Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2025; 16(5): 104409
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.104409
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.104409
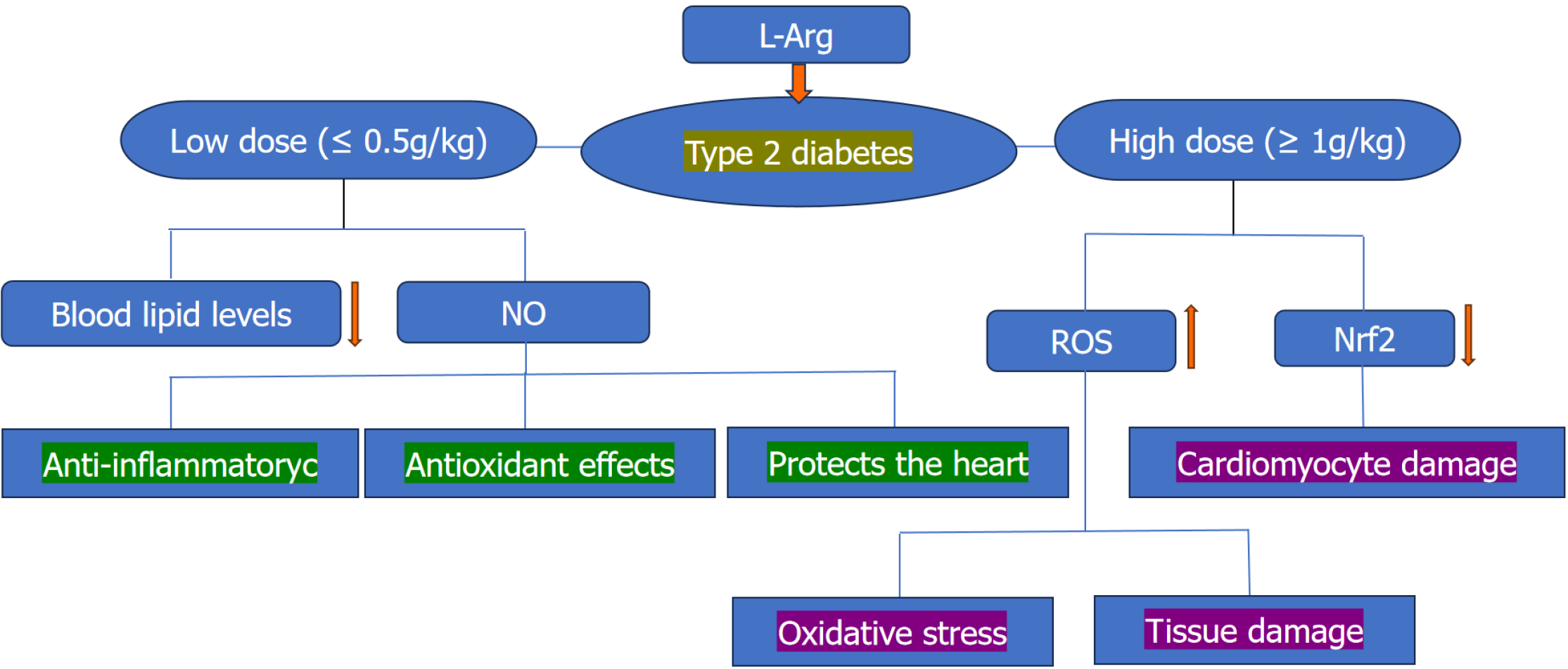
Figure 1 Effects of low-dose and high-dose L-arginine in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Low doses (≤ 0.5 g/kg) of L-arginine can improve blood lipid levels, whereas high doses (≥ 1 g/kg) of L-arginine can exacerbate oxidative stress and cause myocardial damage. NO: Nitric oxide; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
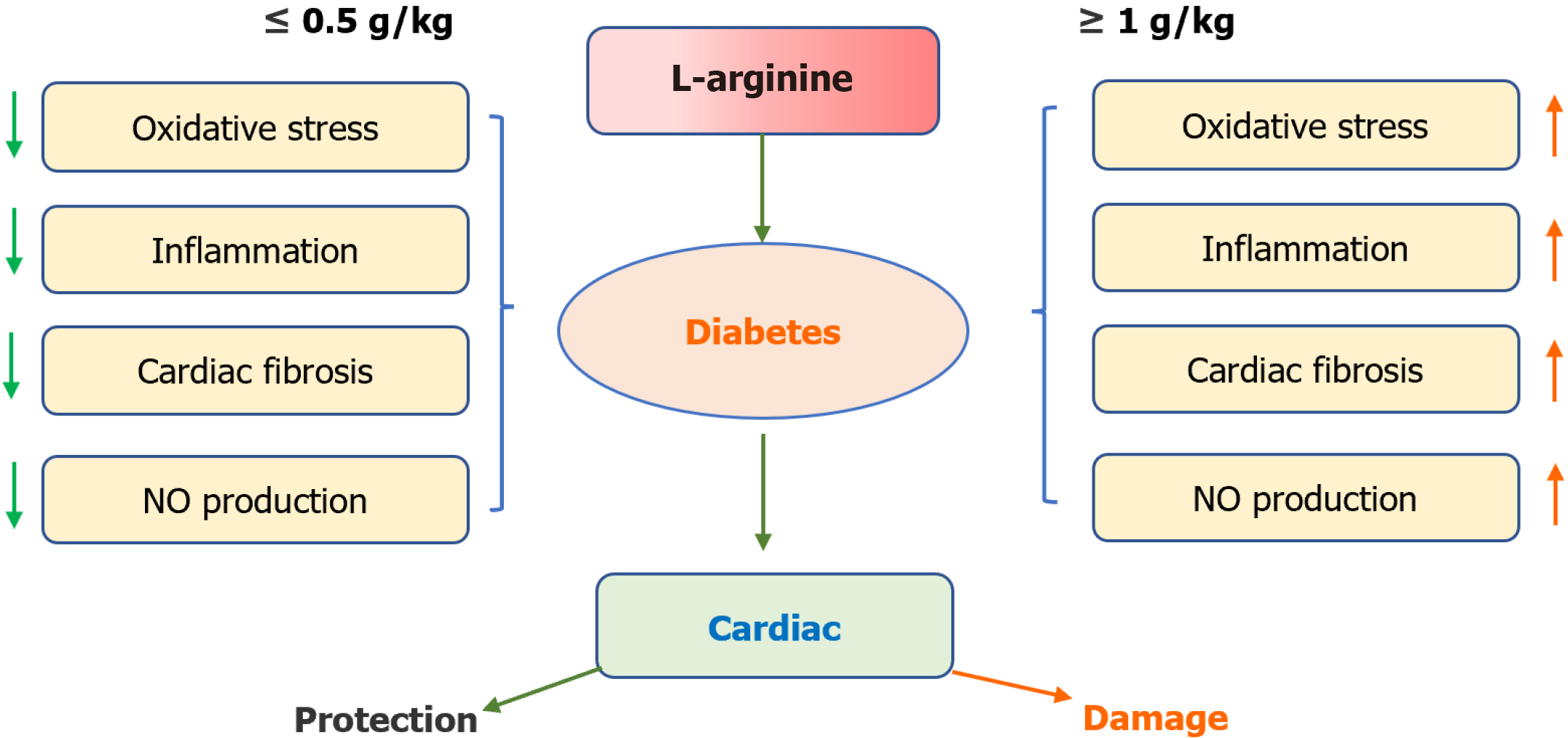
Figure 2 Excess L-arginine daily administration causes cardiac injury in diabetes mellitus patients.
0.5 g/kg L-arginine is beneficial for the treatment of diabetes and is the threshold of cardiac safety. NO: Nitric oxide.
- Citation: Chen Y, Dai MT, Gong GH. L-arginine overdose is a potential risk factor for myocardial injury in patients with type 2 diabetes. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(5): 104409
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i5/104409.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.104409