Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2025; 16(5): 103511
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.103511
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.103511
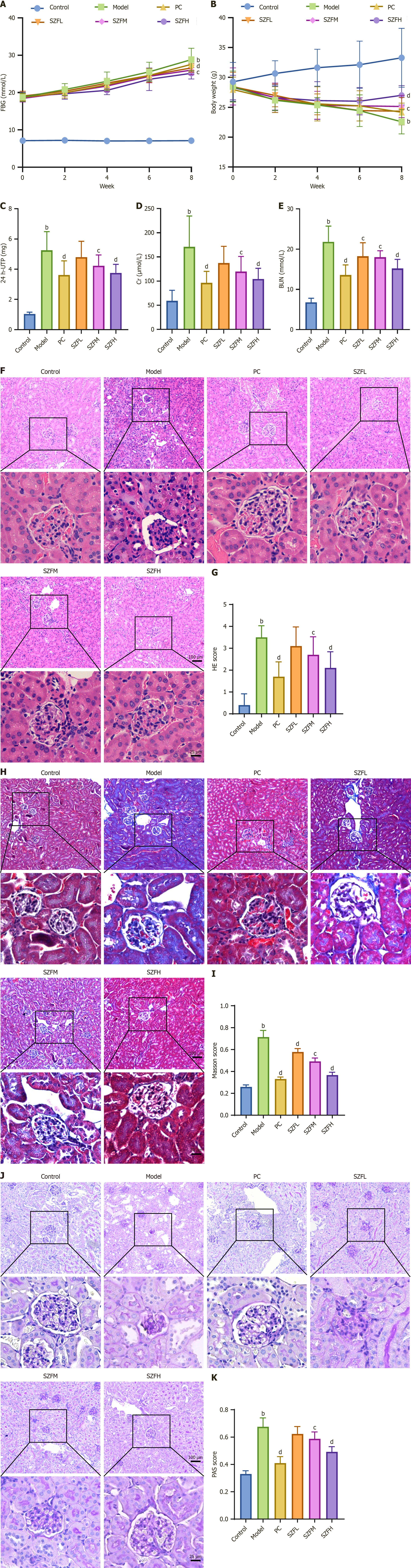
Figure 1 Shenzhuo formulation intervention improves renal injury in diabetic nephropathy mice.
A diabetic nephropathy (DN) mouse model group (Model) was established and Shenzhuo formulation (SZF) intervention was given. A and B: SZF intervention significantly reduced blood glucose (A) and increased body weight (B) in DN mice; C-E: SZF intervention improves renal function in DN mice and reduces levels of 24-hour urinary total protein (C), creatinine (D), and BUN (E); F-G: SZF intervention improves the renal histopathological injury in DN mice; Hematoxylin and eosin staining results showing that SZF improves renal histopathological morphology; H and I: Masson staining results showing that SZF improves renal histopathological morphology and that SZF could reduce renal tissue fibrosis; J and K: PAS staining results showing that SZF could reduce renal tissue glycogen deposition. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. n = 10 per group. bP < 0.01 vs control group; cP < 0.05; dP < 0.01 vs Model; FBG: Fasting blood glucose; UTP: Urinary total protein; Cr: Creatinine; BUN: Blood urea nitrogen; DN: Diabetic nephropathy; HE: Hematoxylin and eosin; PAS: Periodic acid-Schiff; AOD: Average optical density; SZFH: Shenzhuo formulation high dose group; SZFL: Shenzhuo formulation low dose group; Control: Control group; PC: Positive control group; Model: Model group.
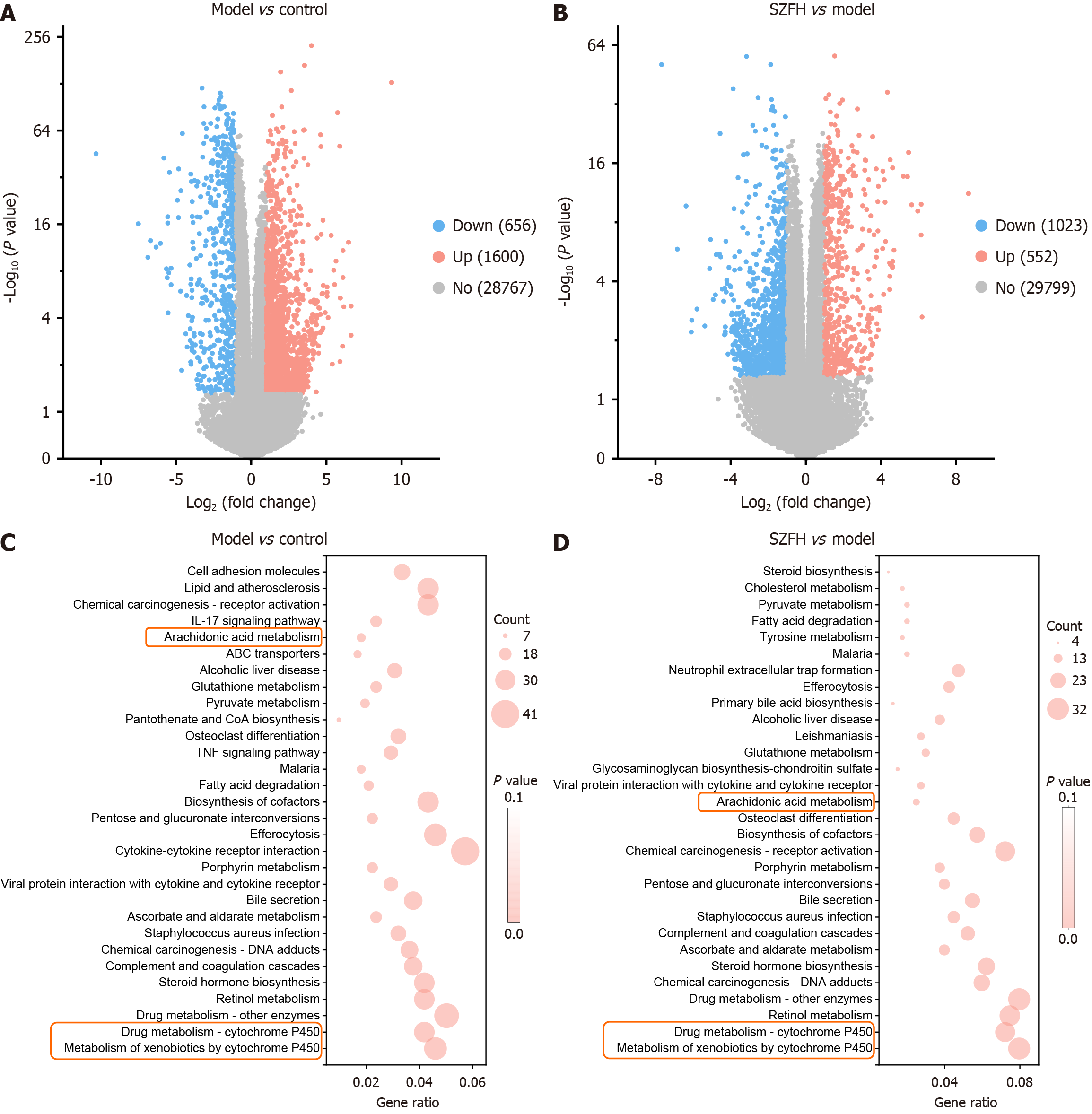
Figure 2 Transcriptomics results of model group vs control and Shenzhuo formulation high dose group vs model group in diabetic nephropathy mice.
We performed transcriptomic analysis for control, model group (Model), and Shenzhuo formulation high dose group (SZFH). DEGs of Model vs control and SZFH vs Model were screened by |Log2 (FoldChange)| ≥ 1, Padj ≤ 0.05, respectively. A and B: DEGs visualized using volcano plots; C and D: KEGG pathway enrichment analysis revealing that DEGs of Model vs control are mainly enriched in metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 (CYP450), drug metabolism-CYP450, drug metabolism-other enzymes, etc. (C), and DEGs of SZFH vs Model are mainly enriched in CYP450, Drug metabolism-CYP450, retinol metabolism etc. (D). AA metabolism, metabolism of xenobiotics by CYP450, drug metabolism-CYP450 are the intersecting pathway. n = 3 per group. DEGs: Differentially expressed genes; Control: Control group; Model: Model group; SZFH: Shenzhuo formulation high dose group.
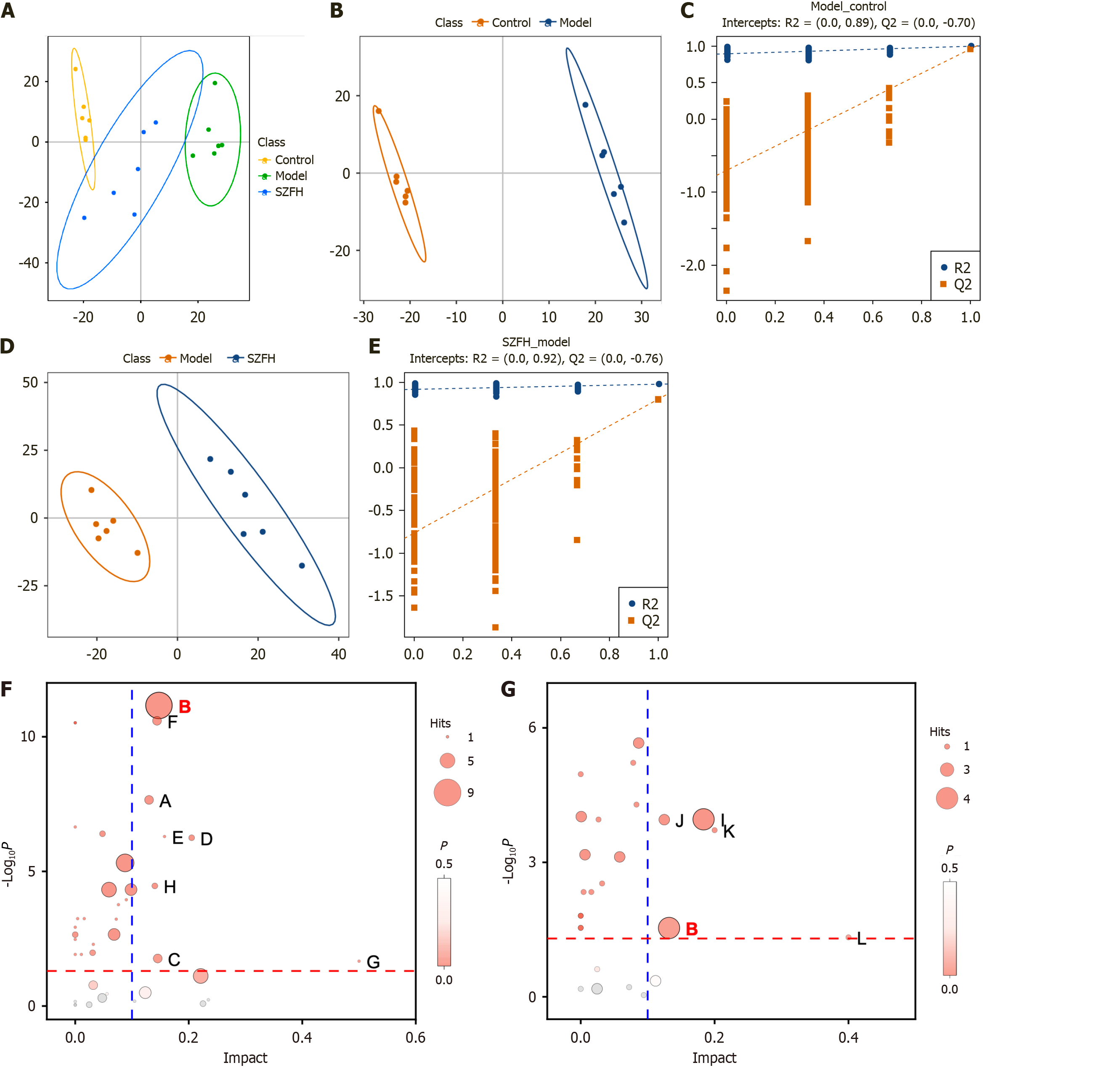
Figure 3 Non-targeted metabolomic results of renal tissues in diabetic nephropathy mice with Shenzhuo formulation intervention.
Non-targeted metabolomic analysis was performed on Control, model group (Model), and Shenzhuo formulation high dose group (SZFH). A: Principal component analysis results showing that the metabolite levels in renal tissues were significantly different among Control, Model, and SZFH groups; B-E: Results of the PLS-DA model and alignment test validation model showing that Model vs Control (B and D) and SZFH vs Model (C and E) exhibits good fit and predictive ability; F and G: KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of Model vs Control (F) and SZFH vs Model (G). Shared pathways between the two are marked in red. Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism, KEGG ID: 00520; Arachidonic acid metabolism, KEGG ID: 00590; Arginine and proline metabolism, KEGG ID: 00330; Cysteine and methionine metabolism, KEGG ID: 00270; Fructose and mannose metabolism, KEGG ID: 00051; Glycerophospholipid metabolism, KEGG ID: 00564; Riboflavin metabolism, KEGG ID: 00564; Sphingolipid metabolism, KEGG ID: 00600; Purine metabolism, KEGG ID: 00230; Pentose phosphate pathway, KEGG ID: 00030; Biotin metabolism, KEGG ID: 00780; Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism, KEGG ID: 00430. n = 6 per group. SZFH: Shenzhuo formulation high dose group; Control: Control group; Model: Model group.
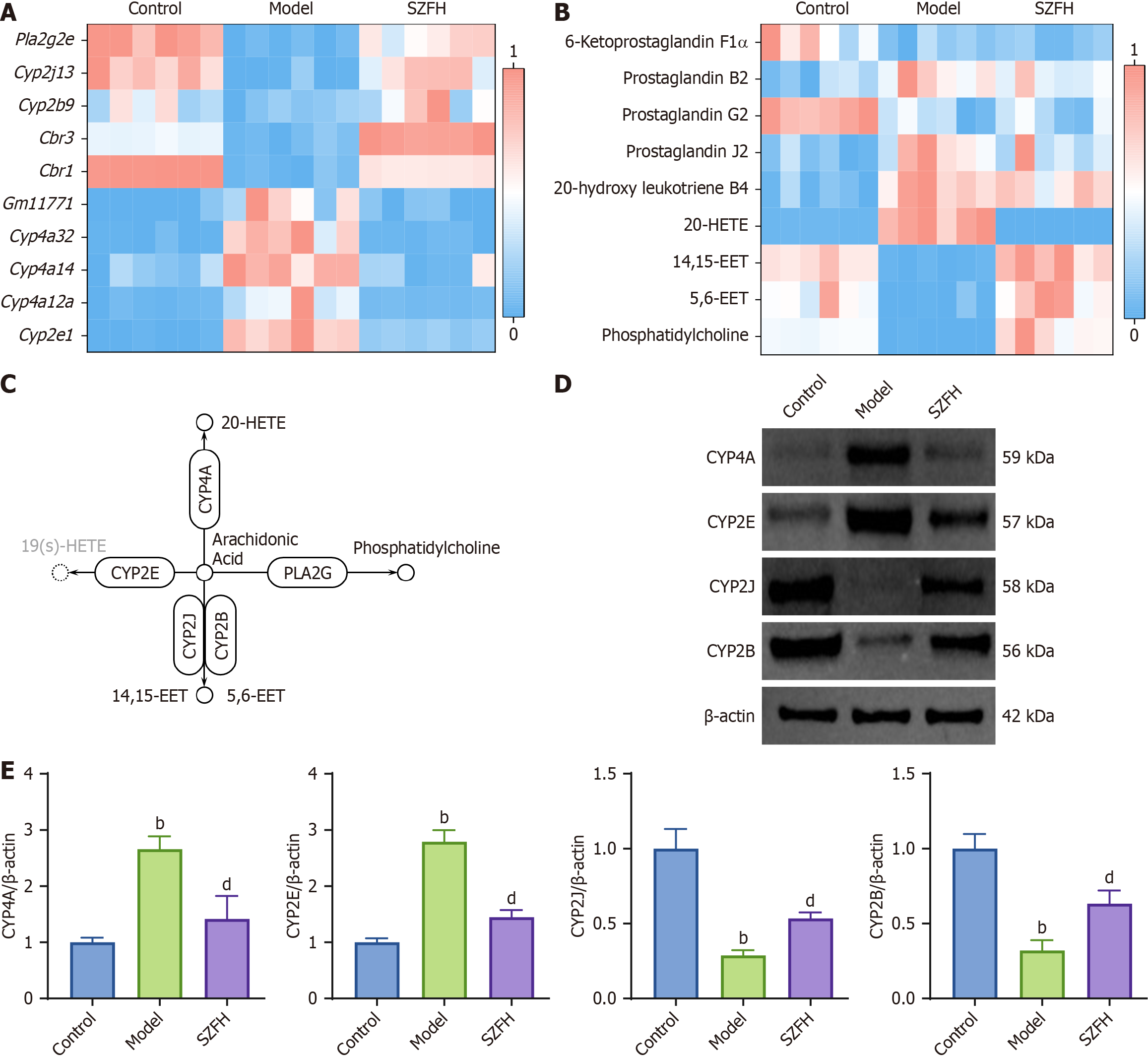
Figure 4 Effect of Shenzhuo formulation intervention on cytochrome P450-mediated AA metabolism in diabetic nephropathy mice.
A: Heatmap of cytochrome P450 (CYP450) metabolism-related gene expression showing that Shenzhuo formulation high dose group (SZFH) intervention significantly up-regulated Cyp2j13, Cyp2b9, Pla2g2e, Cbr3, and Cbr1 mRNA expression and down-regulated Cyp4a12a, Cyp4a32, Cyp2e1, Cyp4a14, and Gm11771 mRNA expression; B: Heatmap of AA metabolism-related product expression showing that SZFH intervened to up-regulated 5,6-EET, 14,15-EET, and Phosphatidylcholine expression and down-regulated 20-HETE expression; C: Translational relationship diagram of CYP450-mediated AA metabolism; D and E: Western blot results showing that CYP4A and CYP2E expression were significantly down-regulated and CYP2J and CYP2B expression were significantly up-regulated after PMS intervention (Supplementary Figure 1). n = 3 for A; n = 6 for B; n = 3 for D and E. bP < 0.01 vs control group; cP < 0.05; dP < 0.01 vs model group; AA: Arachidonic acid; Control: Control group; Model: Model group; CYP450: Cytochrome P450. The original image of Figure 4D is in the Supplementary materials.
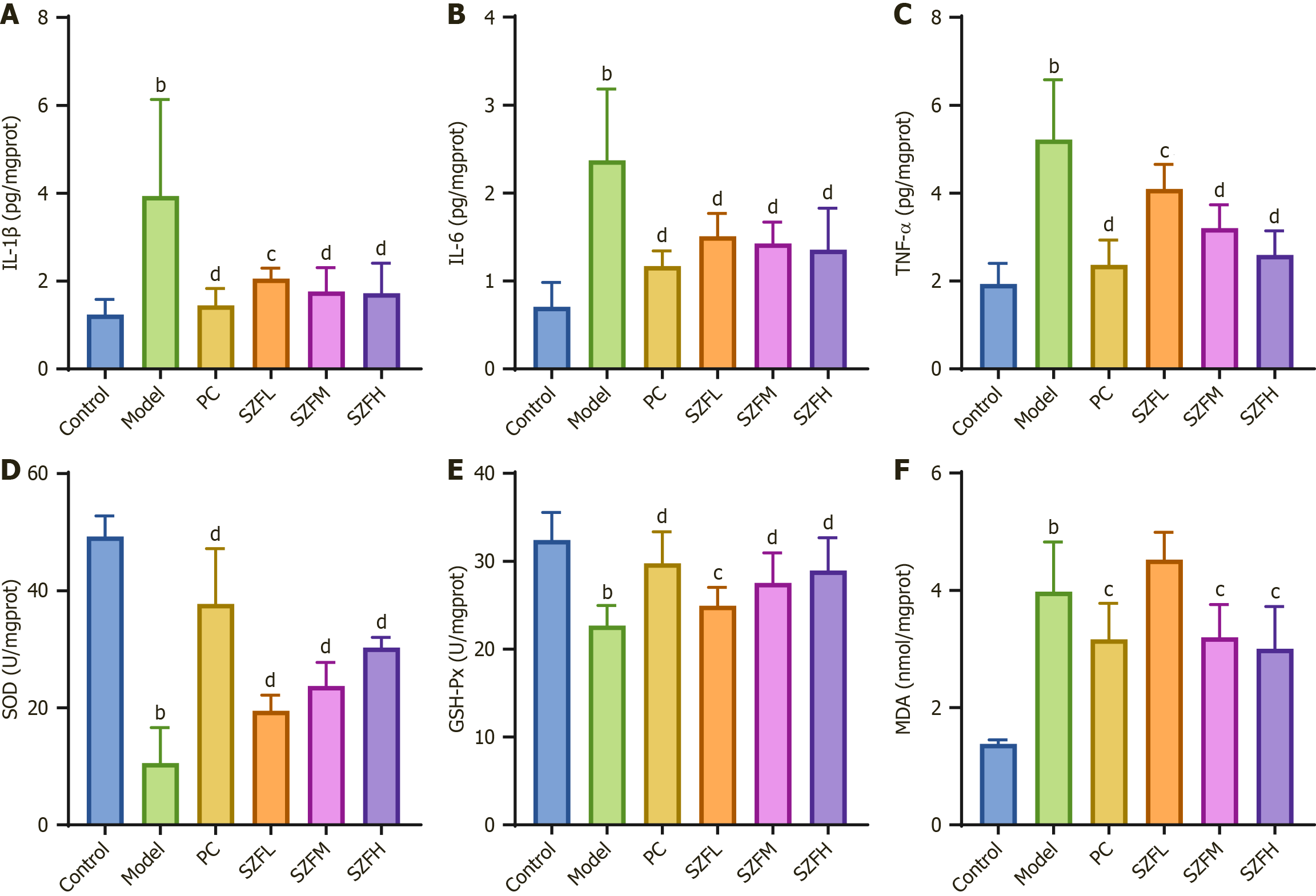
Figure 5 Shenzhuo formulation intervention in diabetic nephropathy mice suppresses inflammatory response and oxidative stress.
A-C: Shenzhuo formulation (SZF) intervention significantly down-regulated the levels of IL-1β (A), IL-6 (B), and TNF-α (C) in renal tissues of diabetic nephropathy (DN) mice, and also attenuated the inflammatory response in DN mice; D-F: SZF intervention significantly up-regulated SOD activity (D) and GSH-Px activity (E), and also down-regulated MDA levels (F). This improved antioxidant capacities and attenuated oxidative stress levels in DN mice. n = 10 per group. bP < 0.01 vs control group; cP < 0.05; dP < 0.01 vs model group; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; IL-6: Interleukin-6; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; GSH-Px: Glutathione peroxidase; MDA: Malondialdehyde; SZFM: Shenzhuo formulation medium dose group; SZFH: Shenzhuo formulation high dose group; SZFL: Shenzhuo formulation low dose group; Control: Control group; PC: Positive control group; Model: Model group.
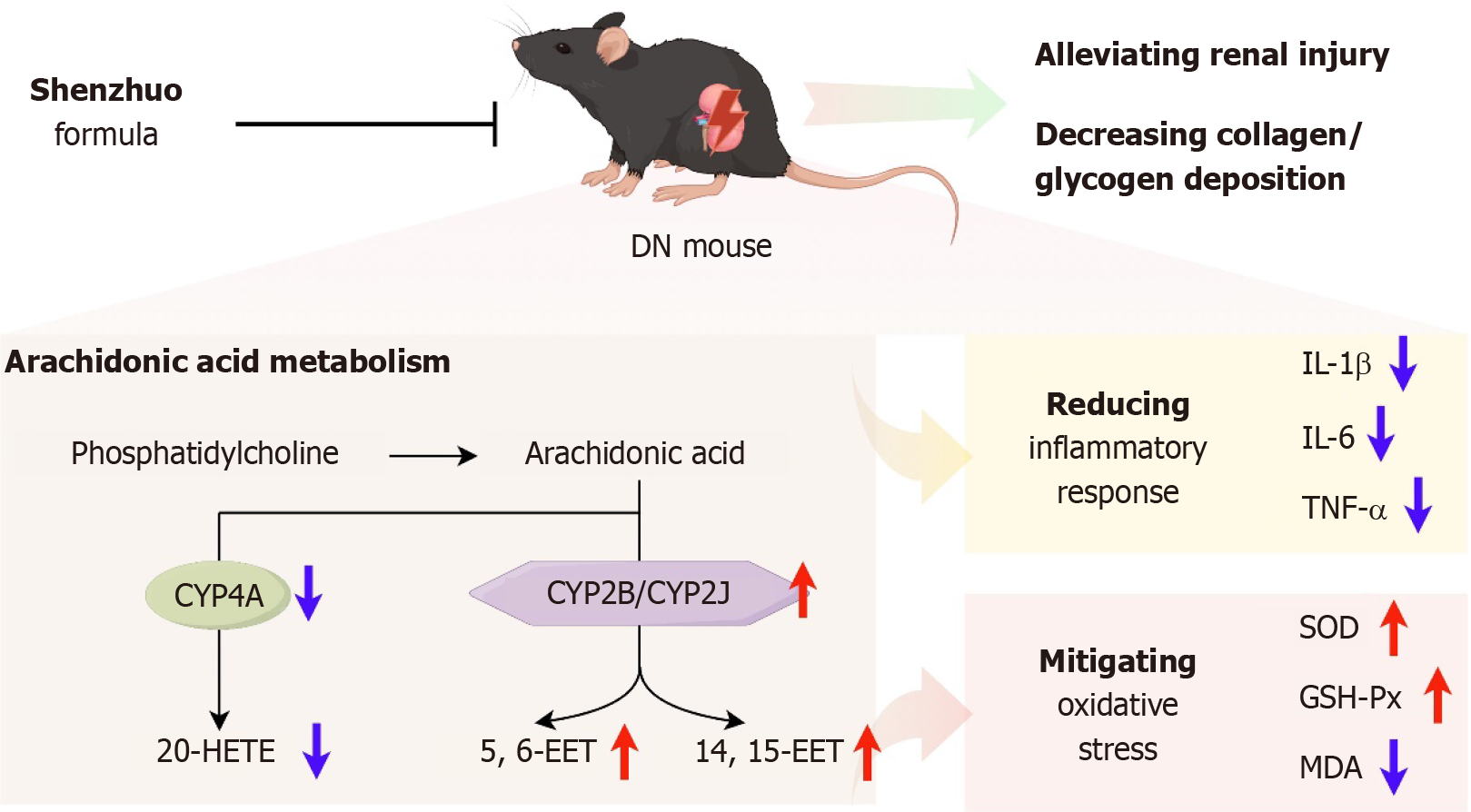
Figure 6 Shenzhuo formulation attenuates inflammatory responses and oxidative stress levels via cytochrome P450-mediated arachidonic acid metabolism, which ameliorates renal injury in diabetic nephropathy mice.
DN: Diabetic nephropathy; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; IL-6: Interleukin-6; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; GSH-Px: Glutathione peroxidase; MDA: Malondialdehyde (Created by FigDraw).
- Citation: Zhang ZY, Wang YM, Wang N, Wang YS, Zhang H, Wang D, Wang LX, Cui HT, Wen WB, Lv SQ, Cao YJ. Shenzhuo formulation ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by regulating cytochrome P450-mediated arachidonic acid metabolism. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(5): 103511
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i5/103511.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.103511