Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Jun 15, 2025; 16(6): 105173
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.105173
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.105173
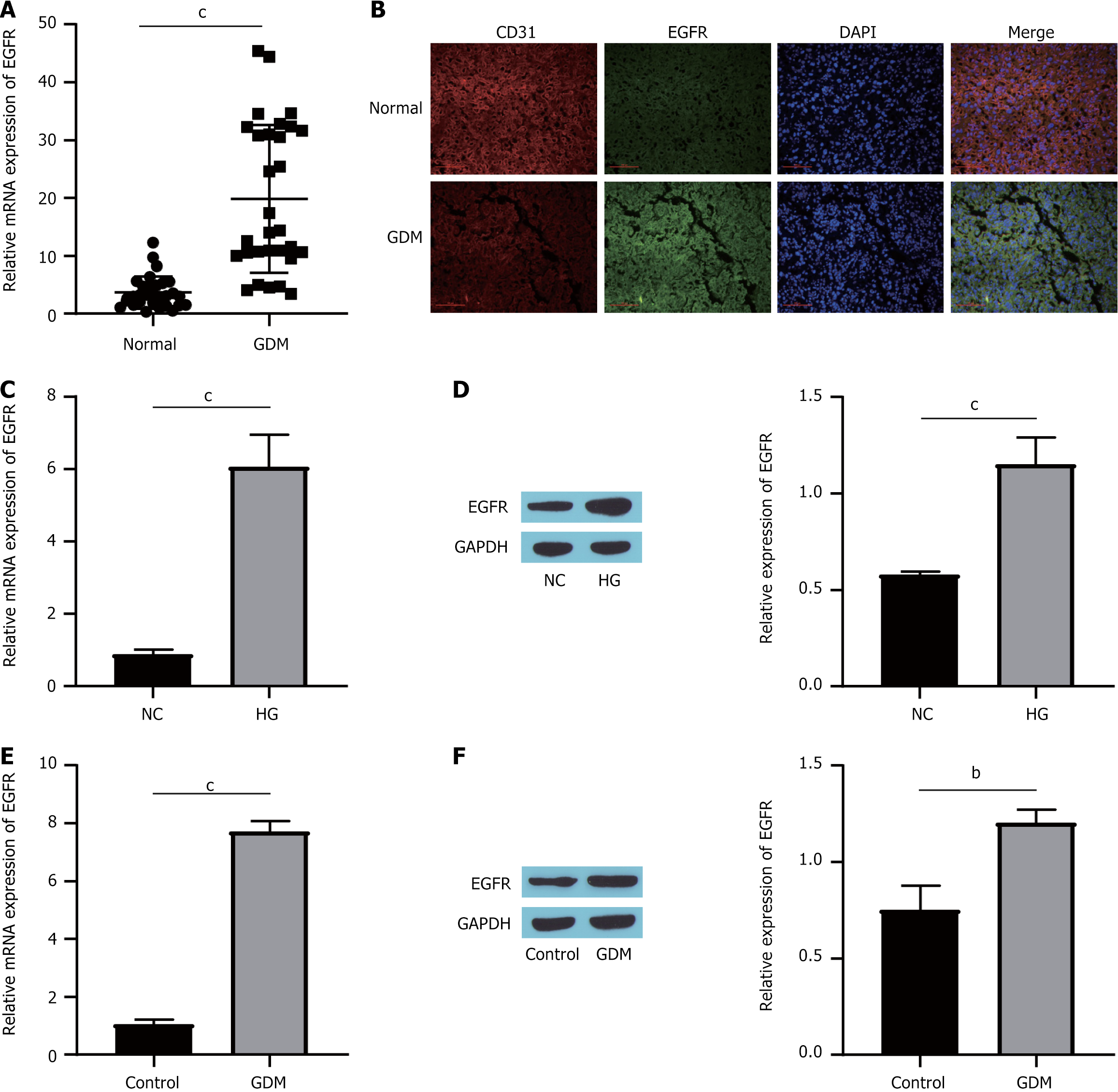
Figure 1 Epidermal growth factor receptor is differentially expressed in gestational diabetes mellitus.
A: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) messenger RNA (mRNA) expression in human placental tissue detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR); B: Colocalization of EGFR and cluster of differentiation 31 detected by immunofluorescence double staining; C: EGFR mRNA expression in cells detected by RT-qPCR; D: The expression of the EGFR protein was detected by Western blotting; E: RT-qPCR detection of EGFR mRNA expression in mouse placental tissue; F: Western blot detection of EGFR protein expression in the mouse placenta. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. mRNA: Messenger RNA; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; CD31: Cluster of differentiation 31; GDM: Gestational diabetes mellitus; DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; NC: Normal control; HG: High glucose; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
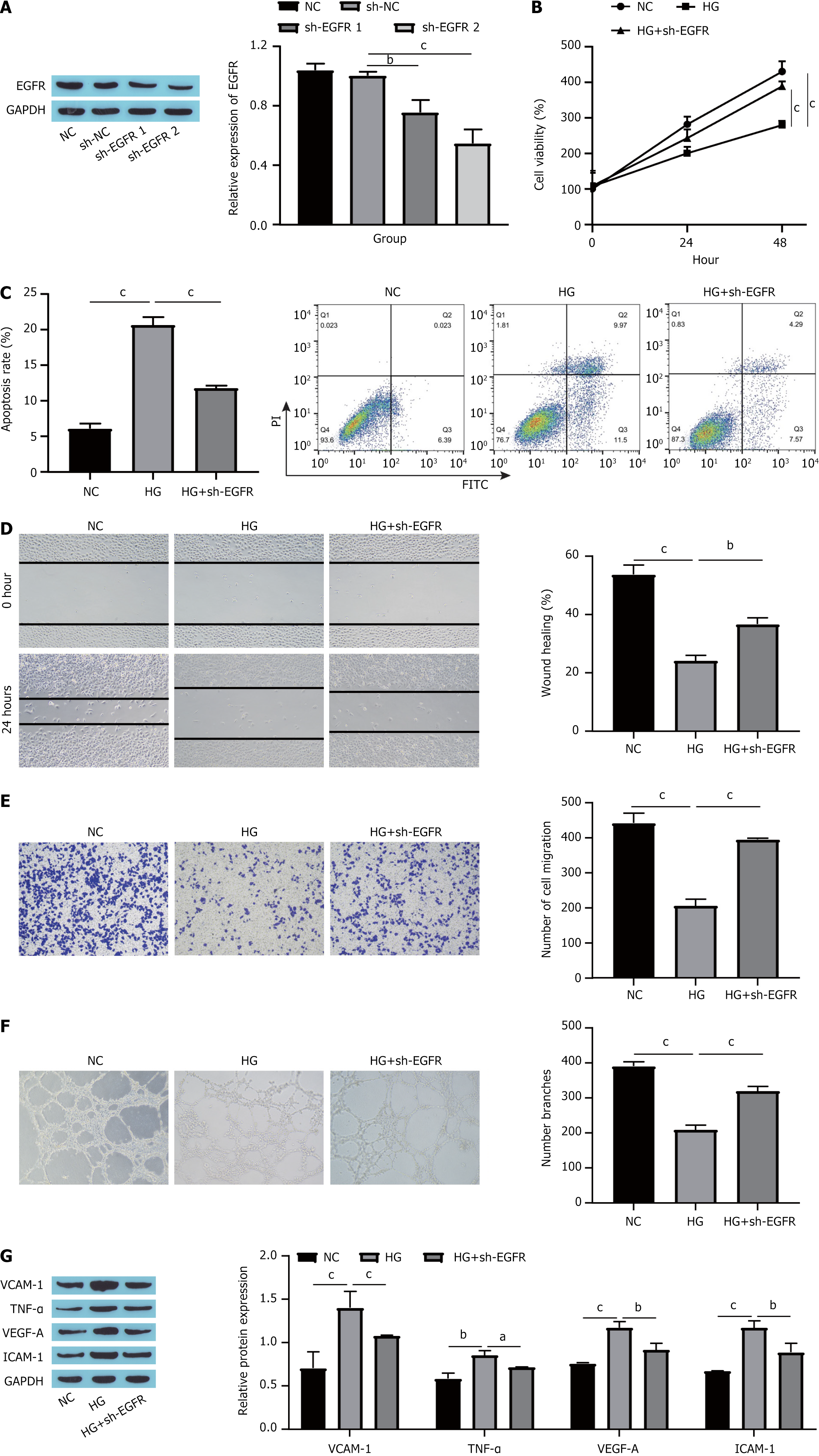
Figure 2 Knocking down epidermal growth factor receptor suppressed high glucose-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells dysfunction.
A: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) knockdown efficiency detected by Western blotting; B: Cell viability detected by cell counting kit-8; C: Cell apoptosis detected by flow cytometry; D: Scratch assay measurement of cell migration; E: Cell migration assessed by Transwell assay; F: Blood vessel formation assessment by tube formation assay; G: Expression of endothelial cell dysfunction markers detected by Western blotting. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; NC: Normal control; sh-NC: Short hairpin-negative control; sh-EGFR: Short hairpin RNA targeting epidermal growth factor receptor; HG: High glucose; PI: Propidium iodide; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; VEGF-A: Vascular endothelial growth factor-A; ICAM-1: Intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1.
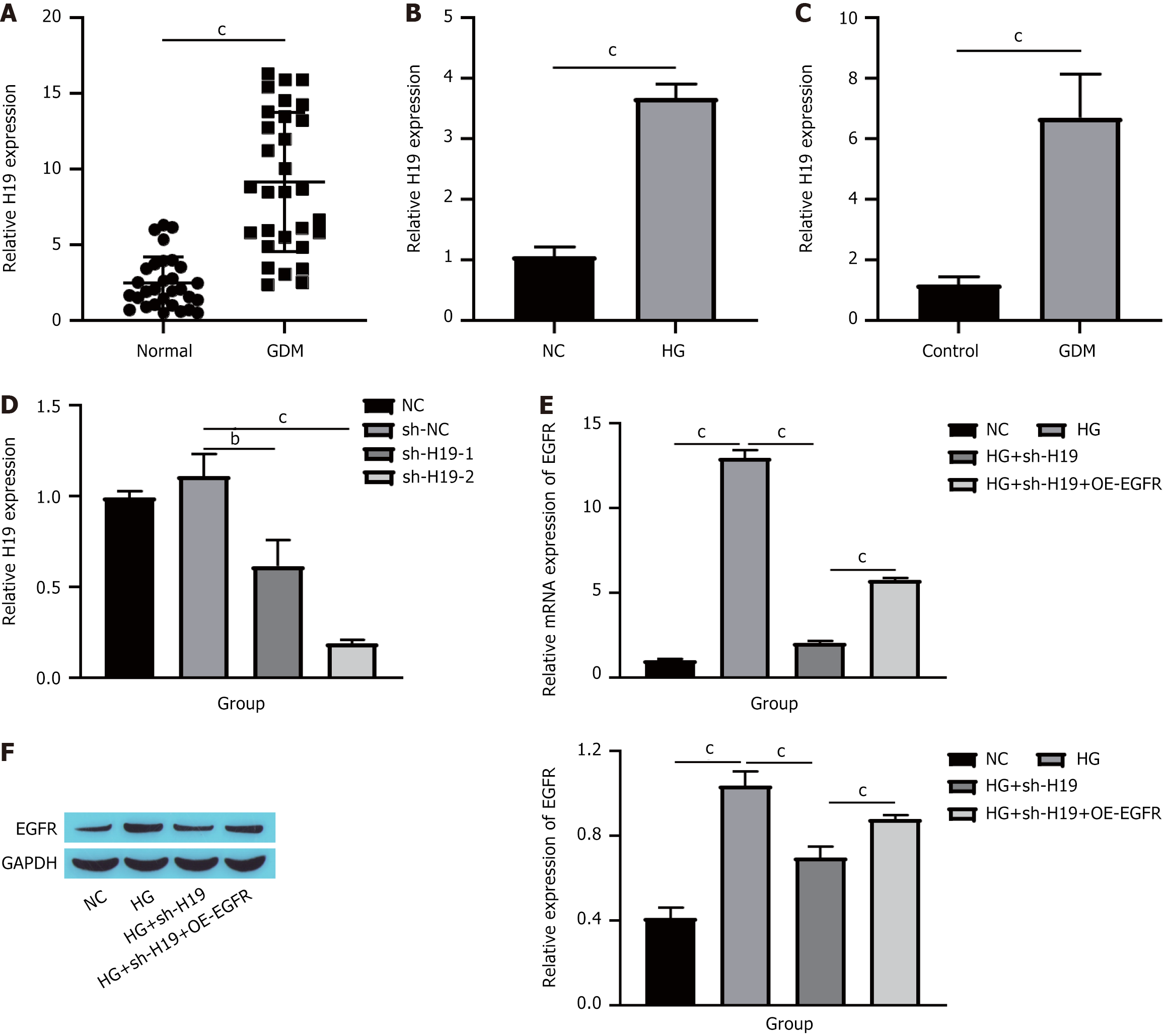
Figure 3 Epidermal growth factor receptor expression is regulated by long noncoding RNAs H19.
A: H19 expression in human placental tissue detected via quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR); B: H19 expression in cells detected via RT-qPCR; C: H19 expression in mouse placental tissue detected via RT-qPCR; D: H19 expression in cells detected via RT-qPCR; E: EGFR messenger RNA expression in cells detected via RT-qPCR; F: EGFR protein expression in cells detected via Western blotting. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. GDM: Gestational diabetes mellitus; NC: Normal control; HG: High glucose; sh-NC: Short hairpin-negative control; sh-H19: Short hairpin RNA targeting H19; OE-EGFR: Overexpression epidermal growth factor receptor; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
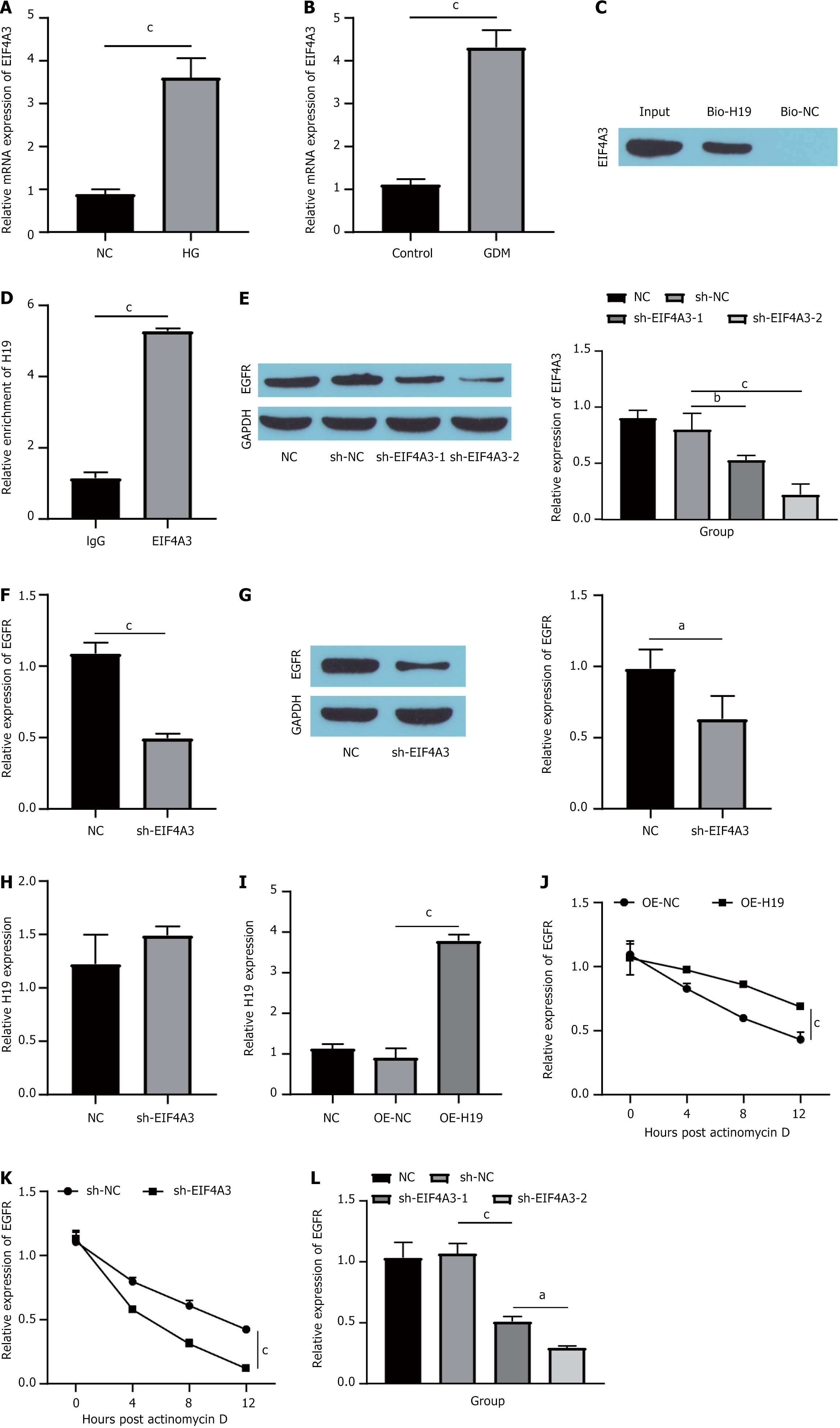
Figure 4 EIF4A3 binds to long noncoding RNAs H19 to increase the stability of epidermal growth factor receptor messenger RNA.
A: The expression of EIF4A3 was detected via quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR); B: The expression of EIF4A3 in mouse placental tissues was detected via RT-qPCR; C: RNA pull-down and Western blotting showing the significant enrichment in EIF4A3 pulled down by H19; D: RNA immunoprecipitation verified the binding of H19 to EIF4A3; E: Western blotting showing the knockdown efficiency of EIF4A3; F: RT-qPCR detection of the expression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) messenger RNA (mRNA); G: EGFR expression detected by Western blotting; H: H19 expression detected by RT-qPCR; I: H19 overexpression efficiency detected by RT-qPCR; J: 5 μg/mL actinomycin D (ActD)-treated cells for 0, 4, 8, and 12 hours, followed by overexpression of H19 to detect the expression of EGFR mRNA; K: Cells treated with 5 μg/mL ActD for 0, 4, 8, and 12 hours, and EGFR mRNA expression was measured after EIF4A3 knockdown; L: The expression of EGFR mRNA in cells was detected via RT-qPCR. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. mRNA: Messenger RNA; NC: Normal control; HG: High glucose; GDM: Gestational diabetes mellitus; Bio-H19: Biotinylated H19; Bio-NC: Biotinylated negative control; sh-NC: Short hairpin-negative control; sh-EIF4A3: Short hairpin RNA targeting EIF4A3; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; OE-NC: Overexpression negative control; OE-H19: Overexpression H19; sh-H19: Short hairpin RNA targeting H19.
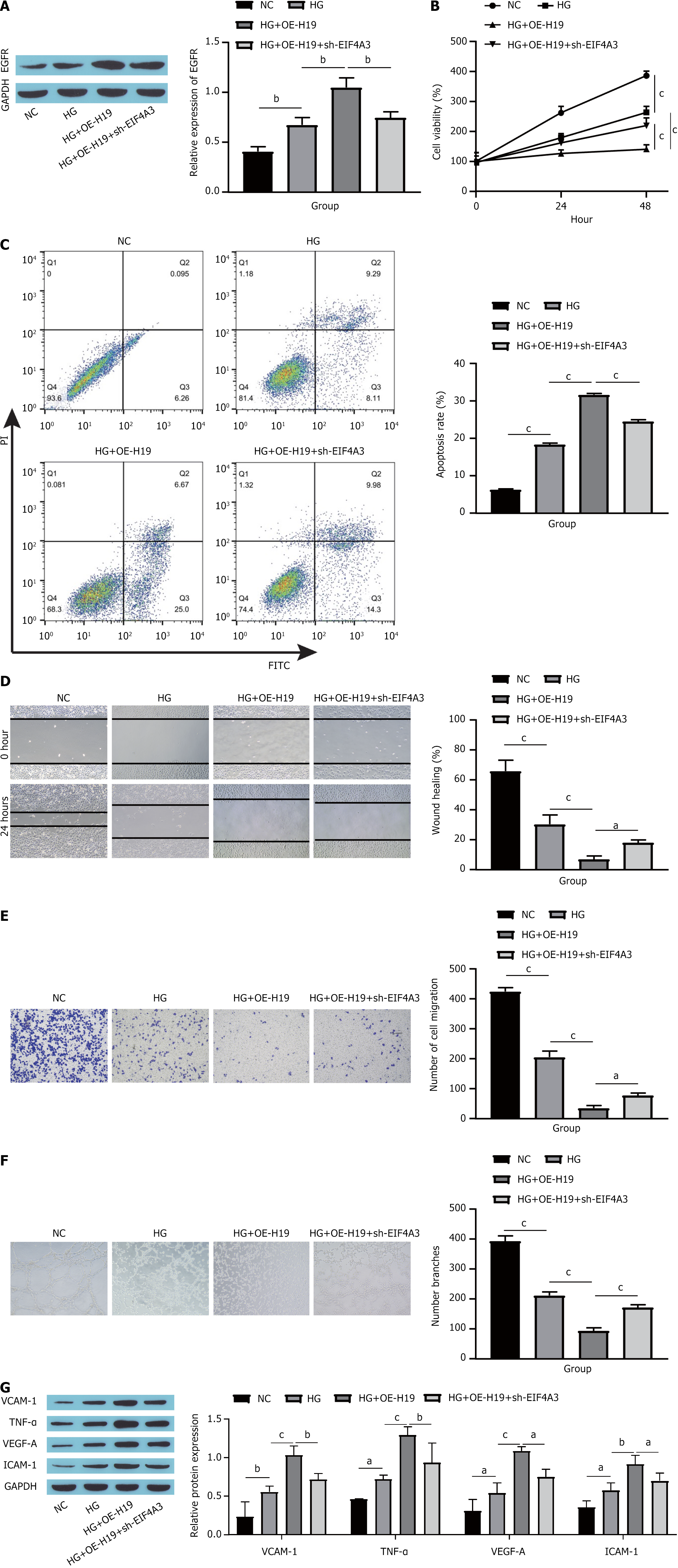
Figure 5 EIF4A3 combined with long noncoding RNAs H19 increases the expression of epidermal growth factor receptor to promote high glucose-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells dysfunction.
A: Epidermal growth factor receptor protein expression detected by Western blotting; B: Cell viability detected by cell counting kit-8; C: Cell apoptosis detected by flow cytometry; D: Cell migration assessed by scratch experiments; E: Cell migration assessed by Transwell assays; F: Tube formation assay to assess angiogenesis in cells; G: Western blot showing the expression of endothelial cell dysfunction markers. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; NC: Normal control; HG: High glucose; OE-H19: Overexpression H19; sh-EIF4A3: Short hairpin RNA targeting EIF4A3; PI: Propidium iodide; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; VEGF-A: Vascular endothelial growth factor-A; ICAM-1: Intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1.
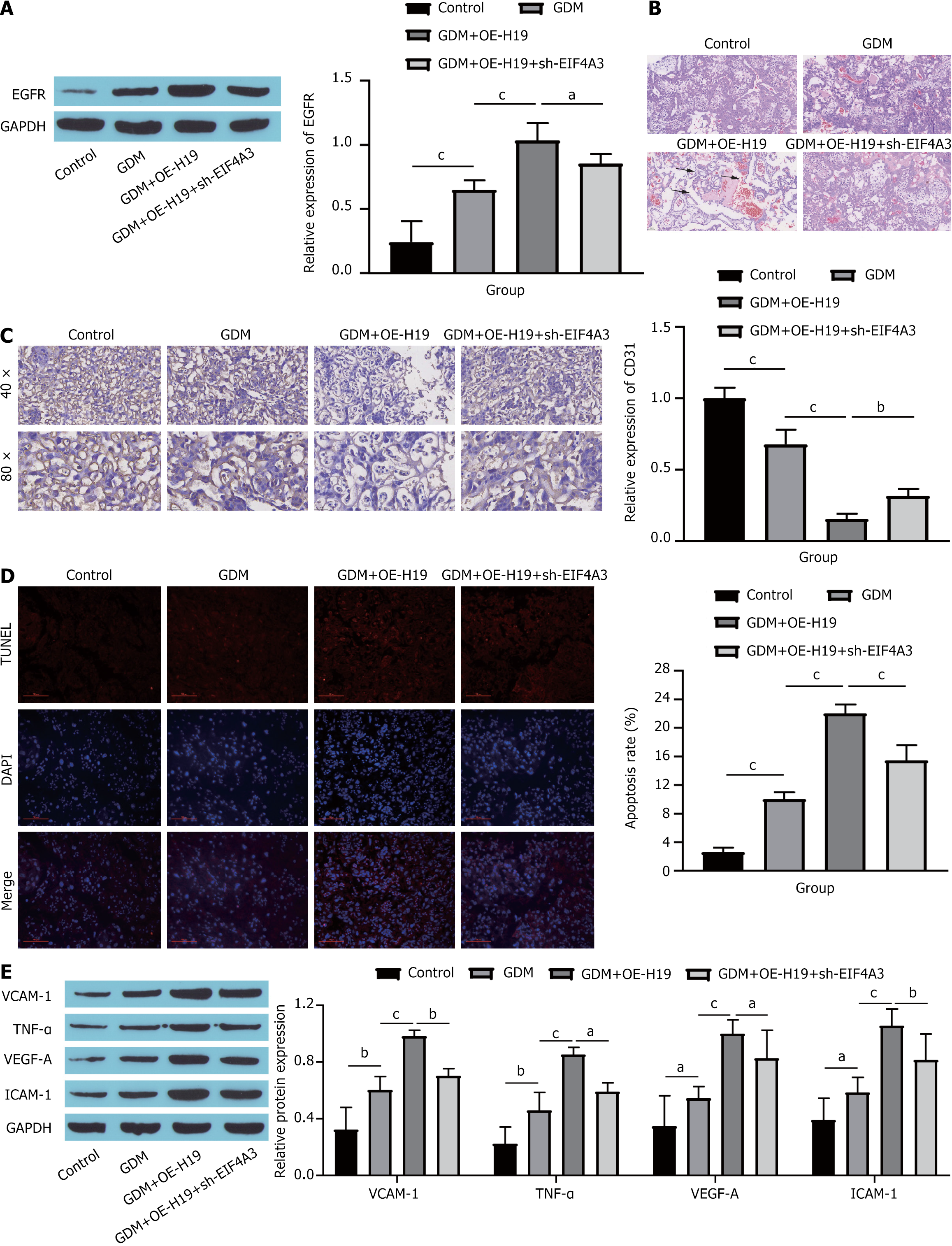
Figure 6 EIF4A3 binding to long noncoding RNAs H19 to increase the expression of epidermal growth factor receptor promotes endothelial cell dysfunction in mice with gestational diabetes mellitus.
A: Western blot showing epidermal growth factor receptor expression in mouse placental tissue; B: Pathological changes in mouse placental tissue observed with hematoxylin-eosin staining; C: Immunohistochemistry of cluster of differentiation 31 in mouse placental tissue; D: Cell apoptosis in mouse placental tissue detected by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-nick end labelling staining; E: Western blot showing the expression of endothelial cell dysfunction markers in mouse placental tissue. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; OE-H19: Overexpression H19; sh-EIF4A3: Short hairpin RNA targeting EIF4A3; GDM: Gestational diabetes mellitus; TUNEL: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-nick end labelling; DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; CD31: Cluster of differentiation 31; VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; VEGF-A: Vascular endothelial growth factor-A; ICAM-1: Intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1.
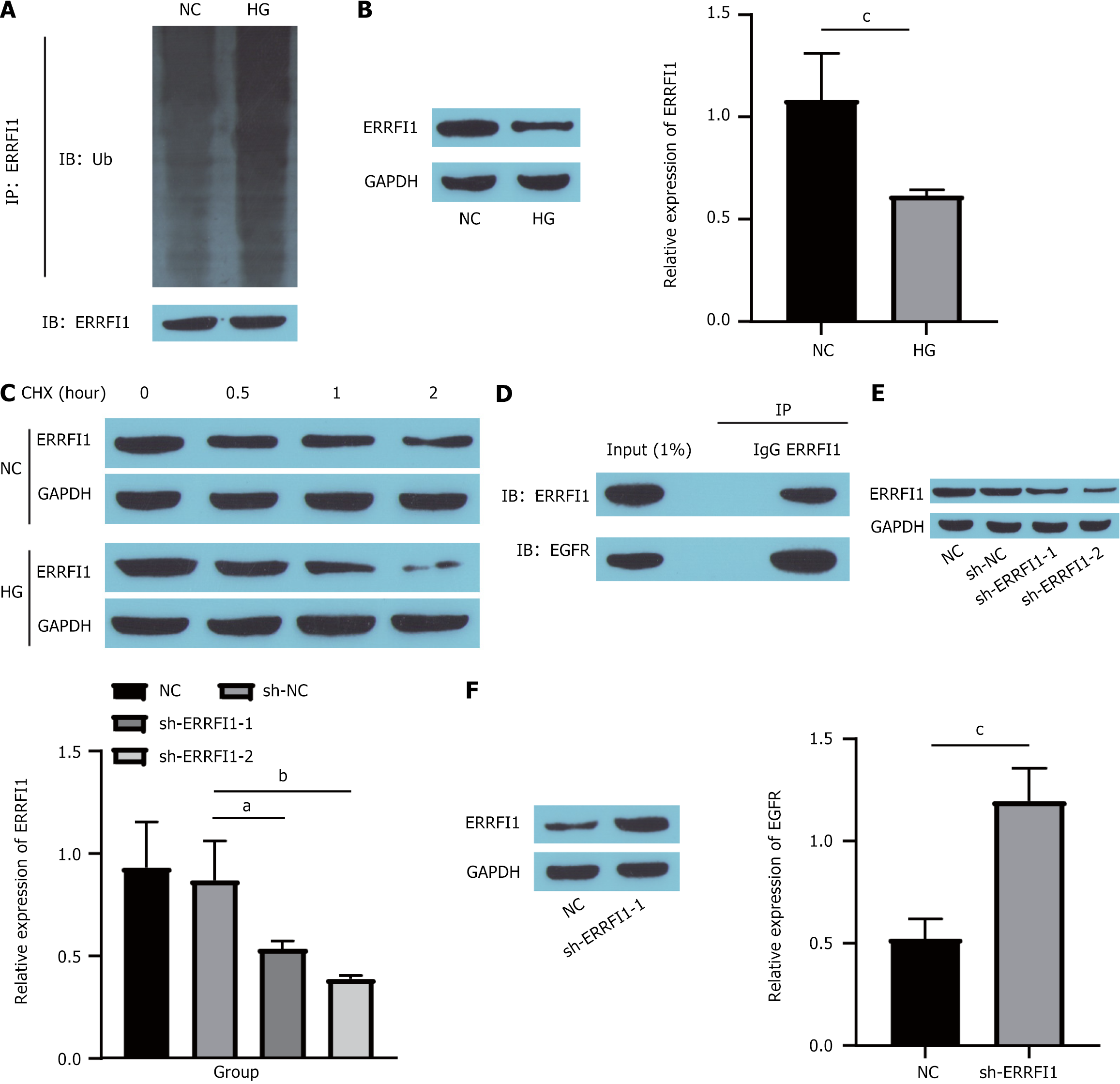
Figure 7 High glucose promotes epidermal growth factor receptor expression by reducing ERRFI1 stability.
A: Detection of the ubiquitination level of ERRFI1; B: ERRFI1 expression detected by Western blotting; C: ERRFI1 stability detected by cycloheximide chase; D: Binding between ERRFI1 and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) detected by coimmunoprecipitation; E: Western blot showing ERRFI1 knockdown efficiency; F: Western blot showing EGFR expression. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. IP: Immunoprecipitation; IB: Immunoblotting; NC: Normal control; HG: High glucose; CHX: Cycloheximide; NC: Normal control; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; sh-NC: Short hairpin-negative control; sh-ERRFI1: Short hairpin RNA targeting ERRFI1; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor.
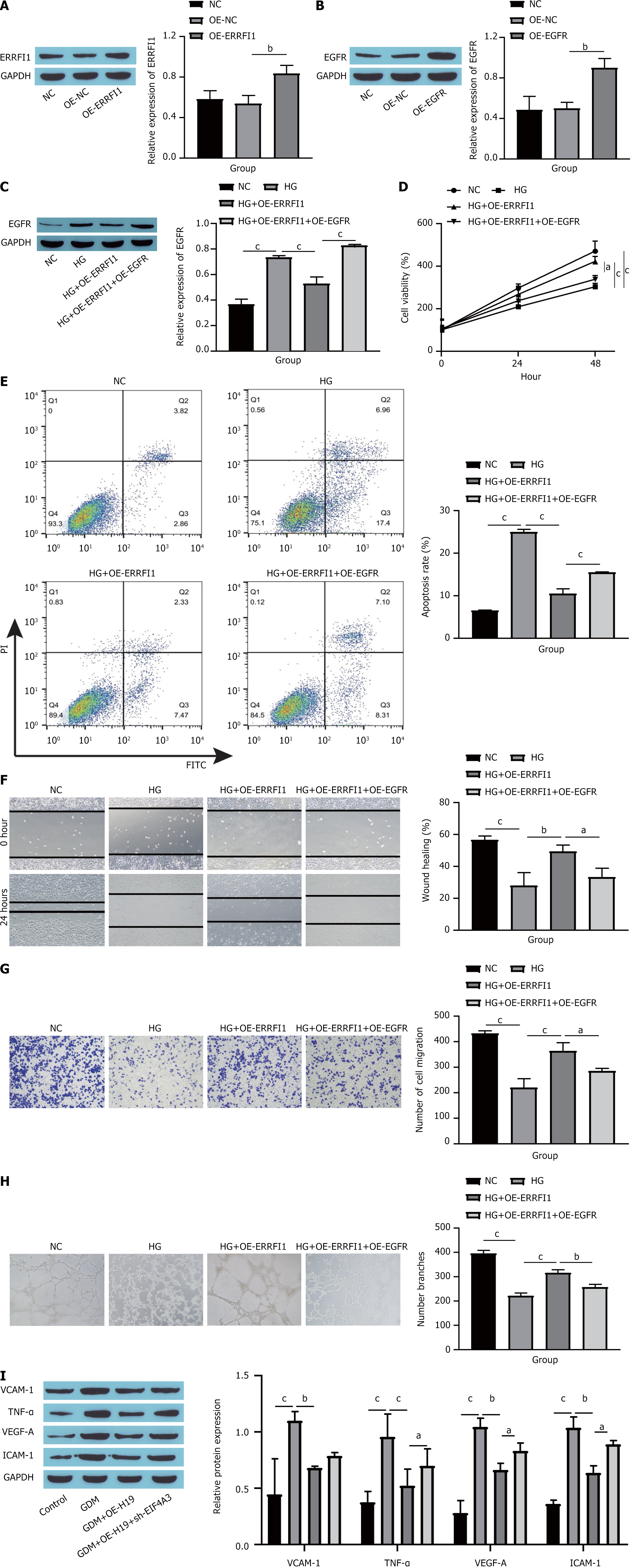
Figure 8 ERRFI1 binds to epidermal growth factor receptor and inhibits its activity to suppress high glucose-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells dysfunction.
A: Western blot showing ERRFI1 overexpression efficiency; B: Western blot showing epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) overexpression efficiency; C: Western blot showing EGFR expression in cells; D: Cell counting kit-8 assay showing cell viability; E: Cell apoptosis as detected by flow cytometry; F: Cell migration as assessed by scratch experiments; G: Cell migration as assessed by Transwell assay; H: Angiogenesis as assessed by tube formation assay; I: Western blot showing the expression of endothelial cell dysfunction markers. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; OE-NC: Overexpression-negative control; OE-ERRFI1: Overexpression ERRFI1; NC: Normal control; OE-EGFR: Overexpression epidermal growth factor receptor; HG: High glucose; PI: Propidium iodide; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; VEGF-A: Vascular endothelial growth factor-A; ICAM-1: Intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1.
- Citation: Tang D, Wang CF, Wang J, Jing XT, Ma J. Mechanism of the epidermal growth factor receptor in promoting endothelial cell dysfunction in gestational diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(6): 105173
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i6/105173.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.105173