Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2024; 15(4): 686-696
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i4.686
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i4.686
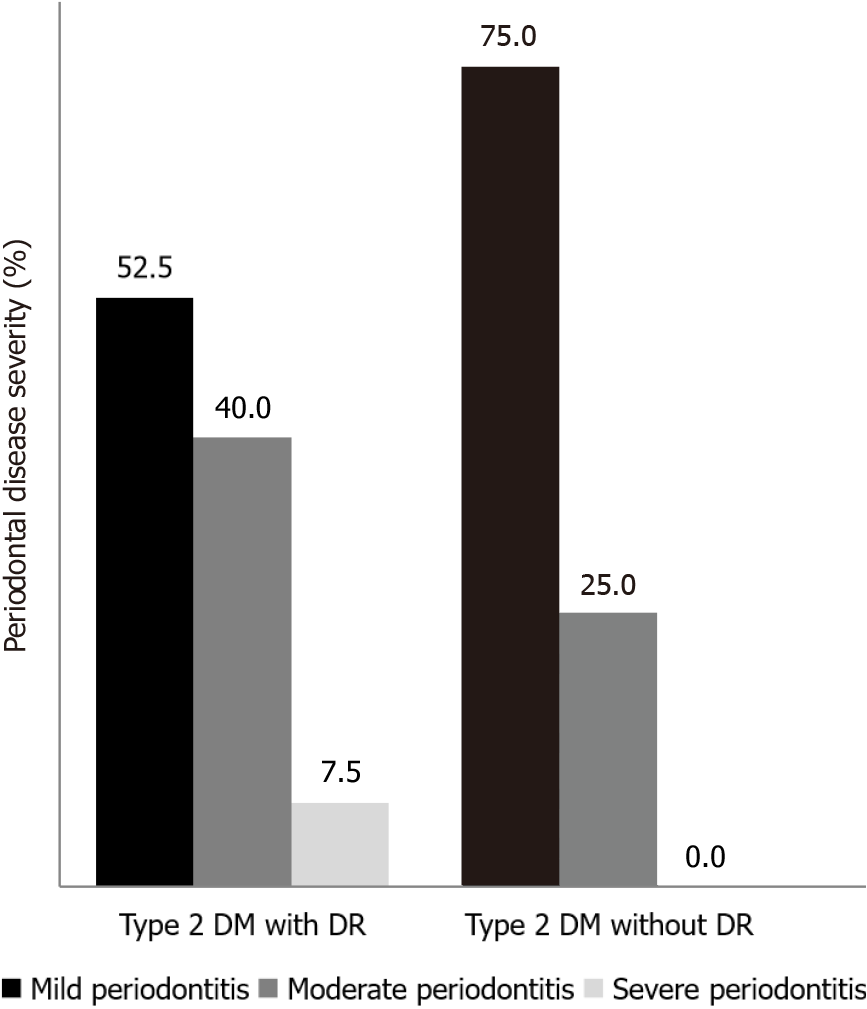
Figure 1 Proportion of periodontal disease severity among subjects in type 2 diabetes mellitus with and without diabetic retinopathy.
DM: Diabetes mellitus; DR: Diabetic retinopathy.
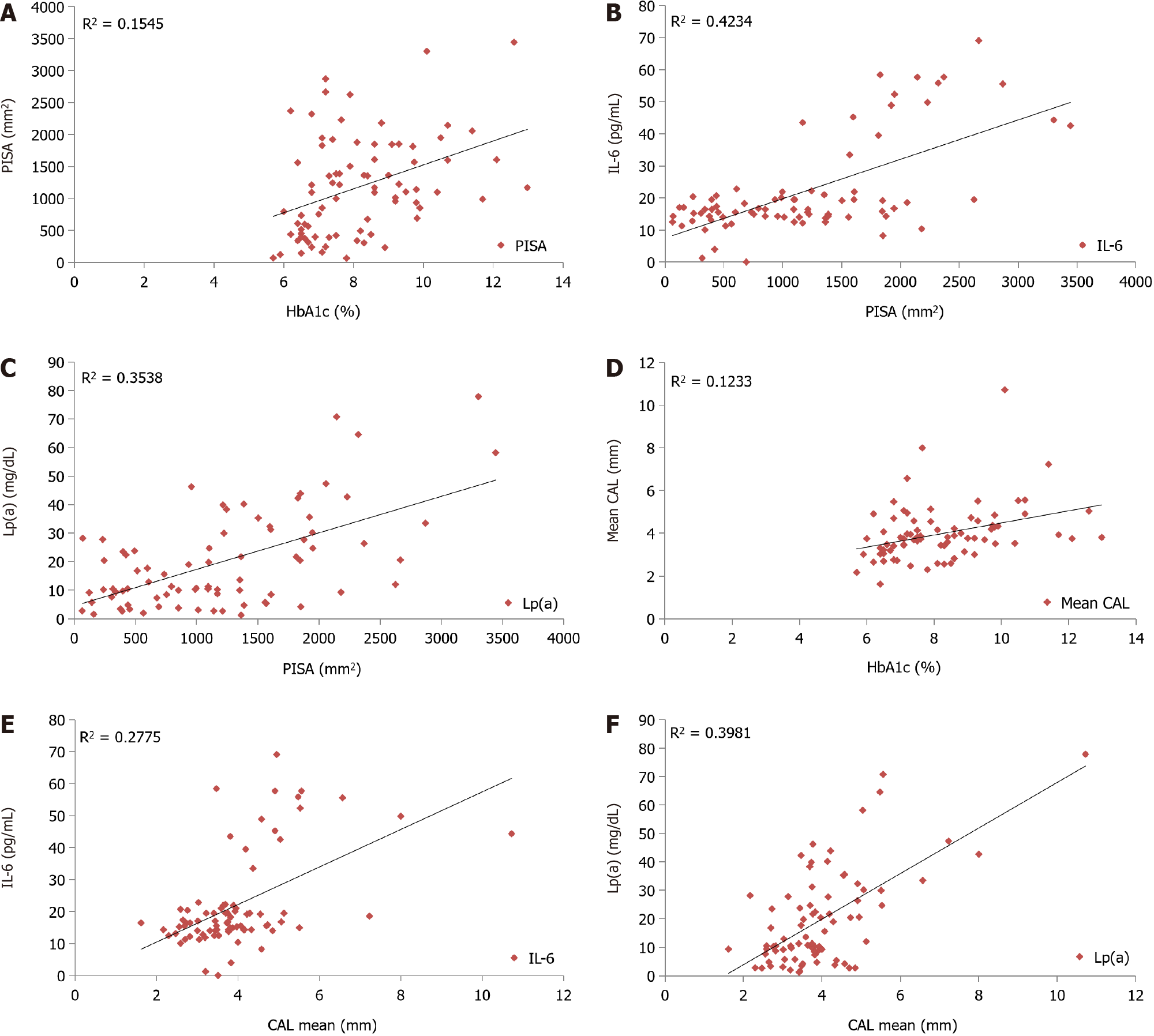
Figure 2 Correlation of periodontal inflamed surface area, and clinical attachment loss between interleukin-6, lipoprotein(a) and glycated hemoglobin.
A: A statistically significant positive correlation had been found between the periodontal inflamed surface area and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) among study subjects (Pearson correlation coefficient 0.393, P value < 0.001); B: A positive correlation had been found between serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and mean periodontal inflamed surface area among study subjects (Pearson correlation coefficient 0.651, P < 0.001); C: Positive correlation had been found between serum lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] and mean periodontal inflamed surface area among study subjects (Pearson correlation coefficient 0.59, P < 0.001); D: A statistically significant positive relation had been found between the mean clinical attachment loss (CAL) and HbA1c in type 2 diabetic mellitus subjects (Pearson correlation coefficient 0.351, P = 0.001); E: A positive correlation had been found between serum IL-6 and mean CAL among study subjects (Pearson correlation coefficient 0.527, P < 0.0001); F: Positive correlation had been found between serum Lp(a) and mean CAL among study subjects (Pearson correlation coefficient 0.631, P < 0.001). HbA1c: Glycated hemoglobin; PISA: Periodontal inflamed surface area; IL-6: Interleukin-6; Lp(a): Lipoprotein(a); CAL: Clinical attachment loss.
- Citation: Thazhe Poyil NJ, Vadakkekuttical RJ, Radhakrishnan C. Correlation of periodontal inflamed surface area with glycated hemoglobin, interleukin-6 and lipoprotein(a) in type 2 diabetes with retinopathy. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(4): 686-696
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i4/686.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i4.686