Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Jul 15, 2025; 16(7): 103468
Published online Jul 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i7.103468
Published online Jul 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i7.103468
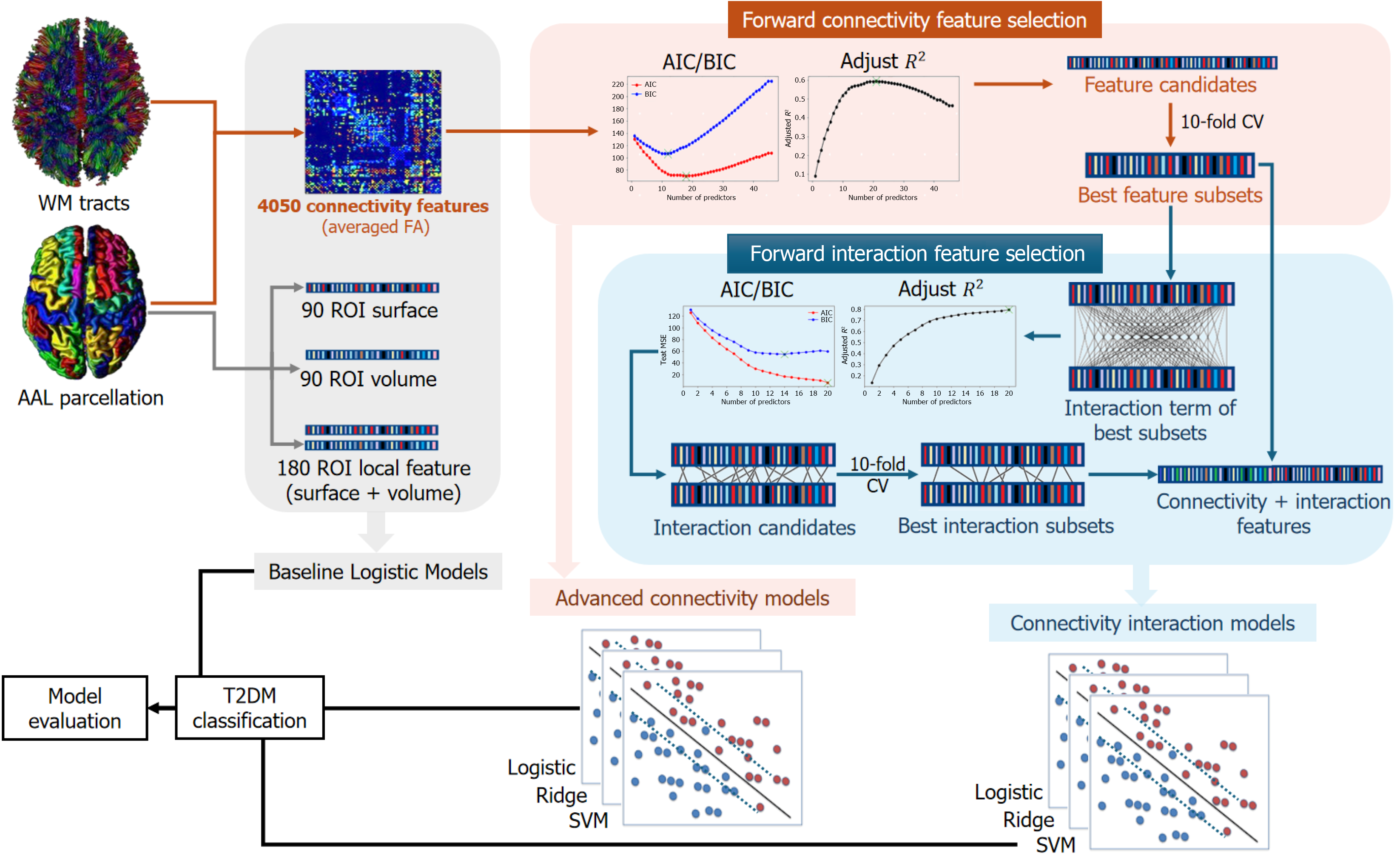
Figure 1 Illustration for the classification schematic flow.
The schematic flow for building the classification models involved the application of feature selection metrics (Akaike information criterion, Bayesian information criterion, and adjusted R2) to select connectivity feature candidates, and 10-fold cross validation (CV) was used to determine the optimal feature subsets. Then, interaction terms were screened on the selected connectivity features to further improve the model's performance. Finally, all the models were evaluated using 10-fold CV on accuracy: Precision, recall and F1-score. The feature selection process is outlined in more detail in Supplementary Figure 2. Note that all baseline models used Logistic classification. WM: White matter; AAL: Automated anatomical labelling atlas; ROI: Region of interest; FA: Fractional anisotropy; AIC: Akaike information criterion; BIC: Bayesian information criterion; CV: Cross validation; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; Logistic: Logistic classification; Ridge: Ridge classification; SVM: Supporting vector machine.
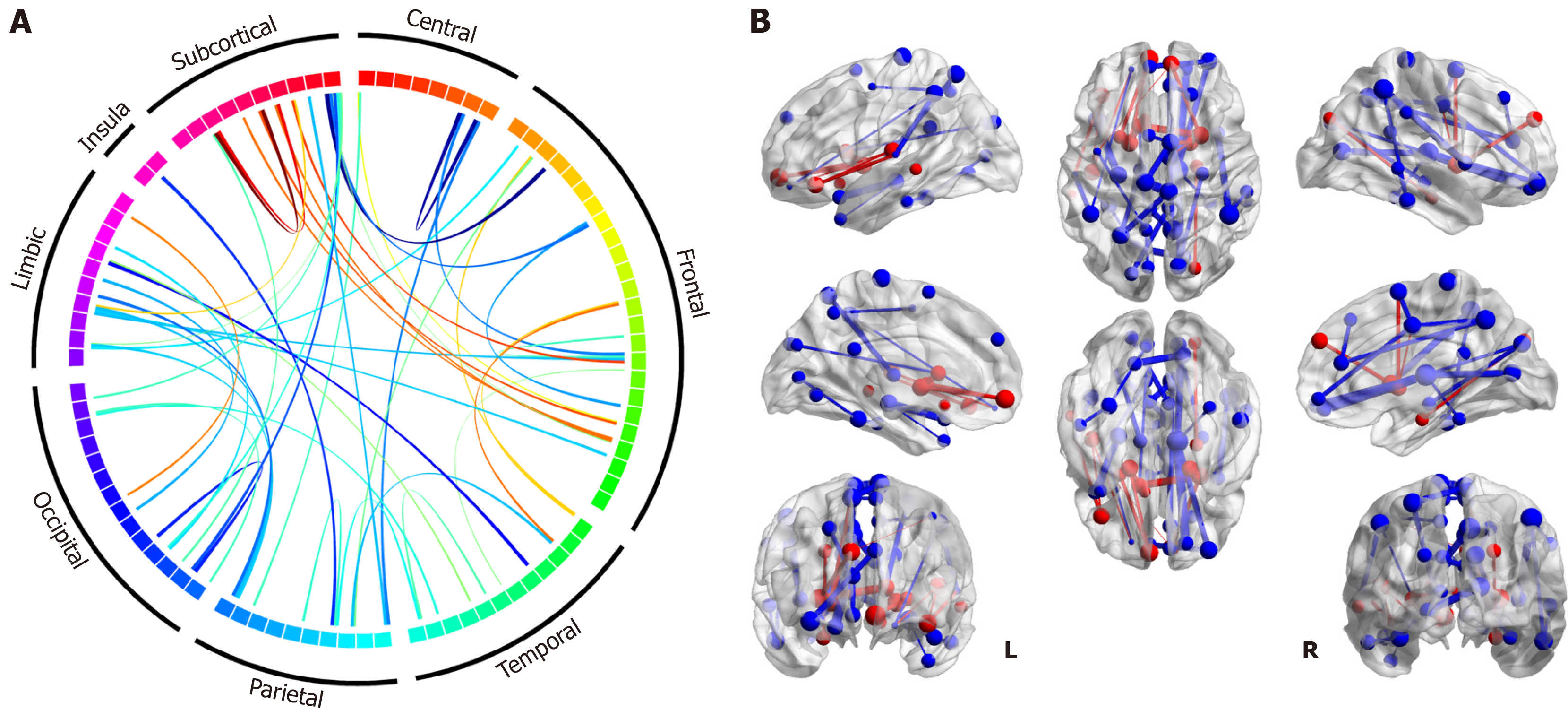
Figure 2 Structural connectivity difference between type 2 diabetes mellitus and healthy control.
The blue line indicates that the connection strength is weaker in the type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) group compared to the healthy control (HC) group. The red line indicates that the connection strength is stronger in the T2DM group. A: Circos plots for structural connections significantly different between two groups. The plot uses AAL90 regions of interest (ROIs) and refers to the eight major regions based on automated anatomical labelling atlas division for the ROIs in cerebral cortex; B: Location of the 47 structural connections significantly different between two groups. Thicker lines indicate larger statistical values, indicating greater significance in the observed differences between the groups.
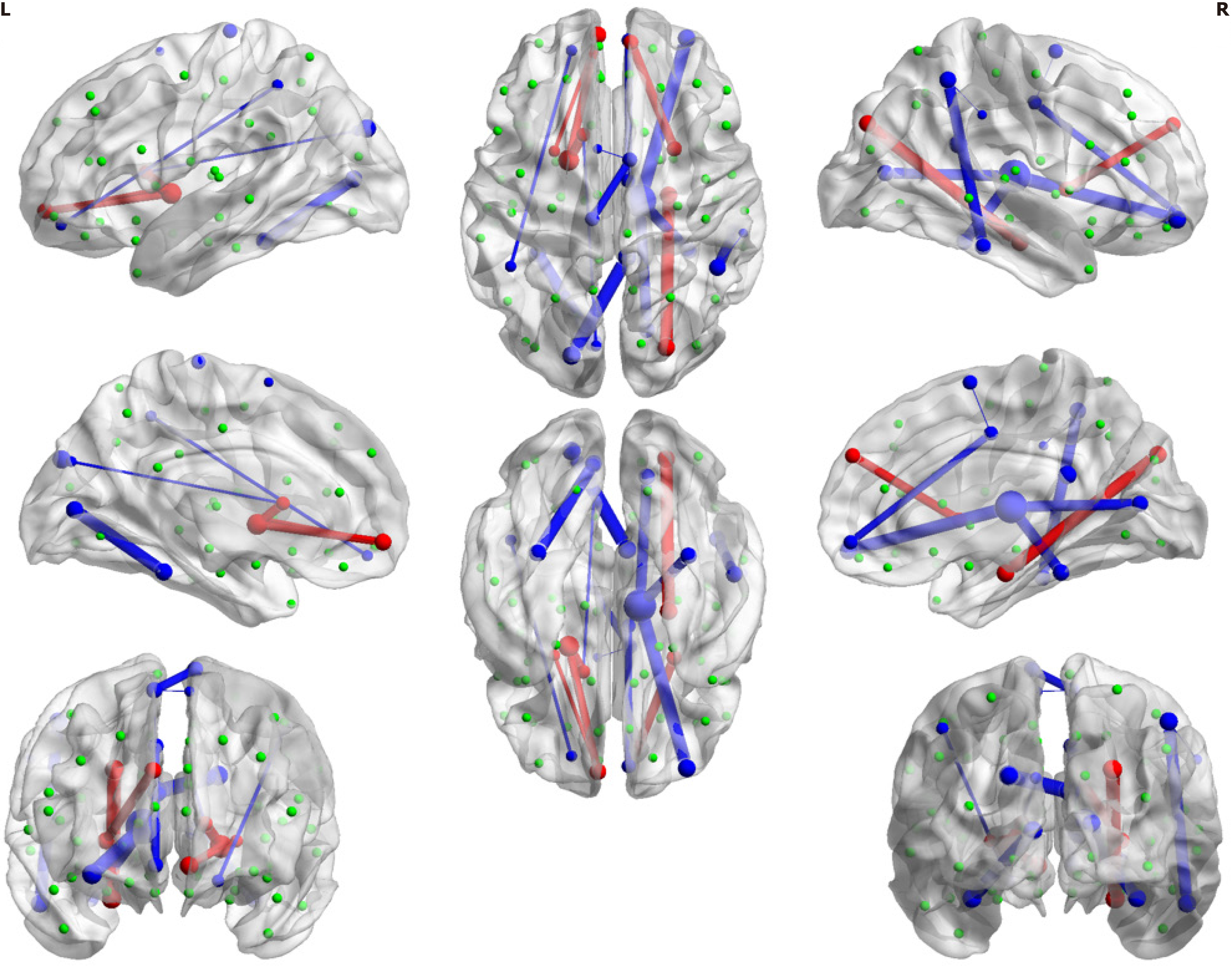
Figure 3 Location of the 18 structural connections selected by forward feature selection.
The blue line indicates that the connection strength is weaker in the type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) group compared to the healthy control group. The red line indicates that the connection strength is stronger in the T2DM group. Thicker lines indicate larger statistical values, indicating greater significance in the observed differences between the groups. The process of the optimal model selection and the model evaluation metrics were included in the Supplementary Figure 2.
- Citation: Li YF, Wei Y, Li MR, Sun ZZ, Xie WY, Li QF, Xie CH, Xiang JY, Tan X, Qiu SJ, Liang Y. Detect the disrupted brain structural connectivity in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients without cognitive impairment. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(7): 103468
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i7/103468.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i7.103468