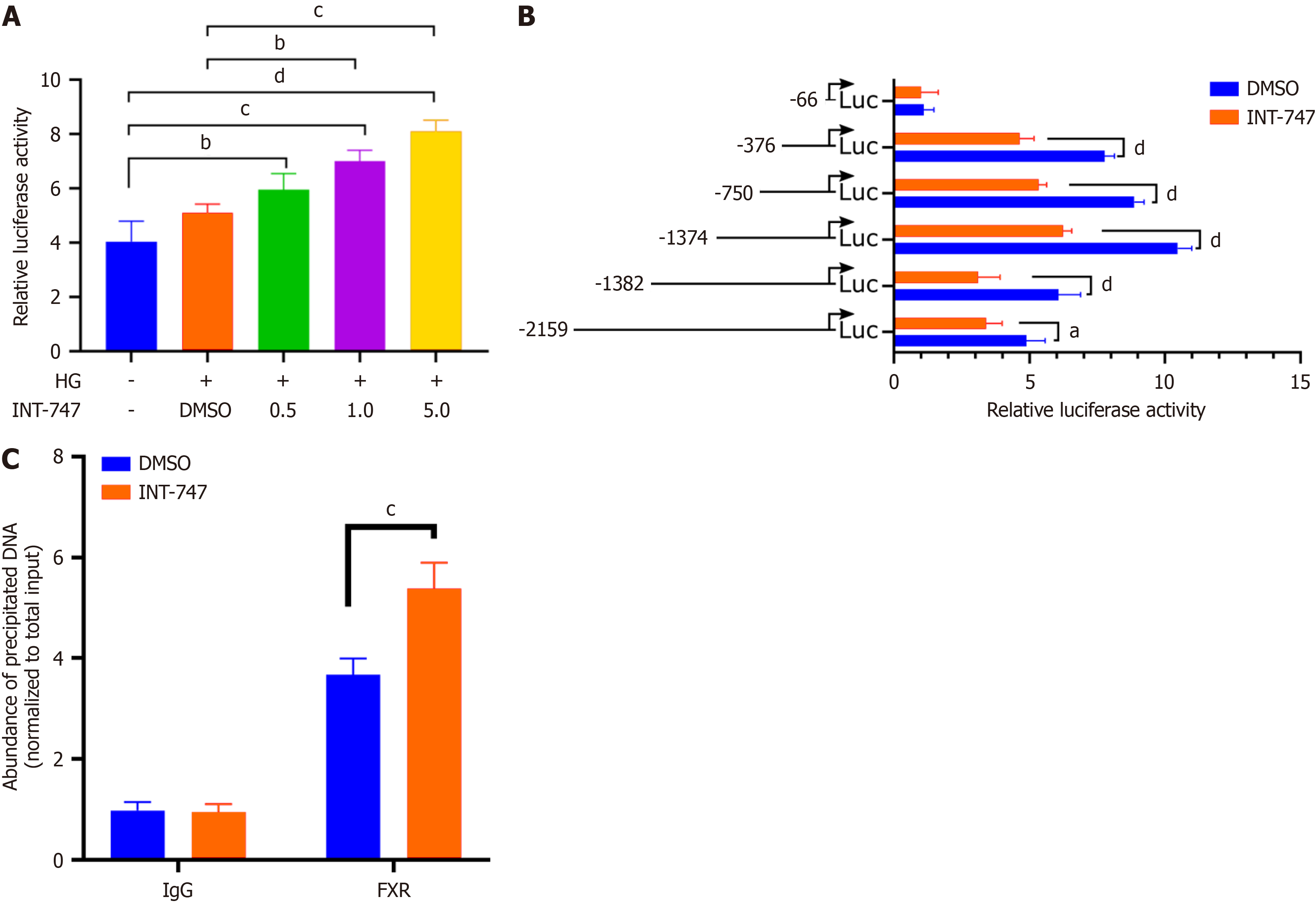
Figure 1 Farnesoid X receptor positively regulates its expression by binding to the binding immunoglobulin protein promoter region.
A: Fluorescent enzyme reporter gene detection showed that the activity of the binding immunoglobulin protein (BiP) gene promoter increased in a dose-dependent manner after treatment with farnesoid X receptor agonist obeticholic acid (INT-747); B: After truncating the BiP gene promoter sequence, luciferase reporter gene detection showed that transcriptional activity was still present in the -376 to +200 sequence of the BiP gene promoter; C: Chromatin immunoprecipitation quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction results show that anti farnesoid X receptor antibodies significantly enrich the promoter sequence of BiP gene. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. dP < 0.0001. HG: High glucose; DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; INT-747: Obeticholic acid; FXR: Farnesoid X receptor; Luc: Luciferase.
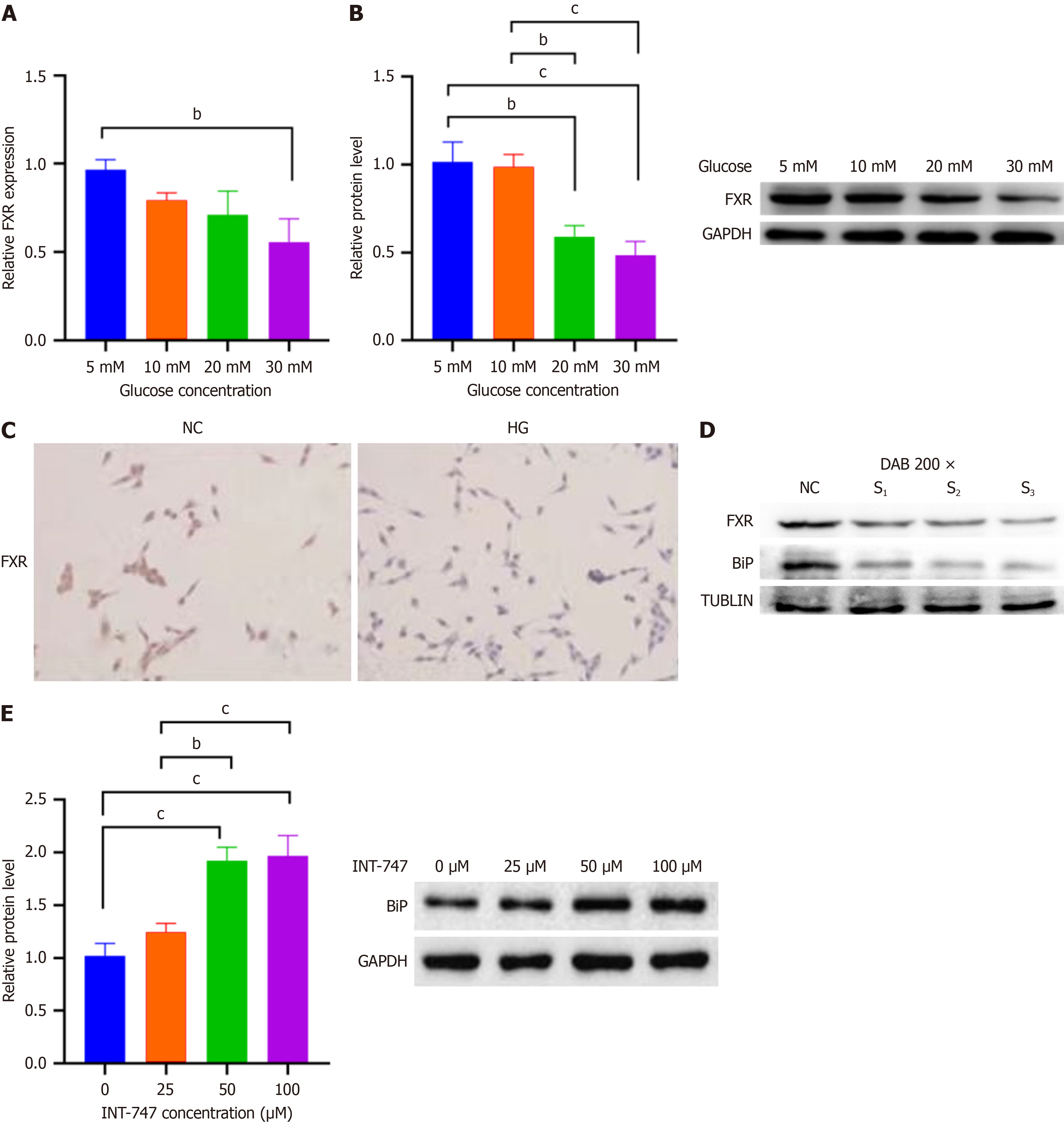
Figure 2 Downregulation of farnesoid X receptor expression in mesangial cells under high glucose conditions, farnesoid X receptor has a positive regulatory effect on binding immunoglobulin protein expression in mesangial cells.
A: Bar chart shows that the message RNA level of farnesoid X receptor (FXR) decreases with increasing glucose concentration, as detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; B: Western blot shows that the protein level of FXR decreases with increasing glucose concentration; C: Immunocytochemical staining detected a decrease in FXR expression in high glucose-treated mesangial cells compared to the control group; D: Western blot detection shows a synchronous decrease in binding immunoglobulin protein (BiP) expression after small interfering RNA inhibition of FXR; E: Western blot detection of the effect of different concentrations of FXR agonists or inhibitors on BiP protein levels in mesangial cells. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. HG: High glucose; INT-747: Obeticholic acid; FXR: Farnesoid X receptor; NC: Negative control; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; DAB: 3,3’-diaminobenzidine color development; BiP: Binding immunoglobulin protein; TUBLIN: Tubulin antibody.
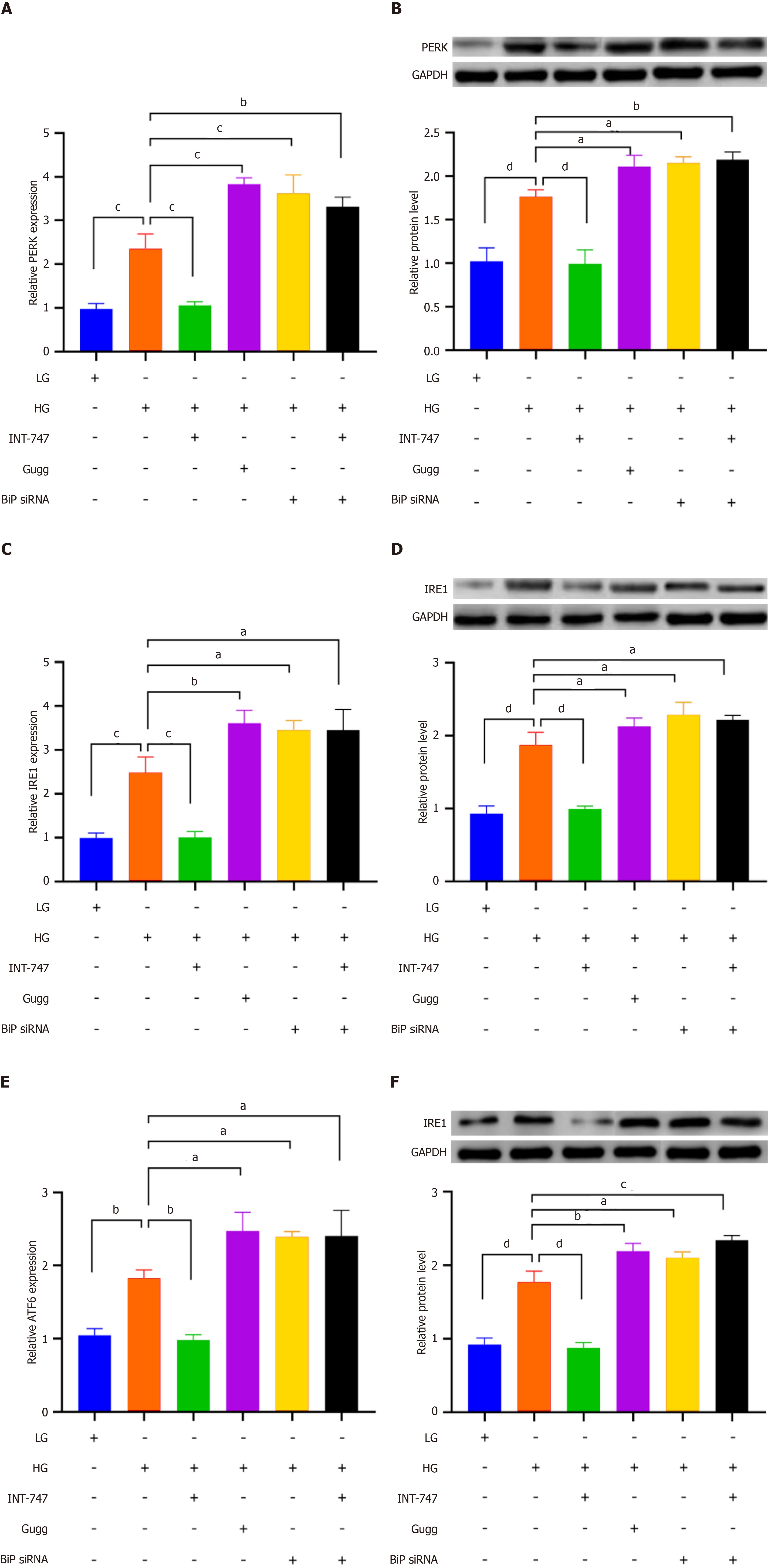
Figure 3 Farnesoid X receptor regulates the effect of binding immunoglobulin protein on downstream endoplasmic reticulum stress related signaling molecules.
A: Bar chart showing the expression levels of protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) message RNA (mRNA) in different treatment groups, detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR); B: Western blot (WB) displays the expression levels of PERK protein in different treatment groups, and the bar chart shows the grayscale values of WB bands; C: Bar chart showing the expression levels of inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1) mRNA in different treatment groups, detected by qRT-PCR; D: WB displays the expression levels of the IRE1 protein in different treatment groups, with the bar chart showing the grayscale values of WB bands; E: Bar chart showing the expression levels of activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6) mRNA in different treatment groups, detected by qRT-PCR; F: WB displays the expression levels of the ATF6 protein in different treatment groups, with the bar chart showing the grayscale values of WB bands. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. dP < 0.0001. HG: High glucose; LG: Low glucose; INT-747: Obeticholic acid; BiP: Binding immunoglobulin protein; Gugg: Guggulsterones; siRNA: Small interfering RNA; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; PERK: Protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; IRE1: Inositol-requiring enzyme 1; ATF6: Activating transcription factor 6.
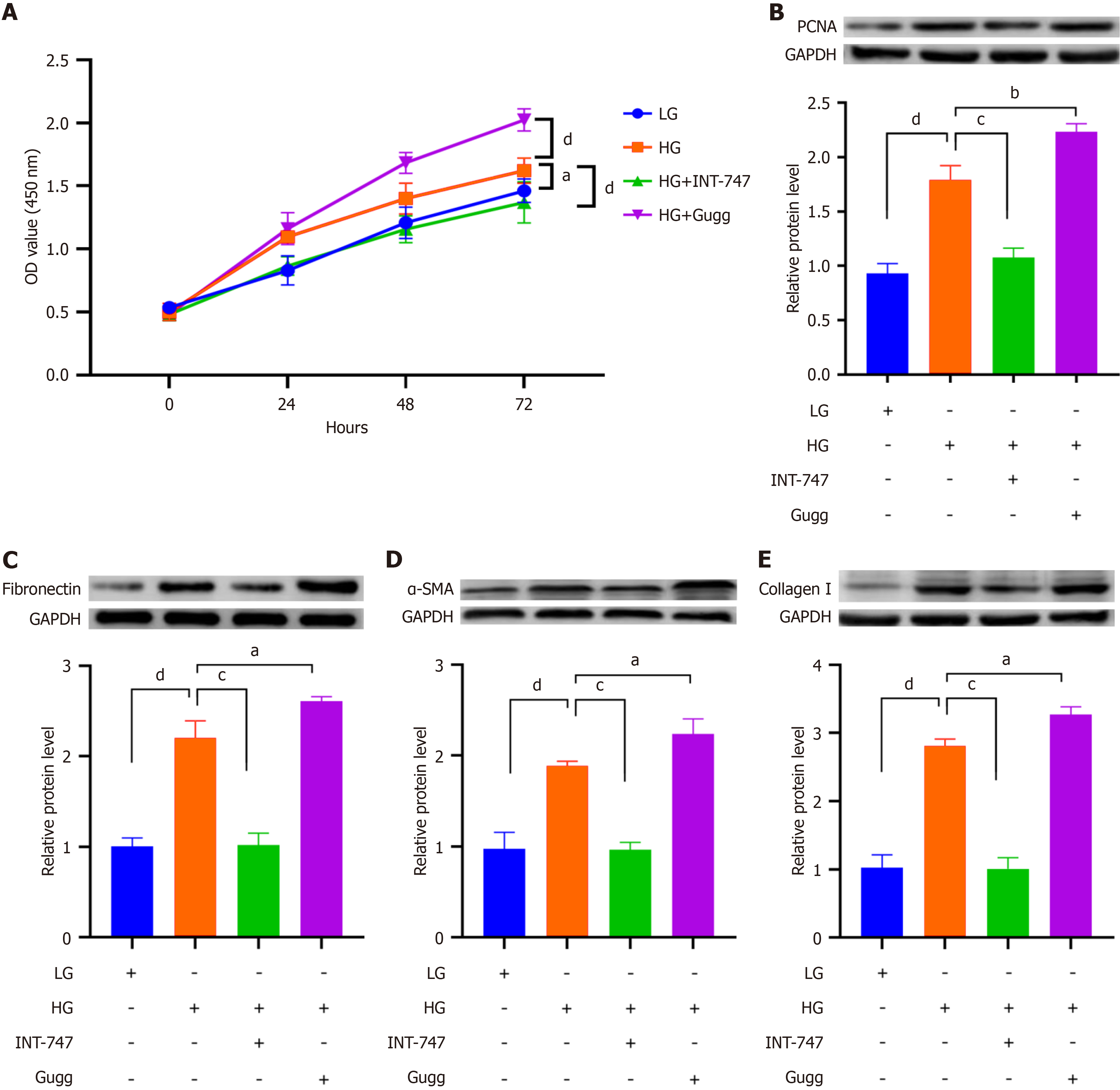
Figure 4 The effect of artificial intervention on farnesoid X receptor activity on mesangial cell proliferation and extracellular matrix synthesis.
A: Cell counting kit-8 detection of mesangial cell proliferation; B-E: Western blot detection of the expression of PCNA, fibronectin, α-smooth muscle actin, and collagen I. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. dP < 0.0001. HG: High glucose; LG: Low glucose; INT-747: Obeticholic acid; Gugg: Guggulsterones; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; OD: Optical density; α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin.
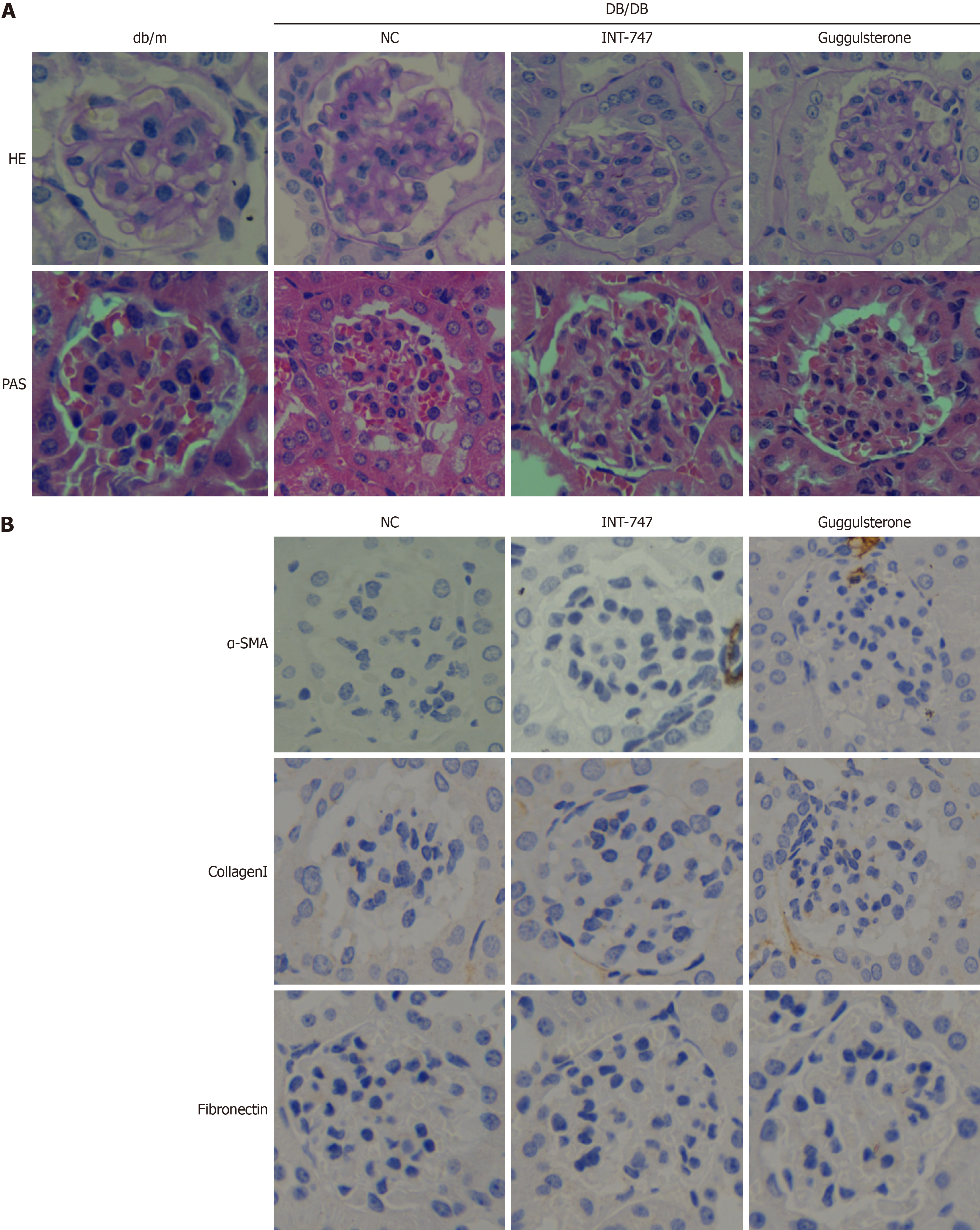
Figure 5 Farnesoid X receptor agonist upregulates binding immunoglobulin protein expression in db/db mice and improves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy mice.
A: Pathological changes in mouse kidneys after treatment with farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonists and inhibitors; B: Immunohistochemical detection of the effects of FXR agonists and inhibitors on the expression of renal fibrosis related proteins. NC: Negative control; HE: Hematoxylin eosin; PAS: Periodic acid-Schiff stain; INT-747: Obeticholic acid; α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin.
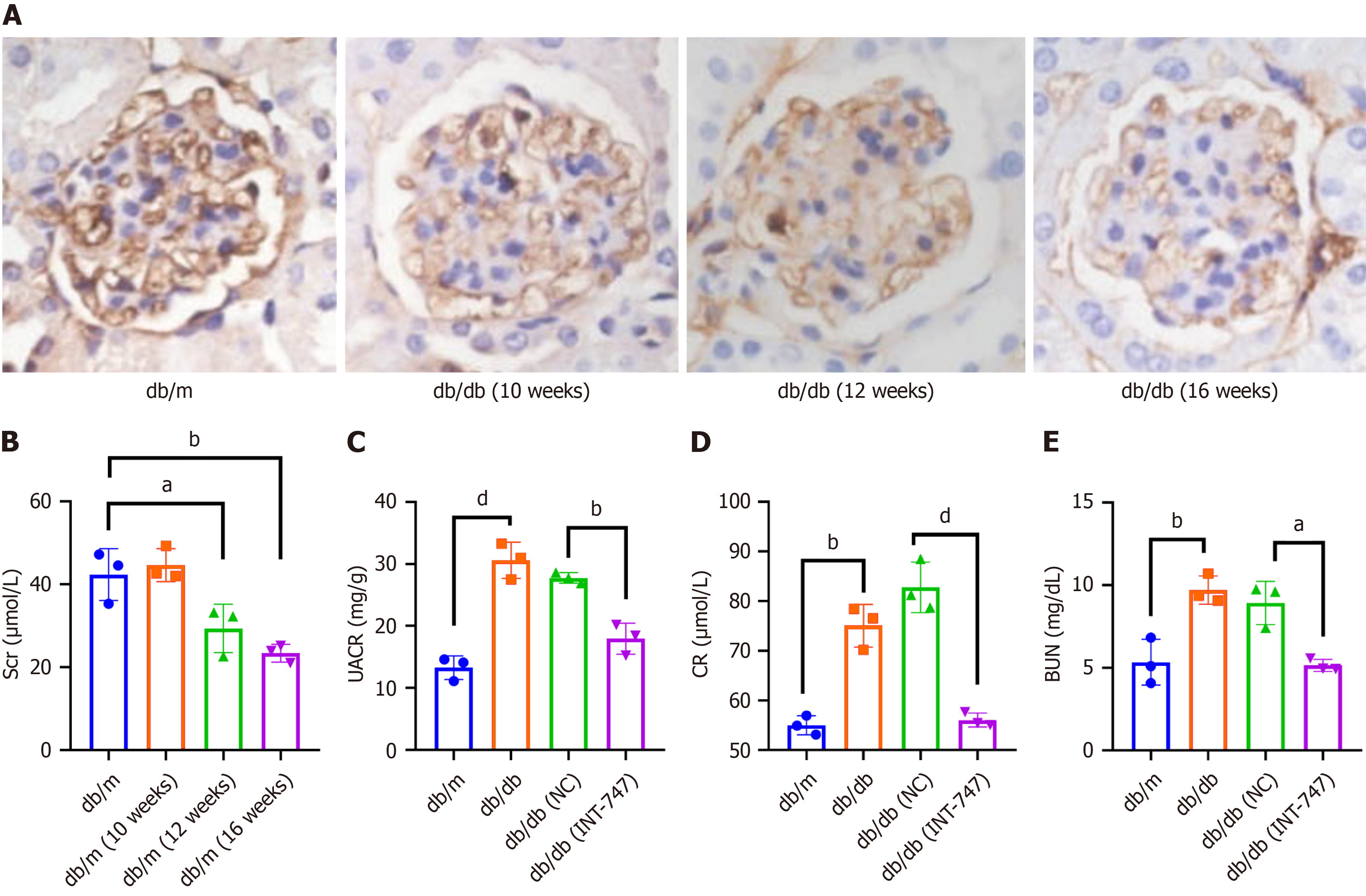
Figure 6 Downregulation of farnesoid X receptor expression in diabetic nephropathy mouse kidney tissue, changes in serum biochemical indicators of mice after farnesoid X receptor agonist intervention.
A: Immunohistochemical staining detection of farnesoid X receptor expression in renal tissue of db/db mice at different weeks of age compared to db/m; B: Changes in blood creatinine levels in db/m and db/db mice at different weeks of age; C-E: Changes in urinary and serum biochemical indicators in db/db mice treated with obeticholic acid. NC: Negative control; INT-747: Obeticholic acid; Scr: Serum creatinine; UACR: Urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio; CR: Creatinine; BUN: Blood urea nitrogen.
- Citation: Tang JY, Chong YJ, Yang L, Li X, Yang Y, Li JC, Mu J. Activation of farnesoid X receptor upregulates binding immunoglobulin protein expression and alleviates diabetic nephropathy. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(8): 105228
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i8/105228.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i8.105228