Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Aug 15, 2024; 15(8): 1704-1711
Published online Aug 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i8.1704
Published online Aug 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i8.1704
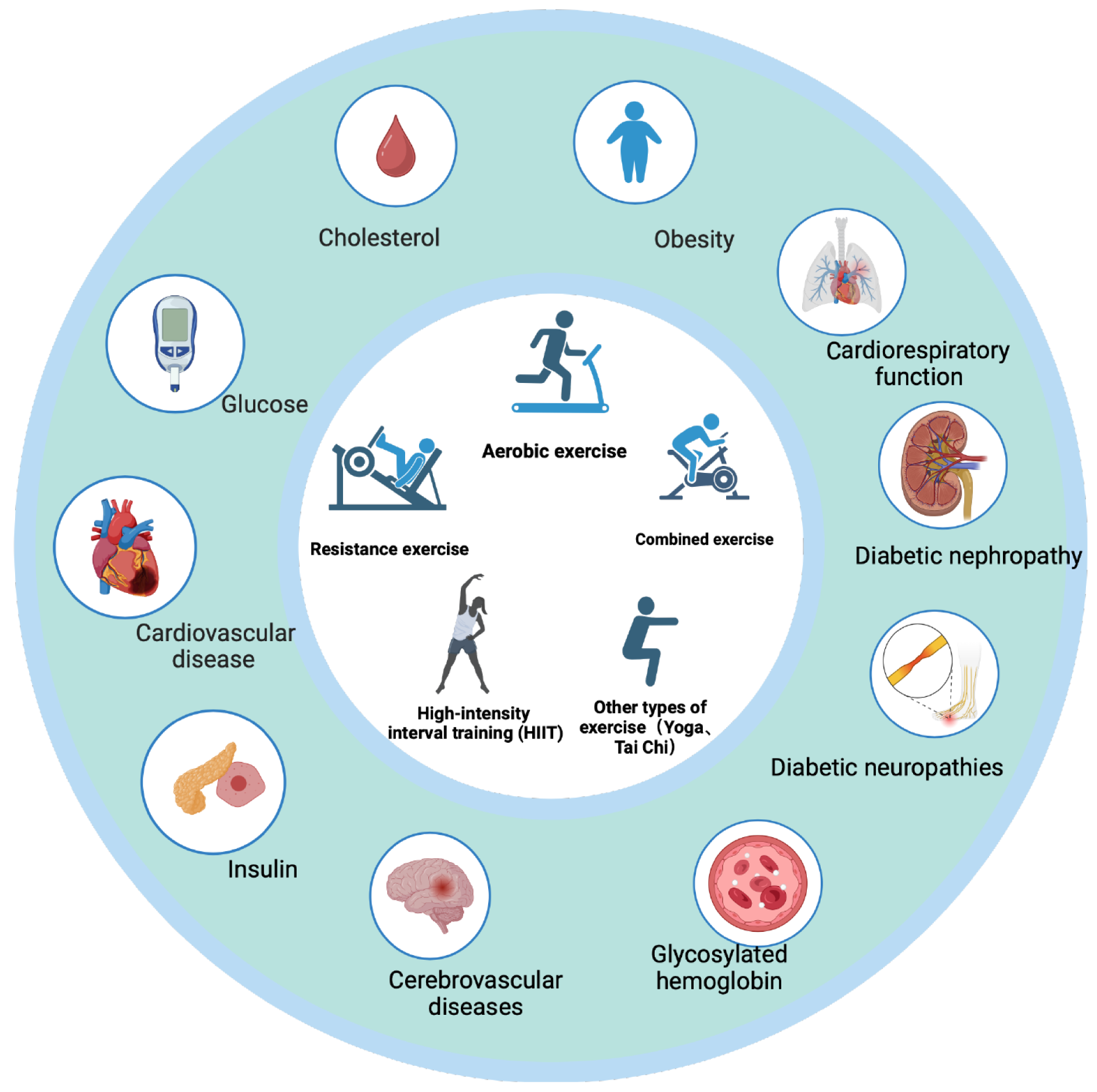
Figure 1 Effects of different types of exercise on type 2 diabetes and the associated complications.
Citation: The authors have obtained the permission for figure using from the BioRender.com (Supplementary material)[41].
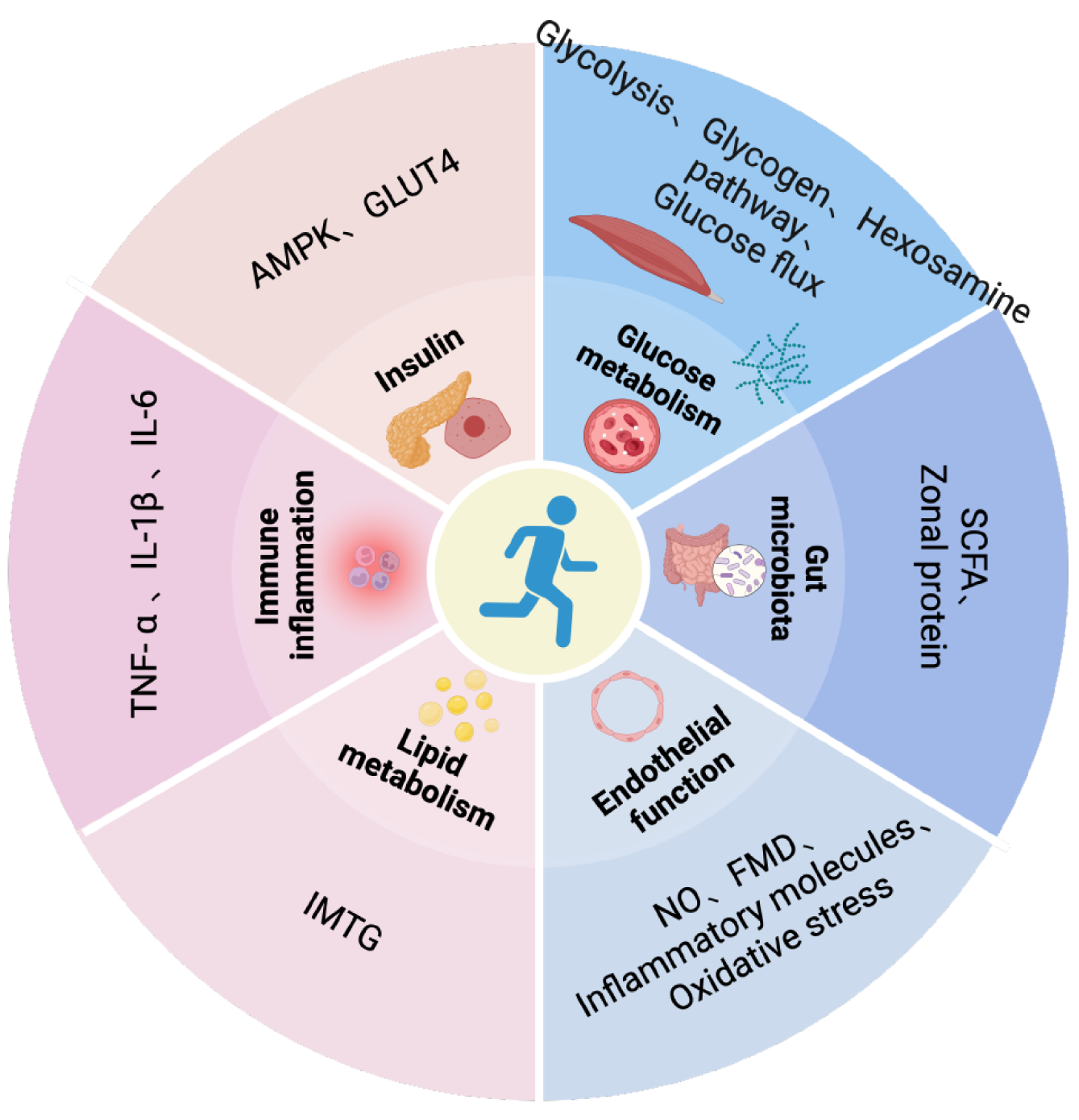
Figure 2 Effects of exercise against type 2 diabetes through reduced insulin resistance, improved insulin sensitivity, increased glucose transport and metabolism, reduced inflammatory response, and regulated lipid metabolism.
AMPK: Activated protein kinase; IMTG: Intramuscular fat; FMD: Flow-mediated dilation; SCFA: Short-chain fatty acid; GLUT: Glucose transporter; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin. Citation: The authors have obtained the permission for figure using from the BioRender.com (Supplementary material)[41].
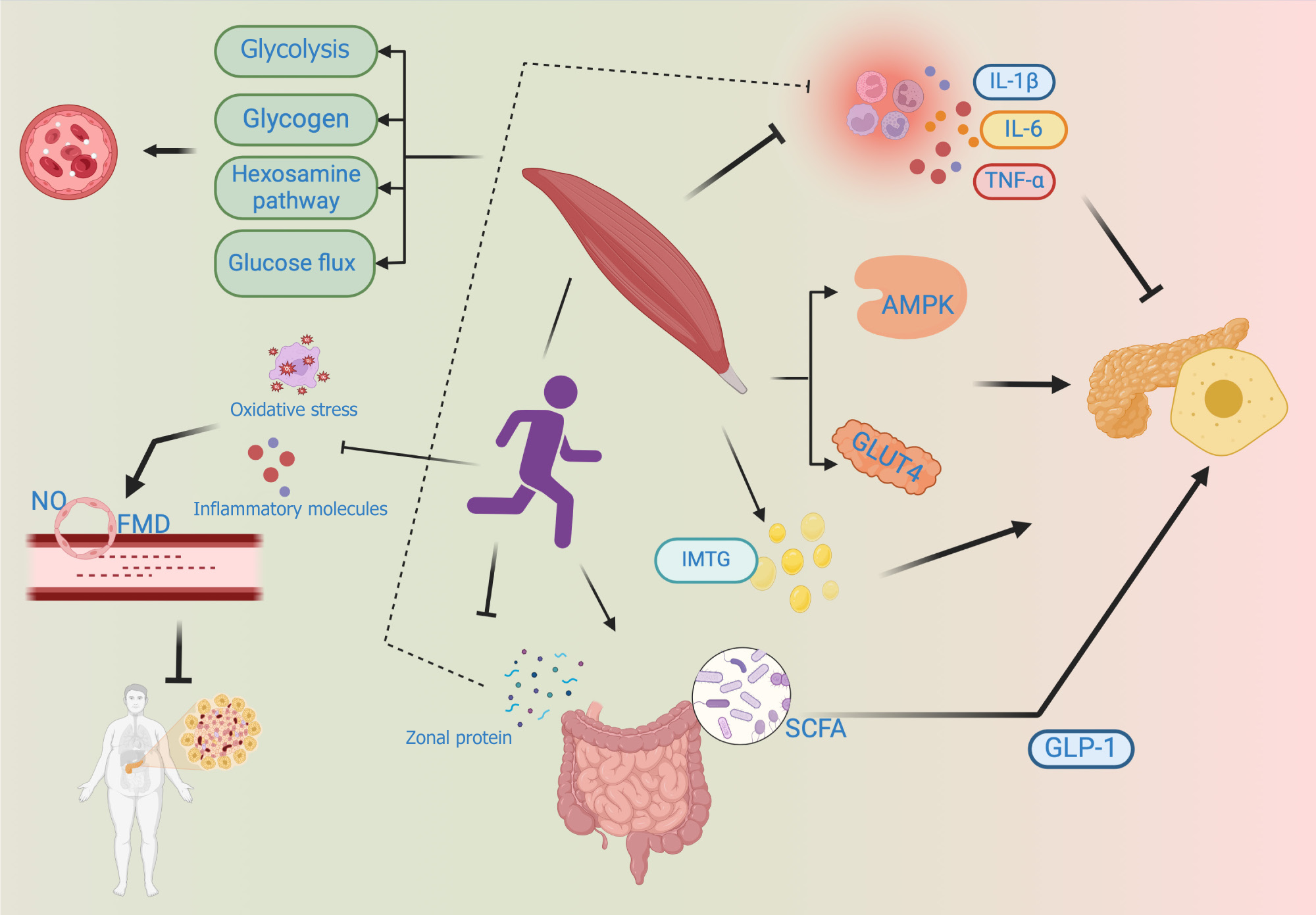
Figure 3 The molecular mechanisms underlying the effect of exercise against type 2 diabetes.
AMPK: Activated protein kinase; IMTG: Intramuscular fat; FMD: Flow-mediated dilation; SCFA: Short-chain fatty acid; GLUT: Glucose transporter; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin. Citation: The authors have obtained the permission for figure using from the BioRender.com (Supplementary material)[41].
- Citation: Peng CJ, Chen S, Yan SY, Zhao JN, Luo ZW, Qian Y, Zhao GL. Mechanism underlying the effects of exercise against type 2 diabetes: A review on research progress. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(8): 1704-1711
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i8/1704.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i8.1704