Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Sep 15, 2024; 15(9): 1942-1961
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1942
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1942
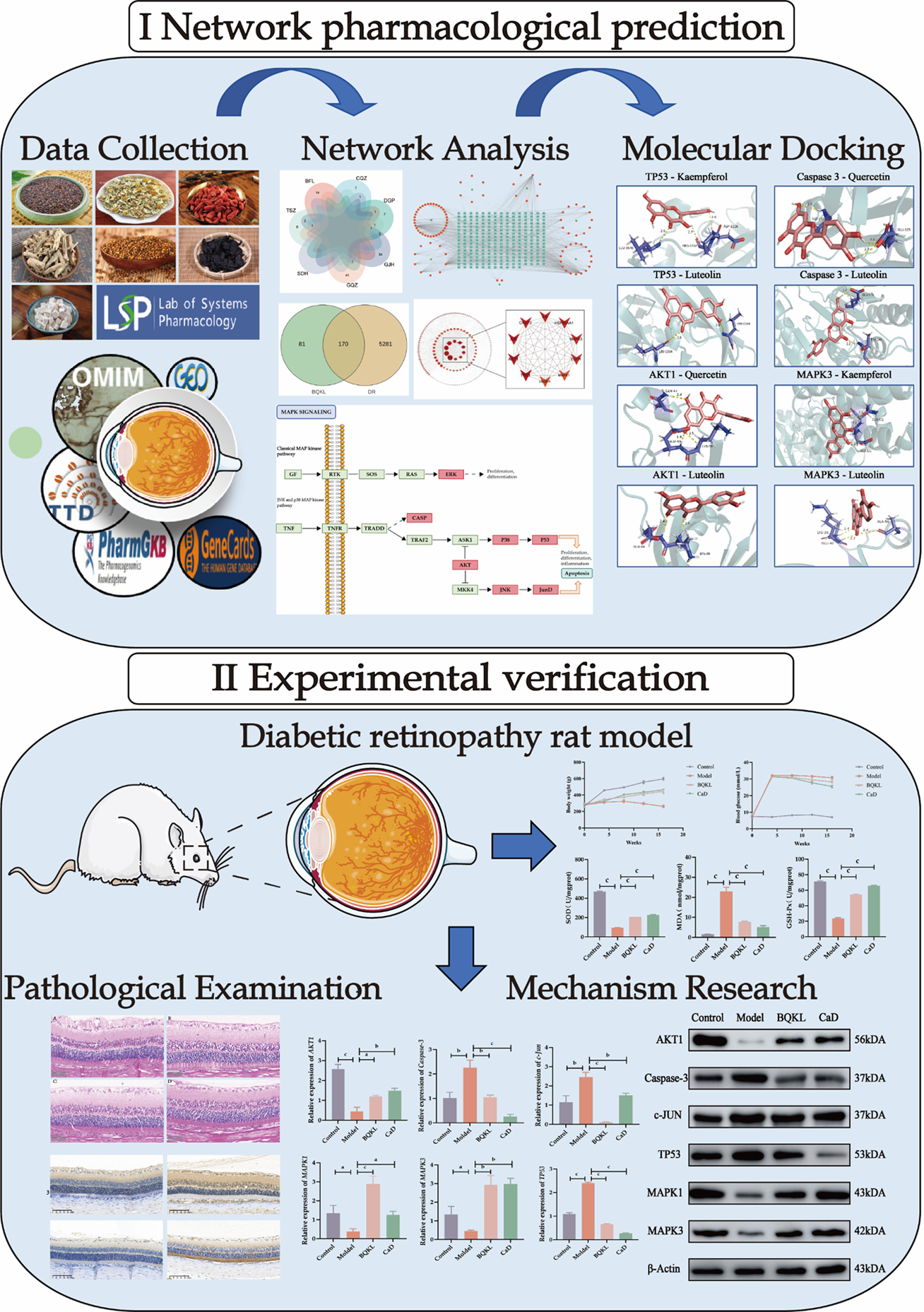
Figure 1 Research flow chart.
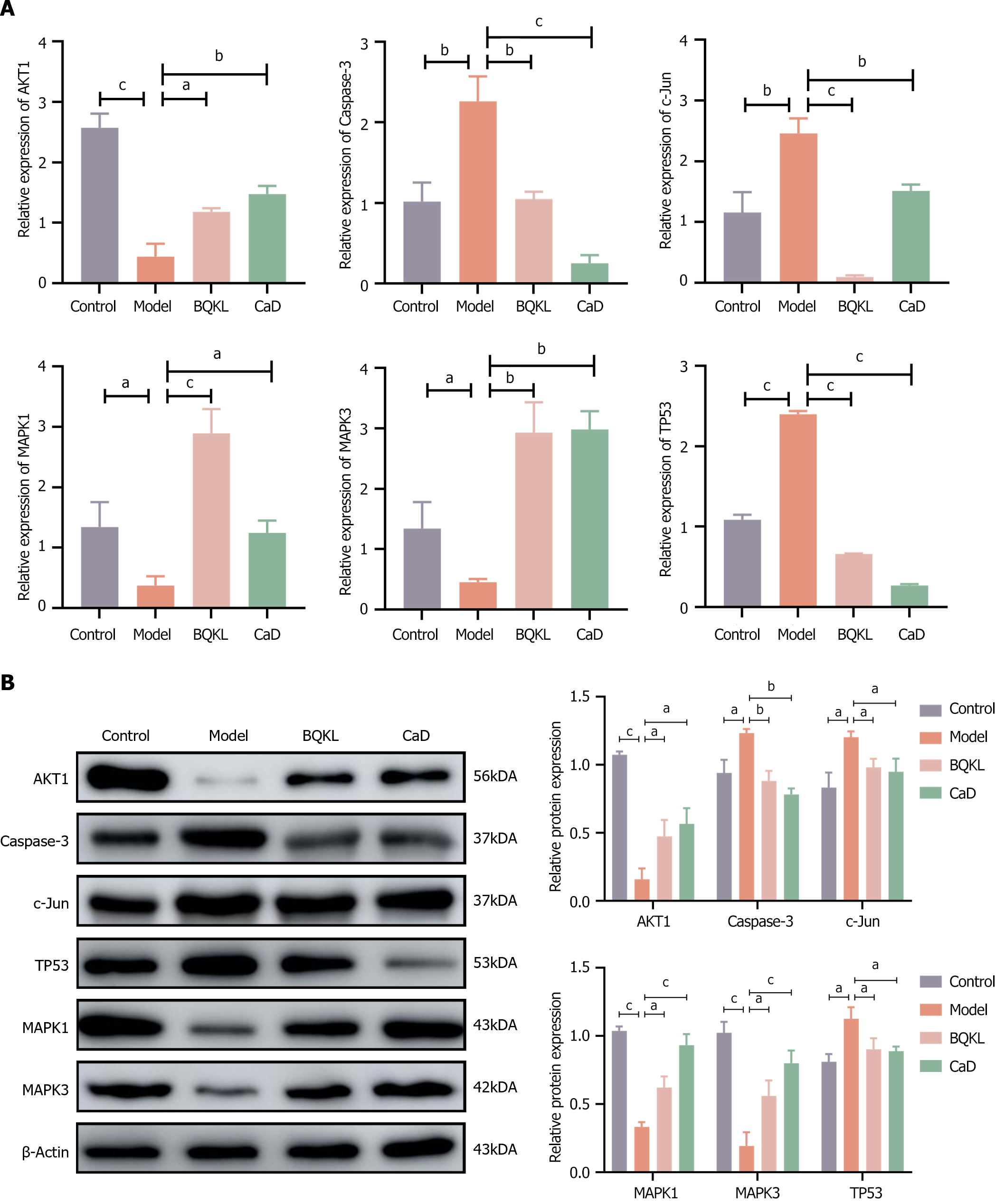
aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
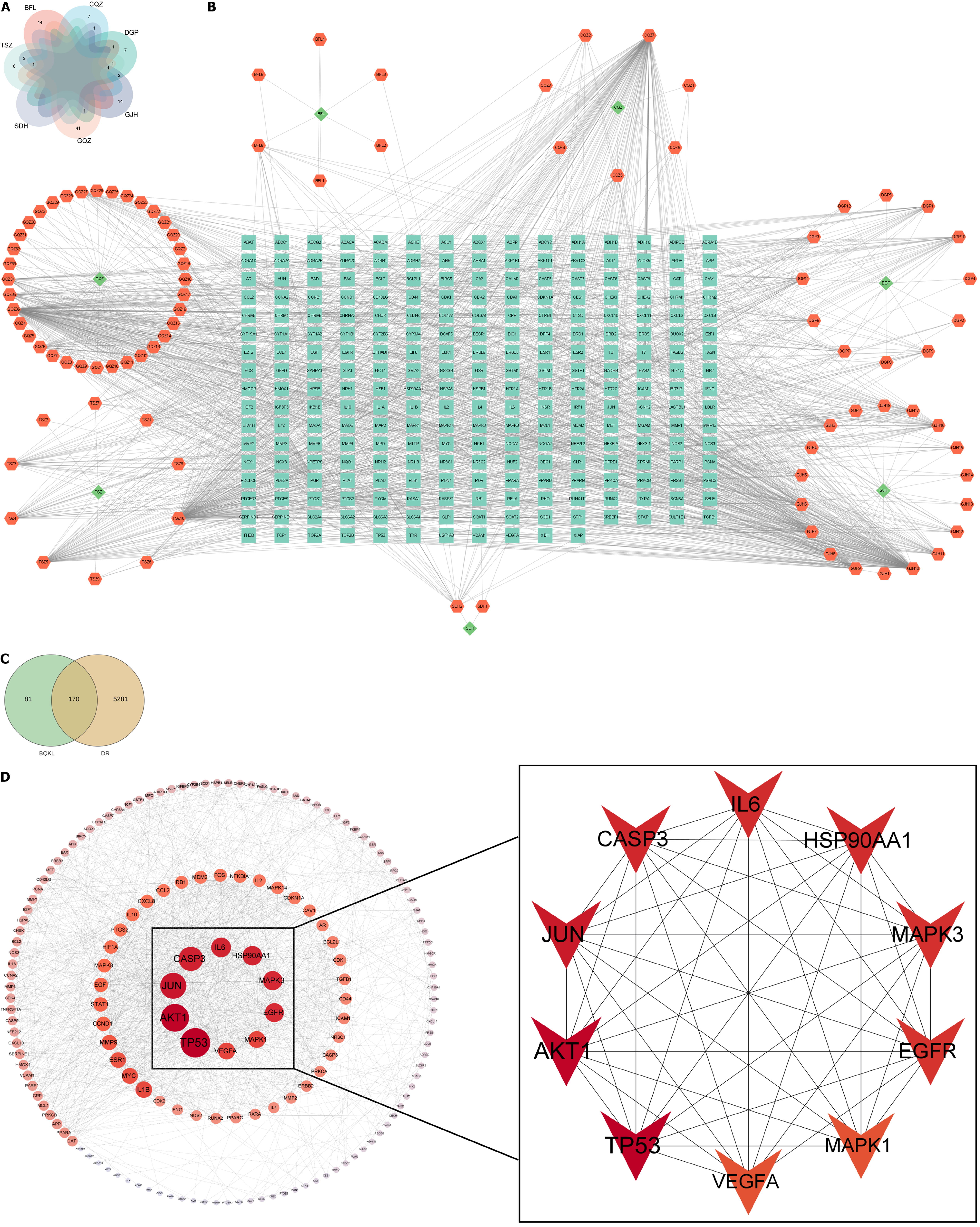
Figure 2 Prediction of diabetic retinopathy components and targets of action of Buqing granule therapy.
A: Main ingredients of Buqing granule (BQKL); B: BQKL-active ingredients-targets of action diagram (The rhombus, square hexagon, and square represent the herbal medicine, active ingredient, and target site, respectively); C: Venn diagram of BQKL and diabetic retinopathy (DR) intersection targets; D: Protein-ptrotein interaction network map and screened core BQKL targets for DR treatment (The darker the color, the larger the icon, the higher the degree value). TSZ: Tusizi; GQZ: Gouqizi; DGP: Digupi; CQZ: Cheqianzi; GJH: Ganjuhua; SDH: Shudihuang; BFL: Baifuling; DR: Diabetic retinopathy; BQKL: Buqing granule.
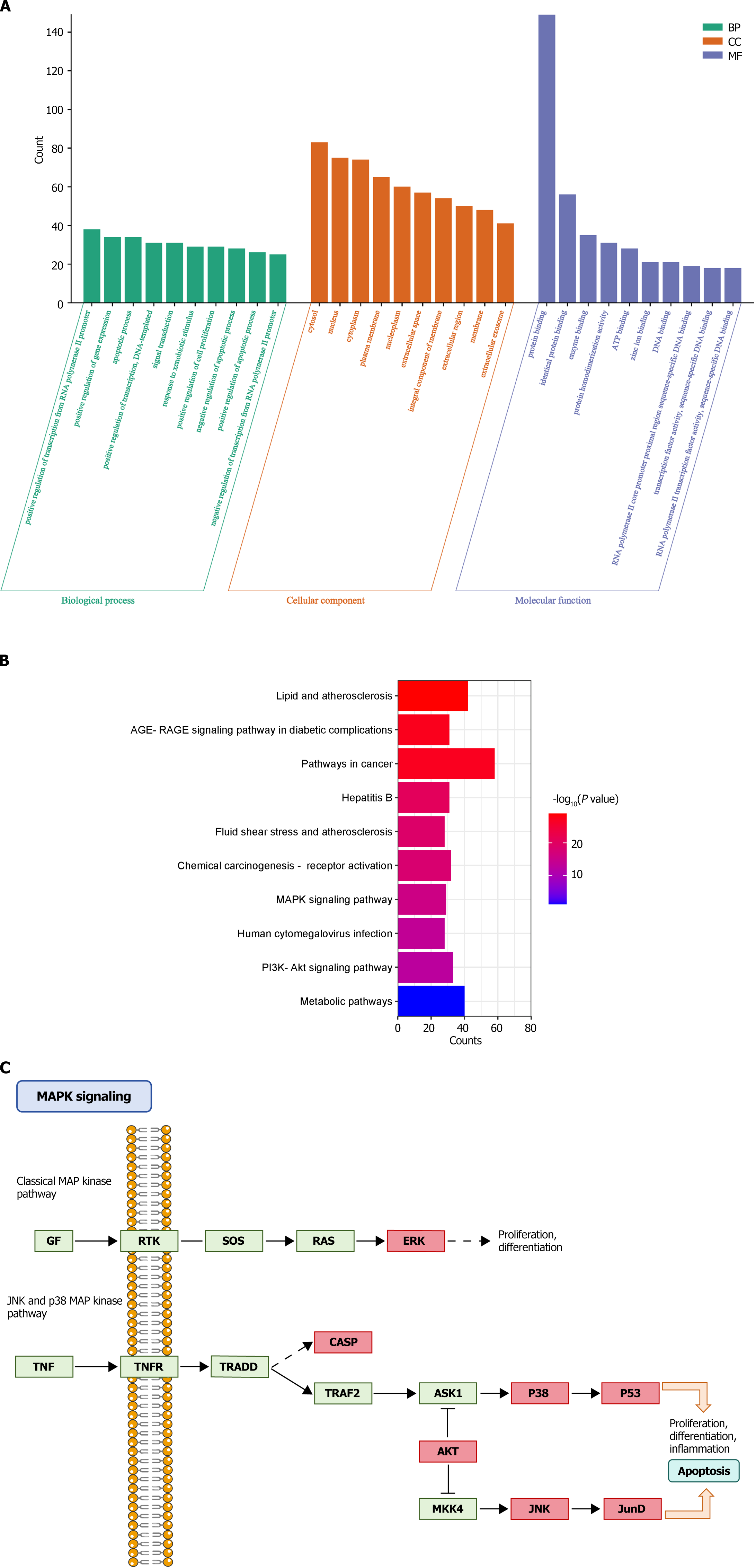
Figure 3 Gene ontology and the Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes enrichment analyses.
A: Gene ontology enrichment analysis; B: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes enrichment analysis; C: Core genes enriched in the MAPK signaling pathway.
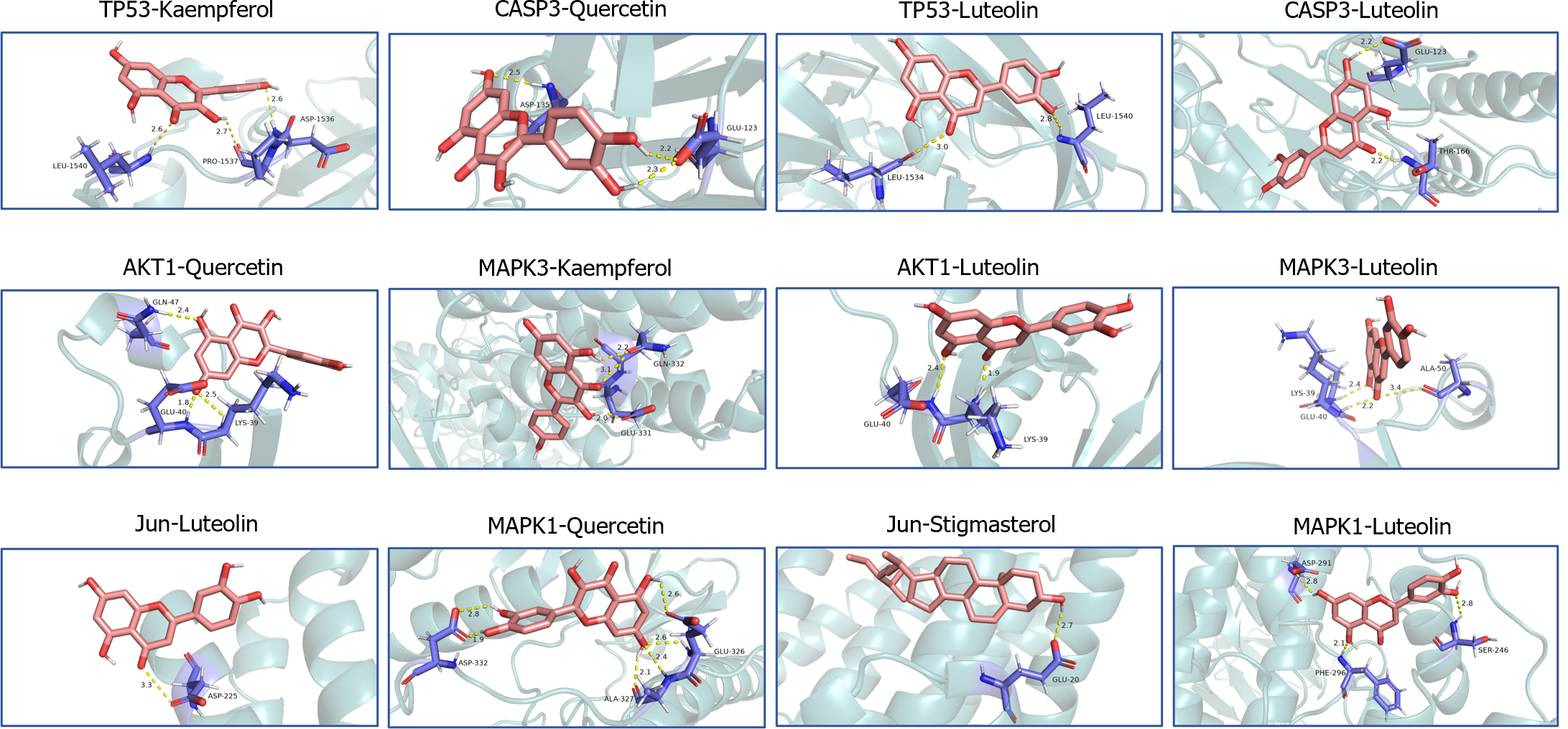
Figure 4 Molecular docking.
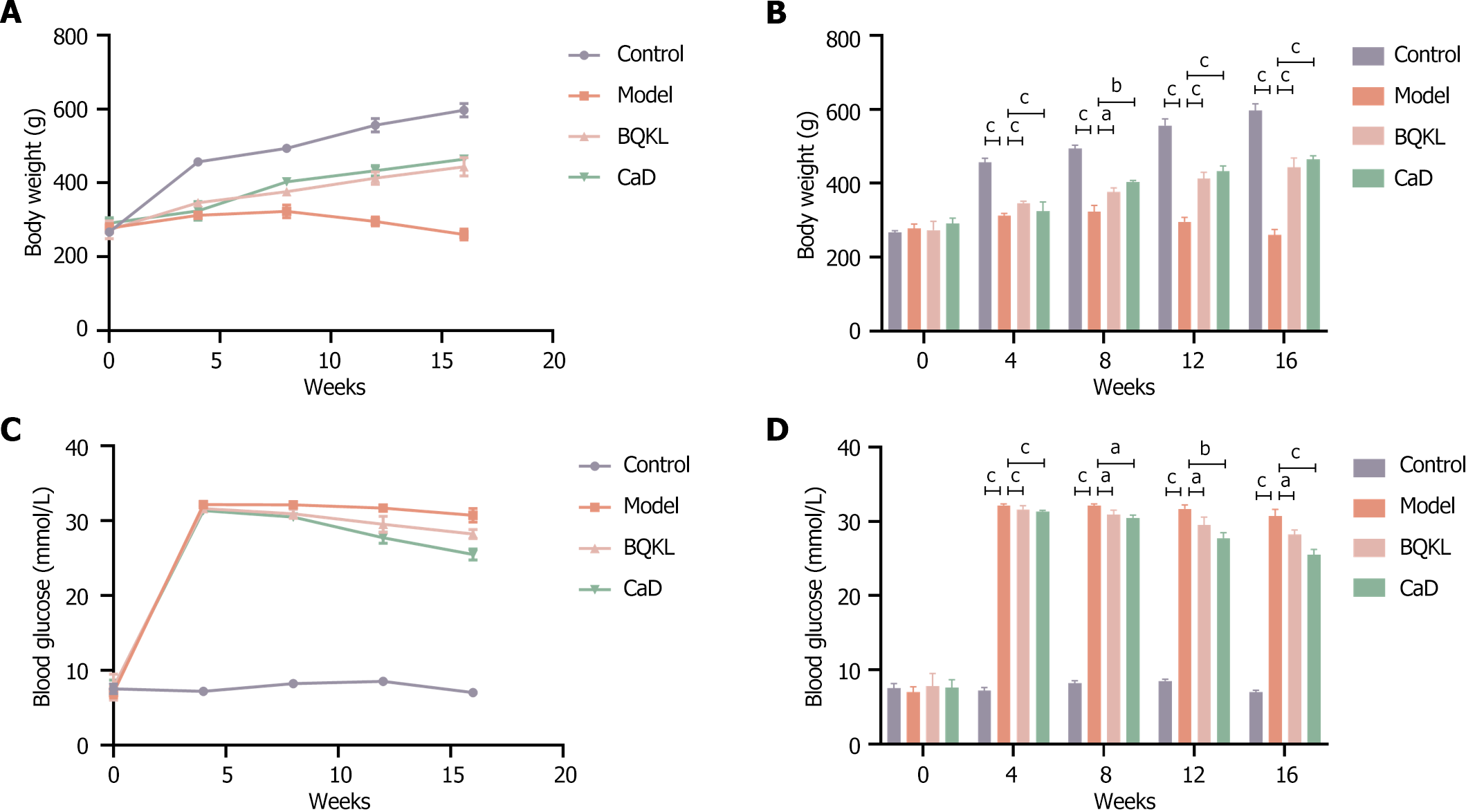
Figure 5 Changes in body weight and blood sugar at different time points.
A: Body weight at different time points; B: Blood glucose at different time points. The sequence from left to right represents the control group, the model group, the BQKL group and the CaD group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. BQKL: Buqing granule; CaD: Calcium dobesilate.
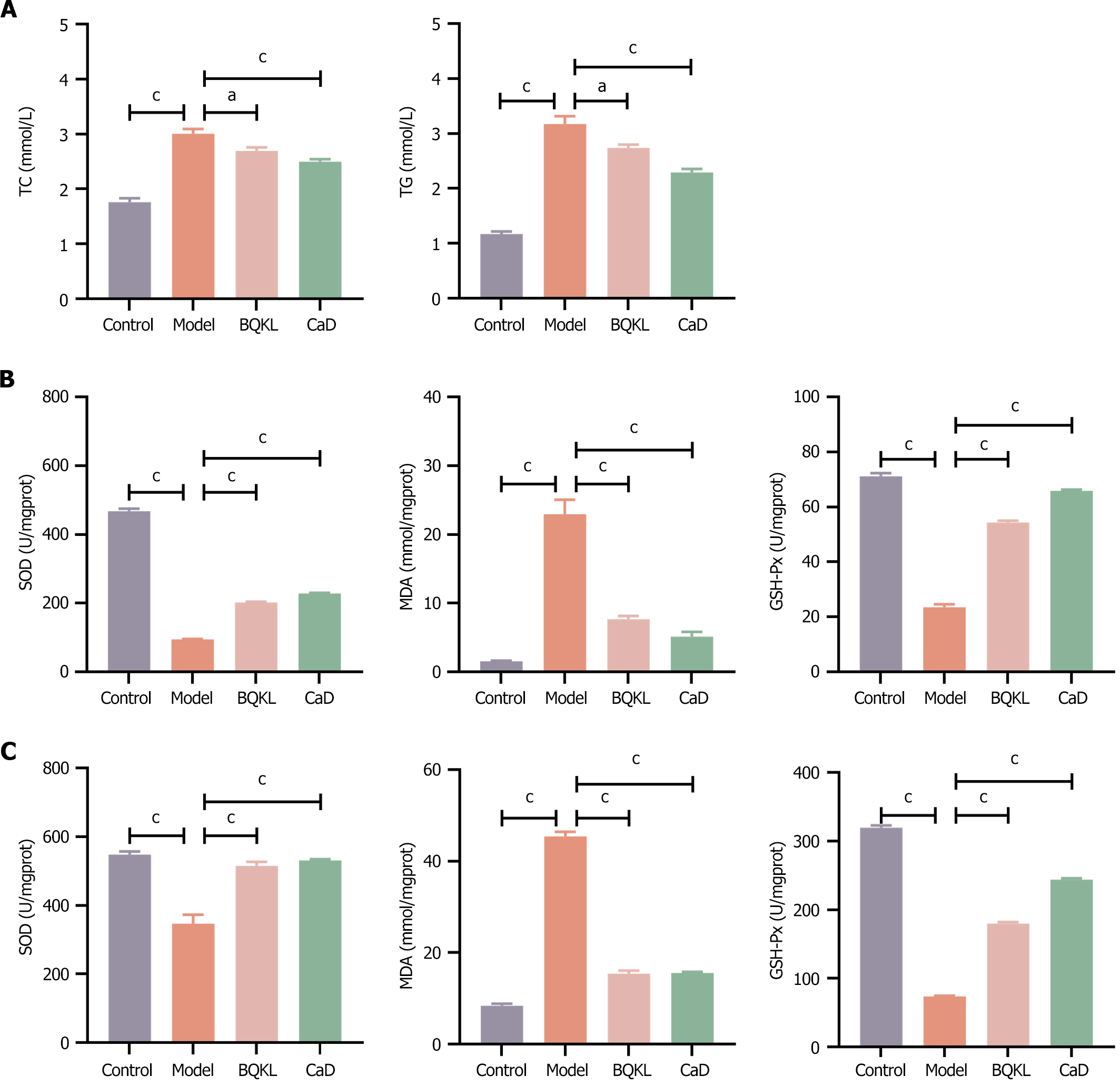
Figure 6 Serum biochemical analyses and ELISA tests.
A: Effect of Buqing granule (BQKL) on total cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the serum of diabetic retinopathy (DR) rats; B: Effect of BQKL on superoxide dismutase, malondialdehyde, and glutathione peroxidase contents in the retina of DR rats; C: Effect of BQKL on oxidative stress in rat serum. The sequence from left to right represents the control group, the model group, the BQKL group and the Calcium dobesilate group. aP < 0.05, cP < 0.001. BQKL: Buqing granule; CaD: Calcium dobesilate.
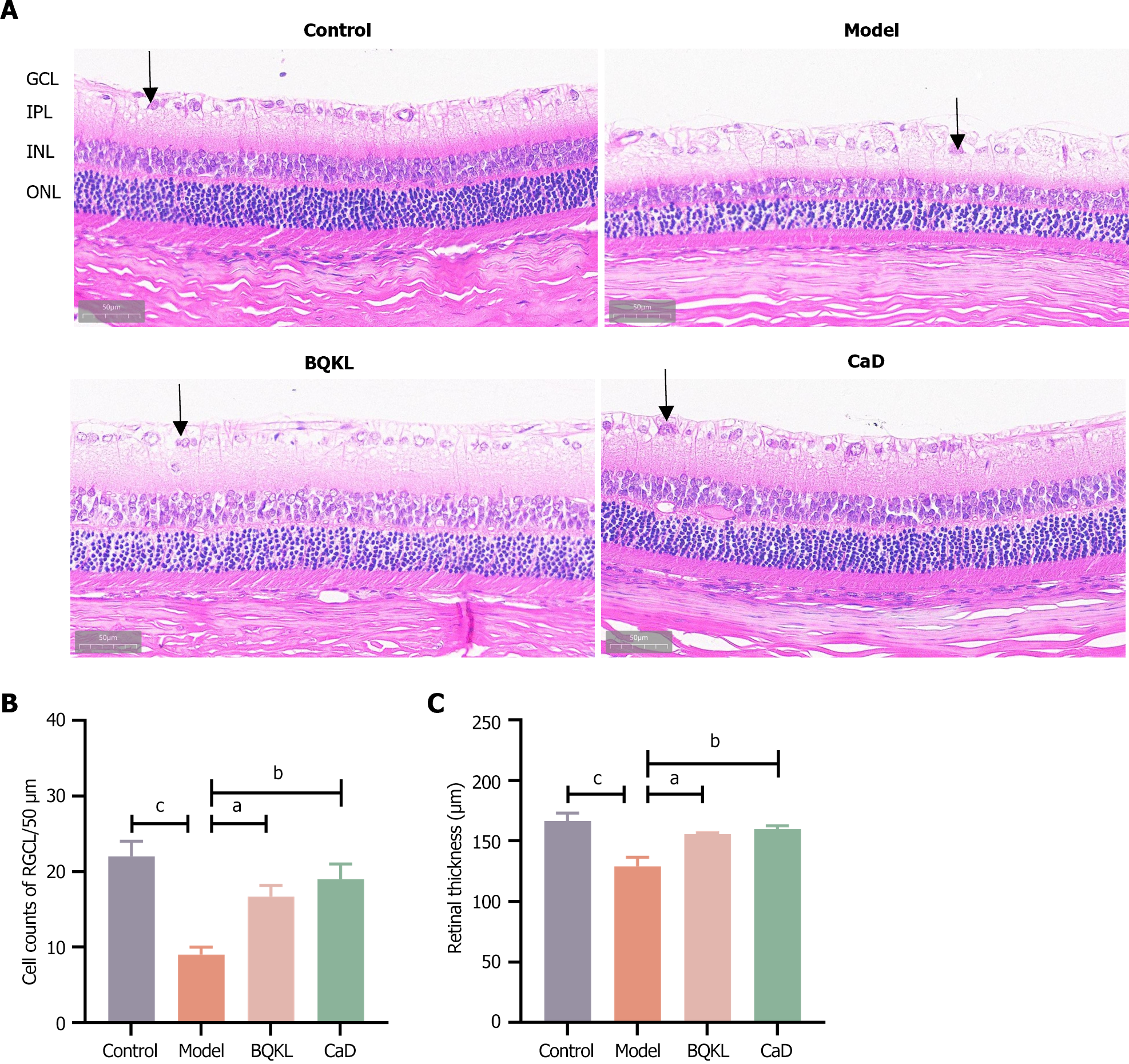
Figure 7 Effects of Buqing granule on retinal morphology in diabetic retinopathy rats.
A: Hematoxylin & eosin staining of the retina of rats in each group (400 ×); B: Retinal ganglion cell count in each group; C: Comparison of retinal thickness in each group. The sequence from left to right represents the control group, the model group, the Buqing granule group and the Calcium dobesilate group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. BQKL: Buqing granule; CaD: Calcium dobesilate. GCL: Ganglion cell layer; IPL: Inner plexiform layer; INL: Inner nuclear layer; OPL: Outer plexiform layer; ONL: Outer nuclear layer.
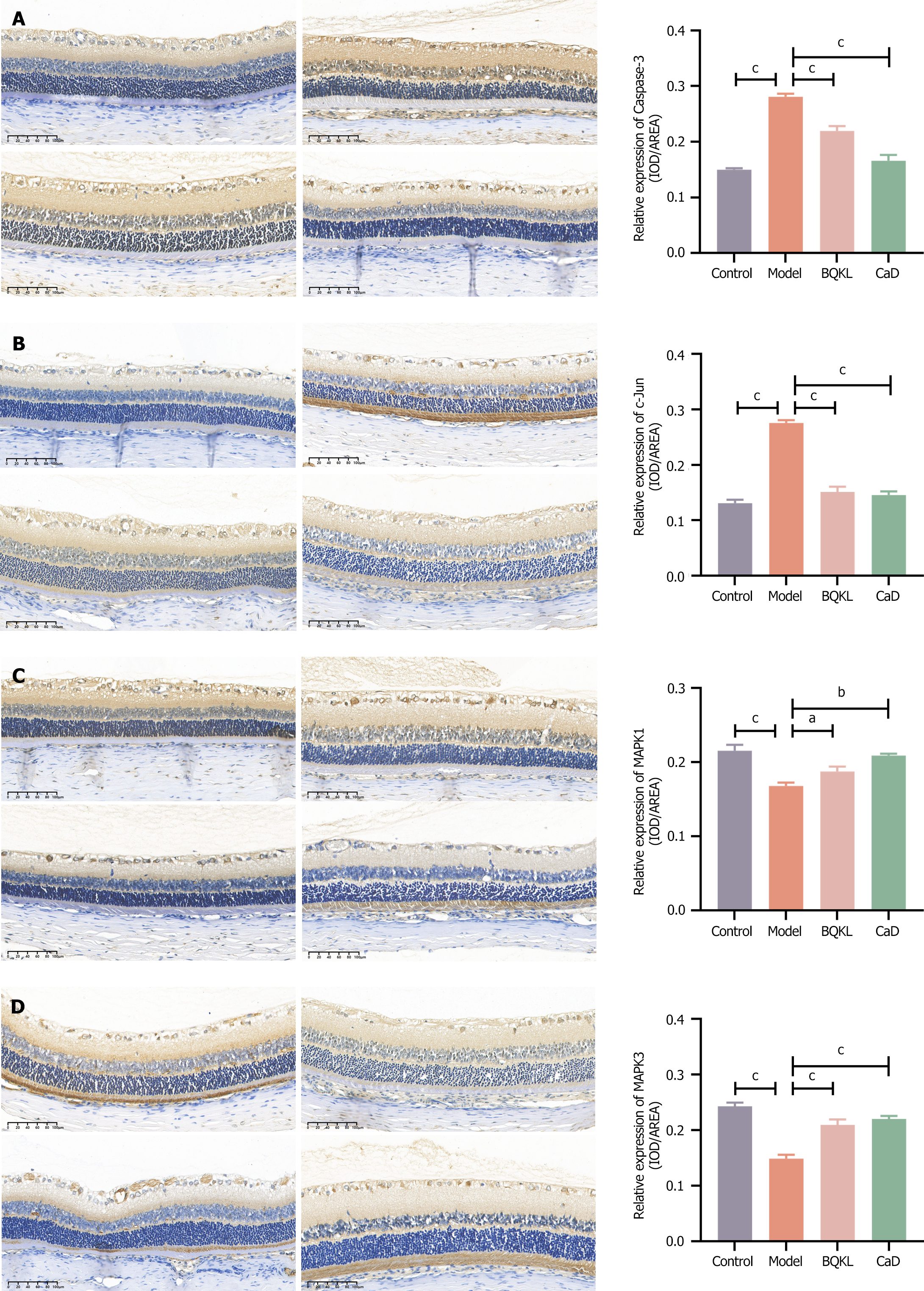
Figure 8 Immunohistochemical results of retinal tissue from different rat models.
A: Immunohistochemical detection of Caspase-3; B: Immunohistochemical detection of c-Jun; C: Immunohistochemical detection of MAPK1; D: Immunohistochemical detection of MAPK3 positive expression (200 ×). The sequence from left to right represents the control group, the model group, the Buqing granule group and the calcium dobesilate group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. BQKL: Buqing granule; CaD: Calcium dobesilate.
Figure 9 A molecular biological perspective on the role of Buqing granule in the diabetic retinopathy treatment.
A: Caspase-3, AKT1, c-Jun, TP53, MAPK1, and MAPK3 mRNA expression levels determined by real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR; B: Protein expression levels determined by western blotting. The sequence from left to right represents the control group, the model group, the Buqing granule group and the calcium dobesilate group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. BQKL: Buqing granule; CaD: Calcium dobesilate.
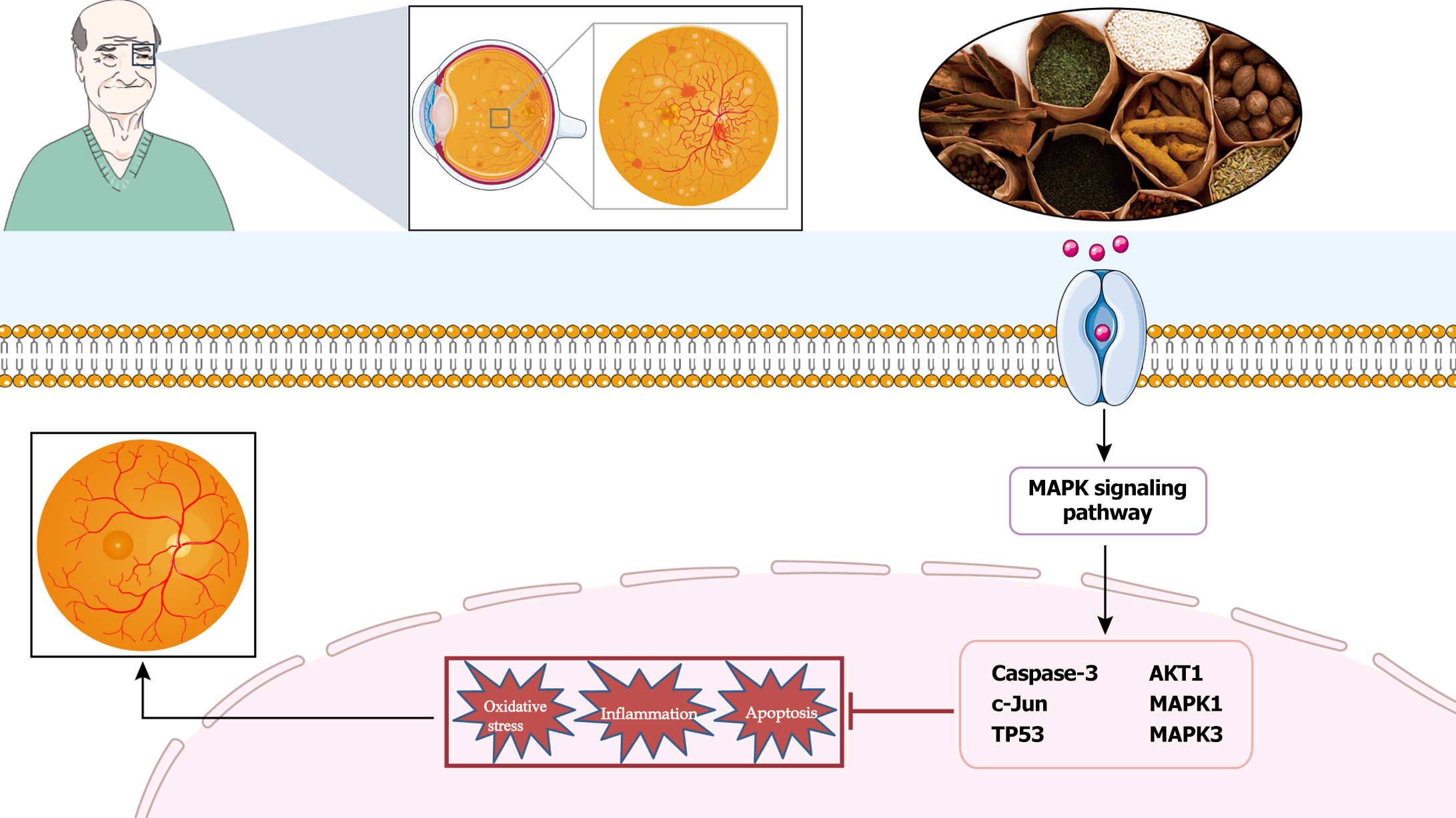
Figure 10 Graphical abstract.
- Citation: Yang YF, Yuan L, Li XY, Liu Q, Jiang WJ, Jiao TQ, Li JQ, Ye MY, Niu Y, Nan Y. Molecular mechanisms of Buqing granule for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy: Network pharmacology analysis and experimental validation. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(9): 1942-1961
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i9/1942.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1942