Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Mar 15, 2024; 15(3): 502-518
Published online Mar 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.502
Published online Mar 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.502
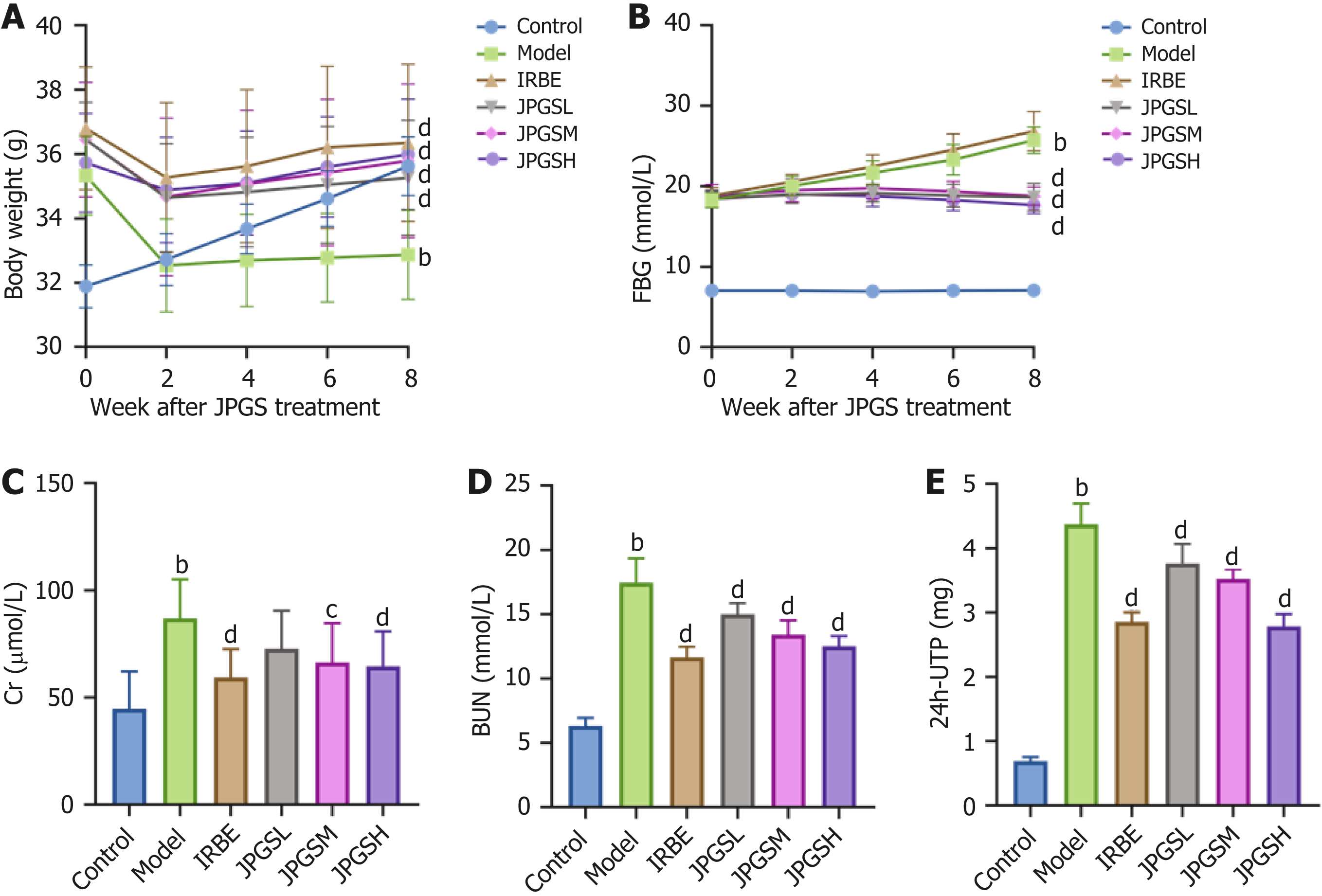
Figure 1 Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction administration improved body weight loss, hyperglycemia, and kidney injury in diabetic nephropathy mice.
A: Curves of body weight changes; B: Curves of fasting blood glucose changes; C: Creatinine levels; D: Blood urea nitrogen level; E: 24 h urine total protein levels. Control, model, irbesartan, low-dose Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction (JPGSL), medium-dose JPGS, and high-dose JPGS groups, n = 10 per group. bP < 0.01 as compared to the control group; cP < 0.05 as compared to the model group; dP < 0.01 as compared to the model group. JPGS: Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction; FBG: Fasting blood glucose; Cr: Creatinine; BUN: Blood urea nitrogen; 24h-UTP: 24 h urine total protein; JPGSL: Low-dose Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction; JPGSM: Medium-dose Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction; JPGSH: High-dose Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction; IRBE: Irbesartan.
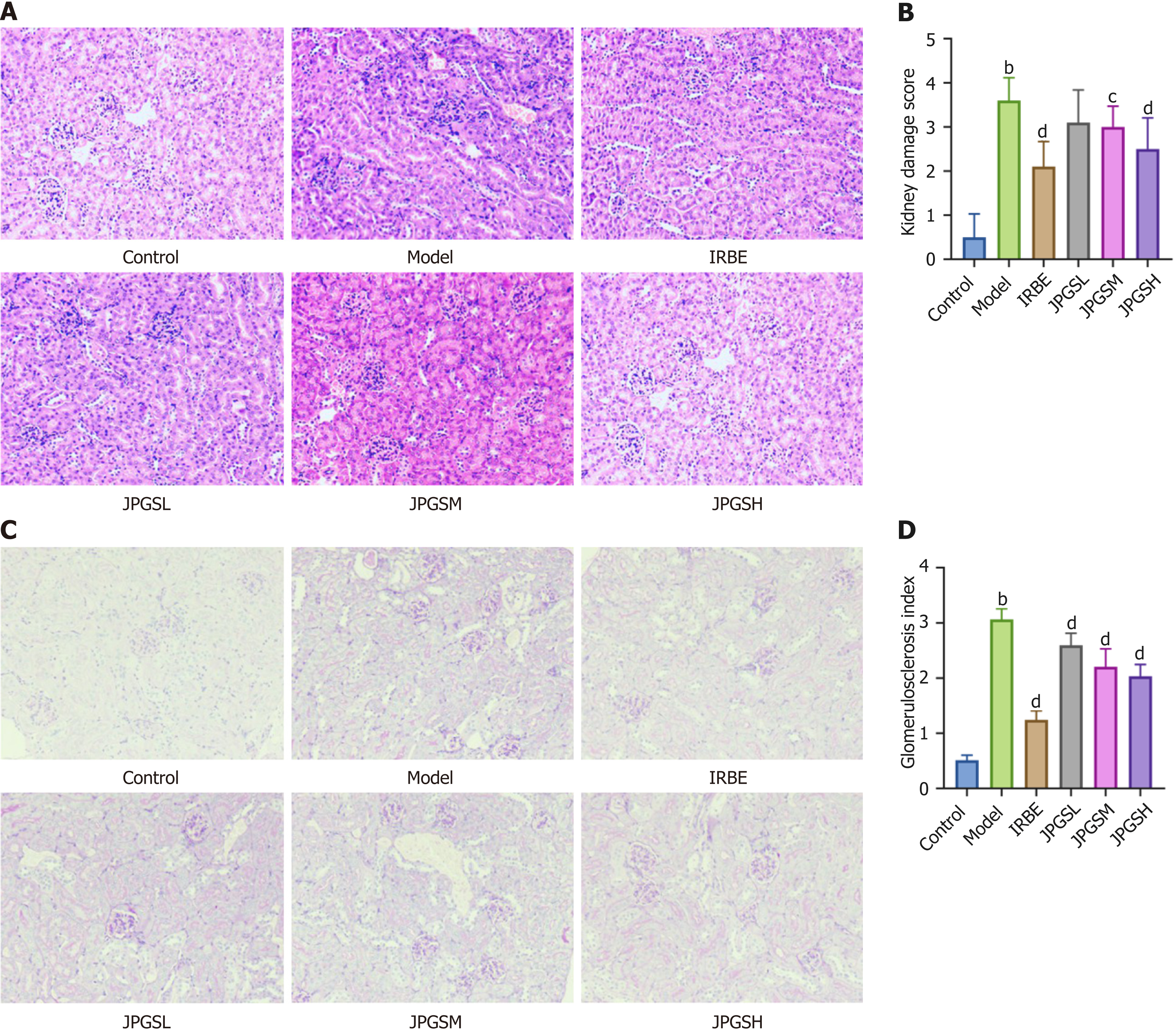
Figure 2 Pathological changes in kidneys were improved following Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction administration.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin staining; B: Kidney damage score; C: Periodic acid Schiff staining; D: Glomerulosclerosis index, magnification × 100. bP < 0.01 as compared to the control group; cP < 0.05 as compared to the model group; dP < 0.01 as compared to the model group. JPGSL: Low-dose Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction; JPGSM: Medium-dose Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction; JPGSH: High-dose Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction; IRBE: Irbesartan.
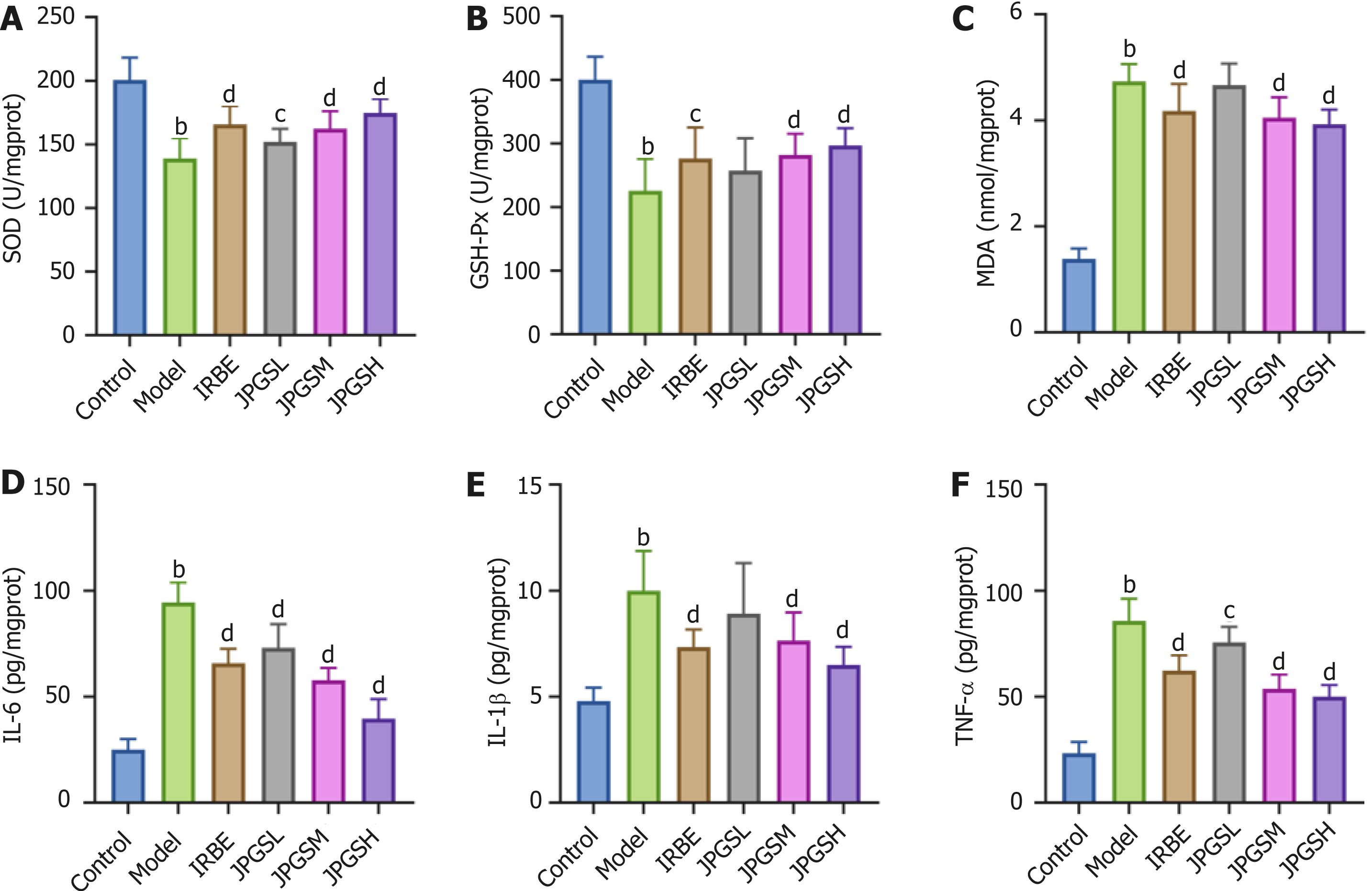
Figure 3 Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction reduced oxidative stress and inflammation in kidneys.
A: The activities of superoxide dismutase; B: The activities of glutathione peroxidase; C: Malondialdehyde level; D: Interleukin (IL)-6 levels; E: IL-1β levels; F: Tumor necrosis factor-α levels. bP < 0.01 as compared to the control group; cP < 0.05 as compared to the model group; dP < 0.01 as compared to the model group. JPGSL: Low-dose Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction; JPGSM: Medium-dose Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction; JPGSH: High-dose Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction; IRBE: Irbesartan; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; GSH-Px: Glutathione peroxidase; MDA: Malondialdehyde; IL-6: Interleukin 6; IL-1β: Interleukin 1 beta; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha.
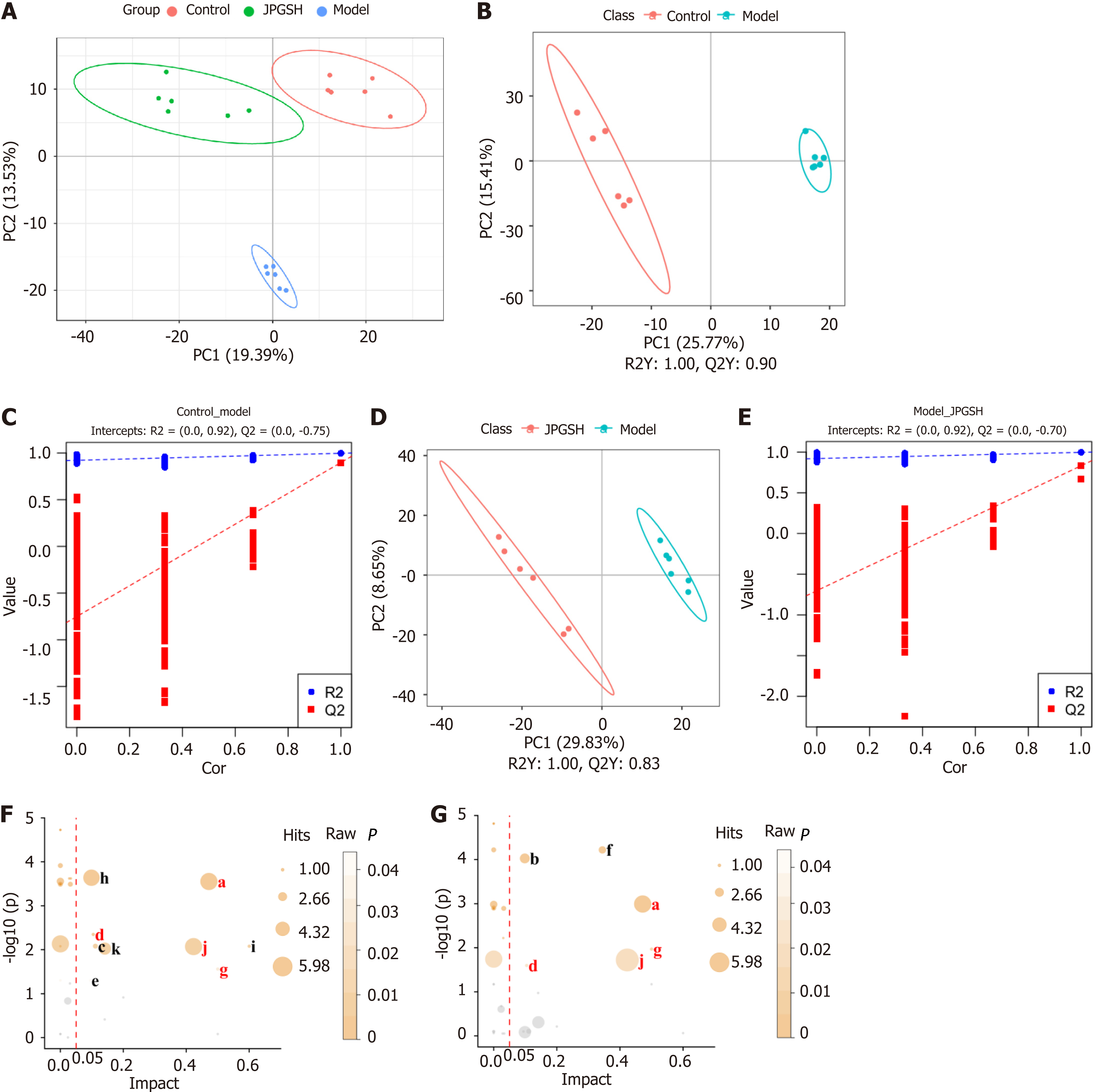
Figure 4 Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction treatment alters the metabolites in kidneys.
A: Score plots of PCA among control, model, and high-dose Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction (JPGSH) groups; B and C: Score plots and permutation tests of partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) between the control and model groups; D and E: Score plots and permutation tests of PLS-DA between the model and JPGSH groups; F: Results of the pathway analysis between the control and model groups; G: Results of the pathway analysis between the model and JPGSH groups. Common pathways are marked in red. The names of the pathways are represented by “a” to “k”: a: Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism; b: Arachidonic acid metabolism; c: Butanoate metabolism; d: Cysteine and methionine metabolism; e: Glycerophospholipid metabolism; f: Histidine metabolism; g: Riboflavin metabolism; h: Steroid hormone biosynthesis; i: Synthesis and degradation of ketone bodies; j: Tryptophan metabolism; k: Tyrosine metabolism. n = 6 per group. JPGSH: High-dose Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction.
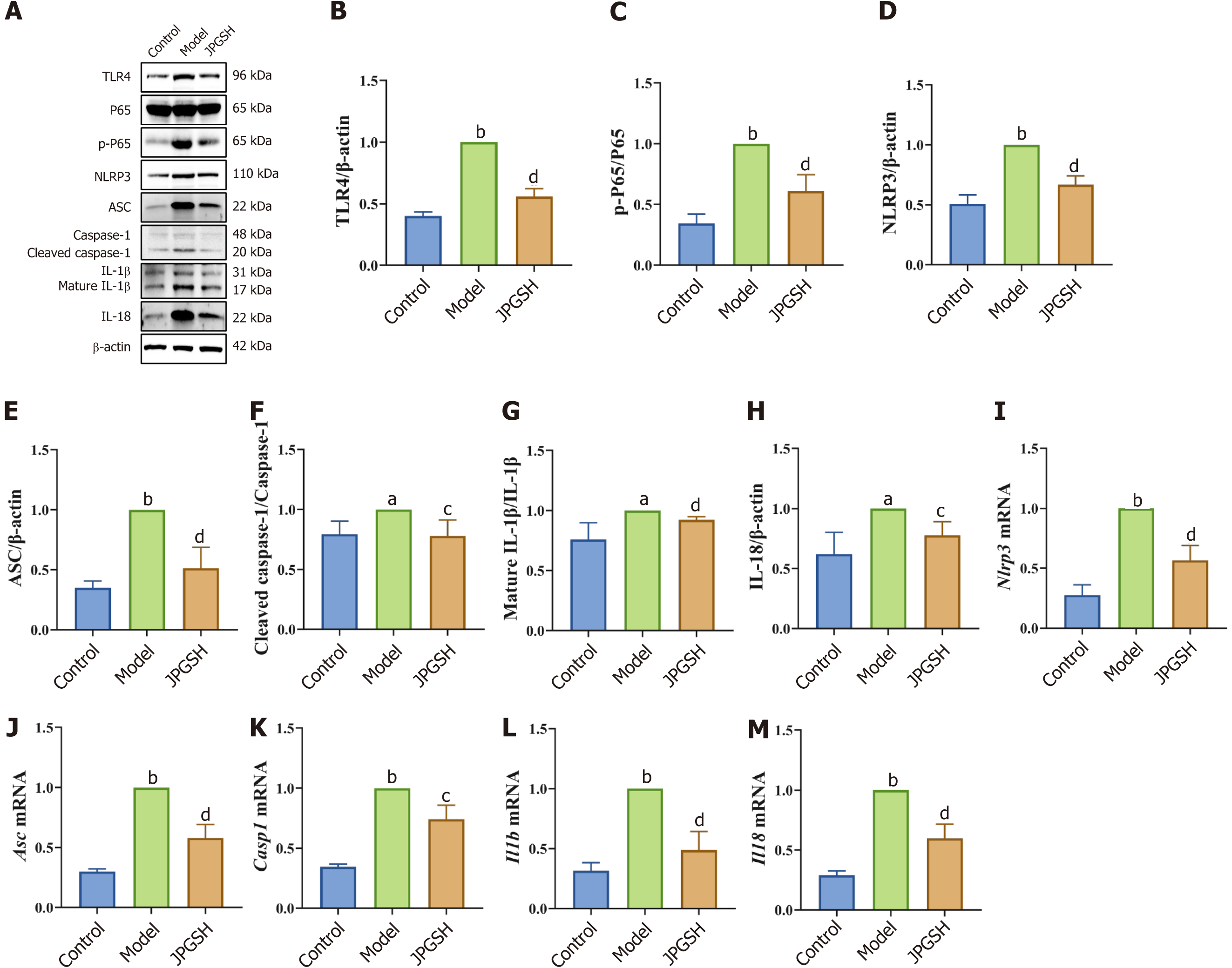
Figure 5 Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction moderated the toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-kappa B/NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 pathway and ameliorated inflammatory injuries to kidneys.
A: Western blotting results; B: Toll-like receptor 4 levels; C: p-P65/P65 levels; D: NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) levels; E: Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC) levels; F: Cleaved caspase-1/caspase-1 levels; G: Mature interleukin (IL)-1β/IL-1β levels; H: IL-18 levels; I: Nlrp3 levels; J: Asc levels; K: Casp1 levels; L: Il1b levels; M: Il18 levels. aP < 0.05 as compared to the control group; bP < 0.01 as compared to the control group; cP < 0.05 as compared to the model group; dP < 0.01 as compared to the model group. JPGSH: High-dose Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction; TLR4: toll-like receptor 4; NLRP3: NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3; ASC: Protein apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; IL: Interleukin.
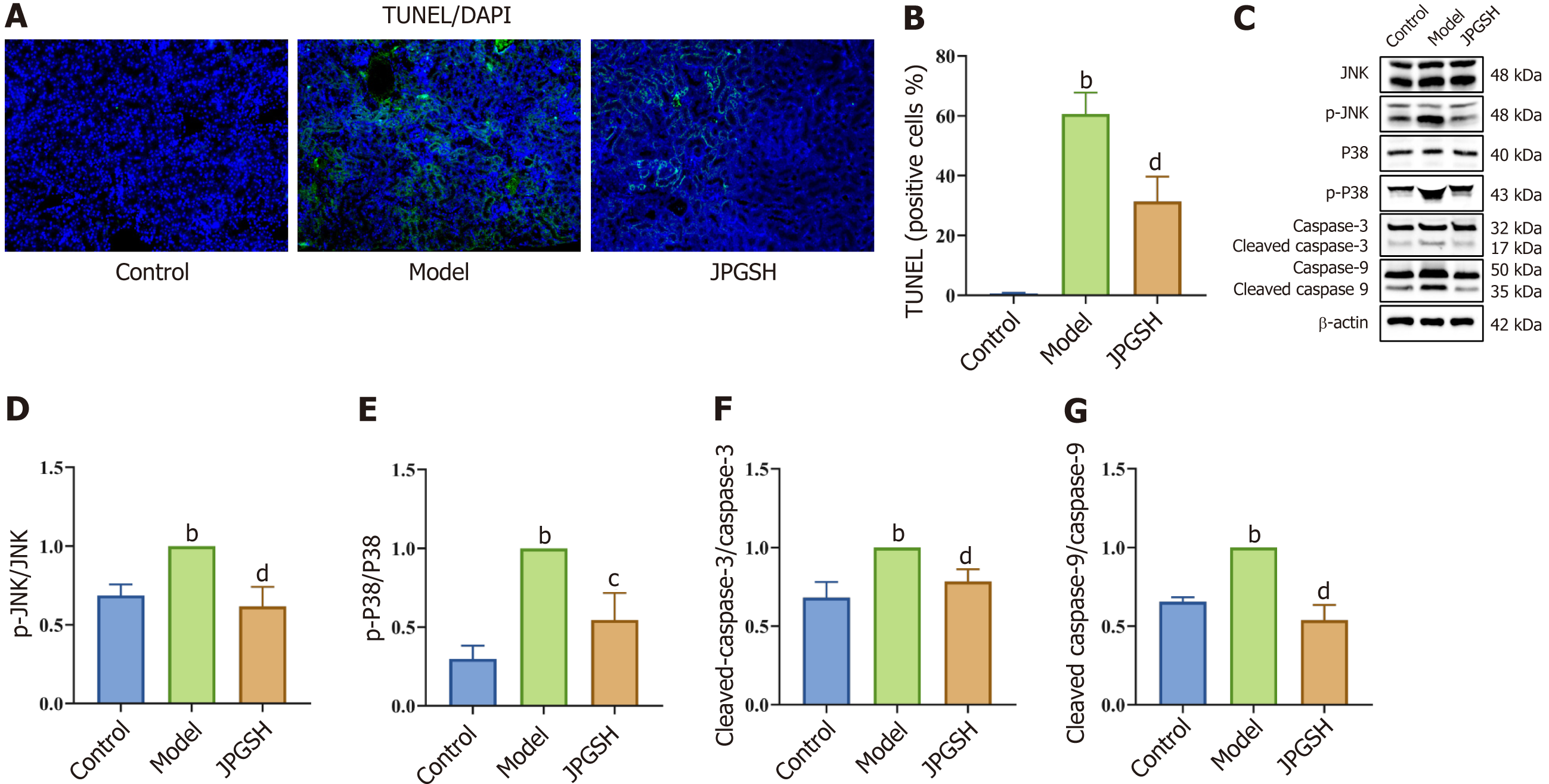
Figure 6 Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction inhibited c-Jun N-terminal kinase/P38 pathway mediated apoptosis and improved kidney injury.
A: TUNEL staining; B: Percentage of positive cells in TUNEL staining; C: Western blotting results; D: p-c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)/JNK level; E: p-P38/P38 levels; F: Cleaved-caspase-3/caspase-3 levels; G: Cleaved caspase-9/caspase-9 levels. bP < 0.01 as compared to the control group; cP < 0.05 as compared to the model group; dP < 0.01 as compared to the model group. JPGSH: High-dose Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase.
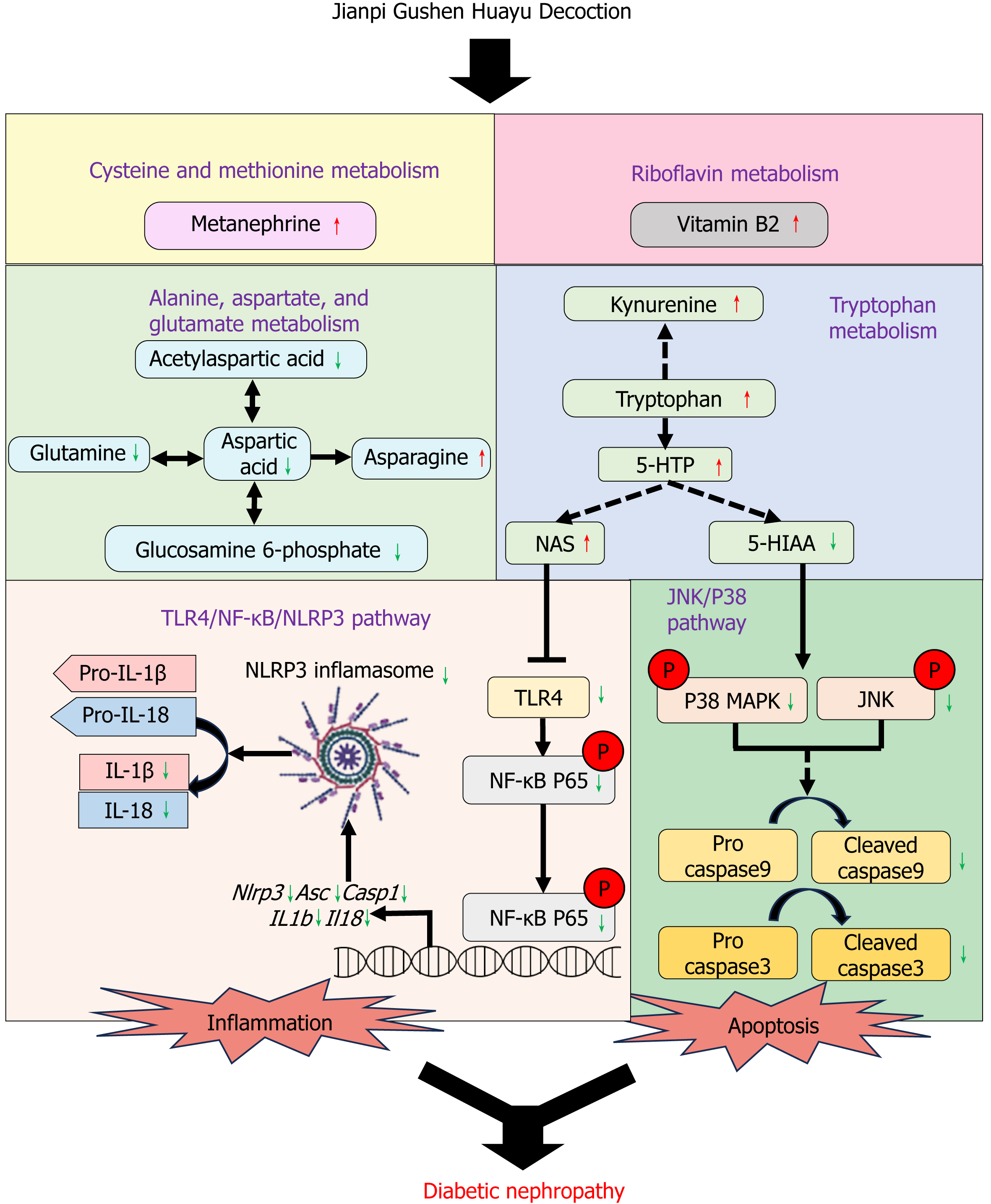
Figure 7 Jianpi Gushen Huayu Decoction could improve kidney inflammatory responses and kidney injury in diabetic nephropathy mice via the toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-kappa B/NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 pathway and inhibit kidney cell apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy mice via the JNK/P38 pathway.
It is possibly related to regulate cysteine and methionine metabolism, alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism, tryptophan metabolism and riboflavin metabolism in kidney. NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; 5-HTTP: 5-hydroxytryptophan; NAS: N-acetylserotonin; 5-HIAA: 5-hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; TLR4: toll-like receptor 4; NLRP3: NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3; ASC: Protein apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Ma ZA, Wang LX, Zhang H, Li HZ, Dong L, Wang QH, Wang YS, Pan BC, Zhang SF, Cui HT, Lv SQ. Jianpi Gushen Huayu decoction ameliorated diabetic nephropathy through modulating metabolites in kidney, and inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 and JNK/P38 pathways. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(3): 502-518
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i3/502.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.502