Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Feb 15, 2023; 14(2): 92-109
Published online Feb 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i2.92
Published online Feb 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i2.92
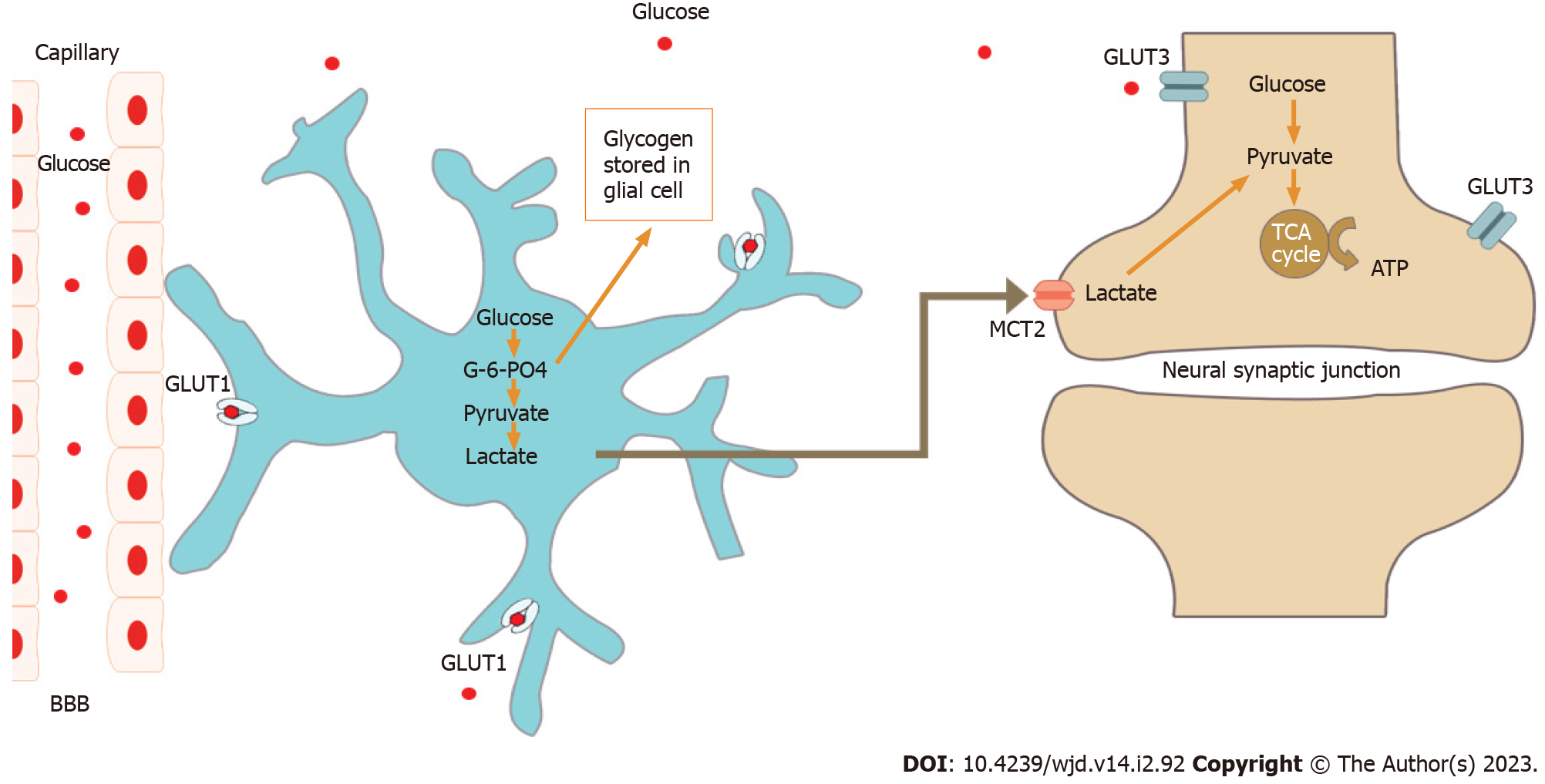
Figure 1 Neuronal utilisation of glucose under normal resting condition.
G-6-PO4: Glucose 6-phosphate; BBB: Blood brain barrier; TCA: Tricarboxylic acid; GLUT: Glucose transporter; MCT2: Monocarboxylate transporter.
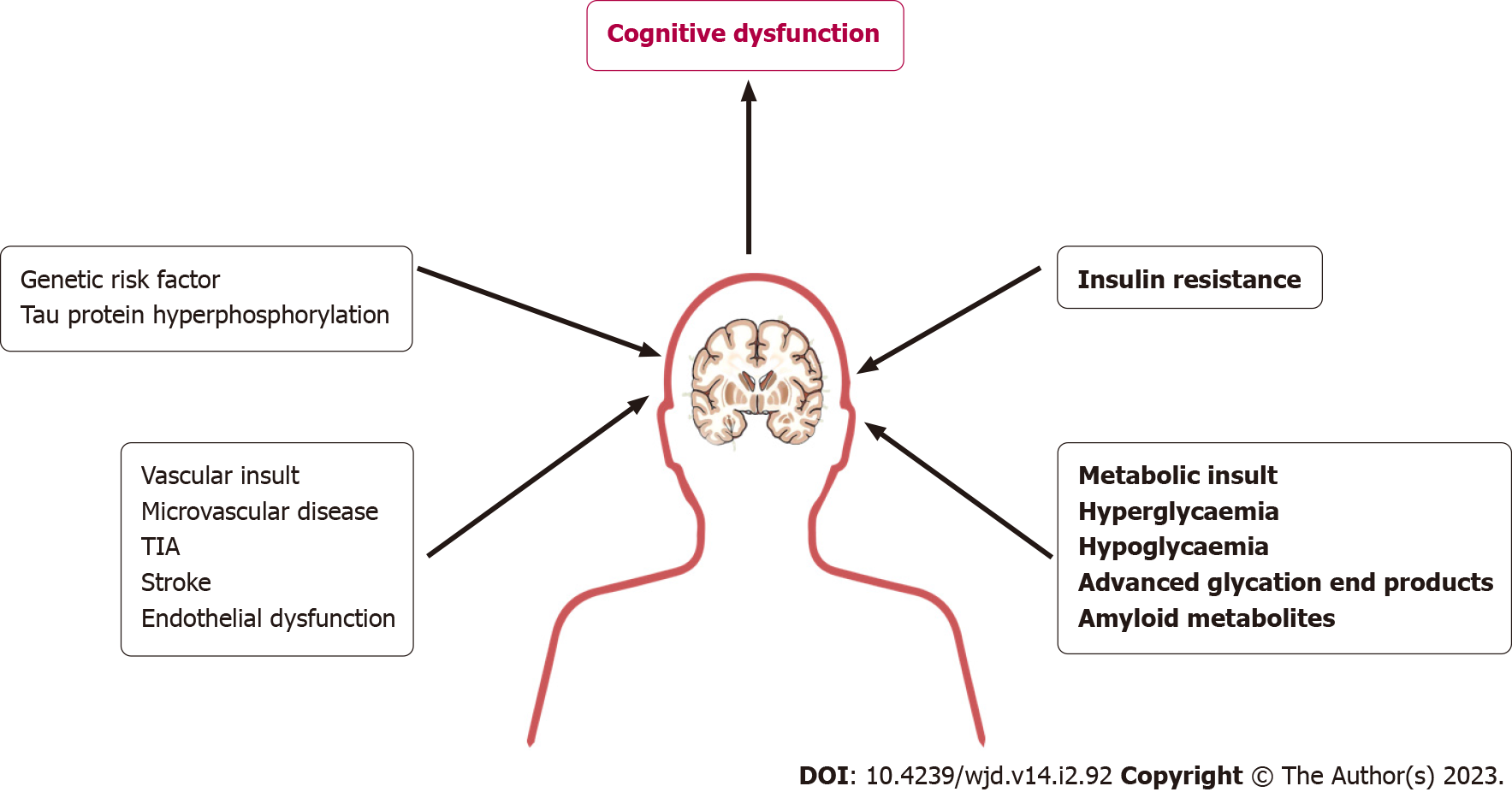
Figure 2 A graphical representation of the pathobiology of cognitive dysfunction in patients with diabetes.
TIA: Transient ischemic attack.
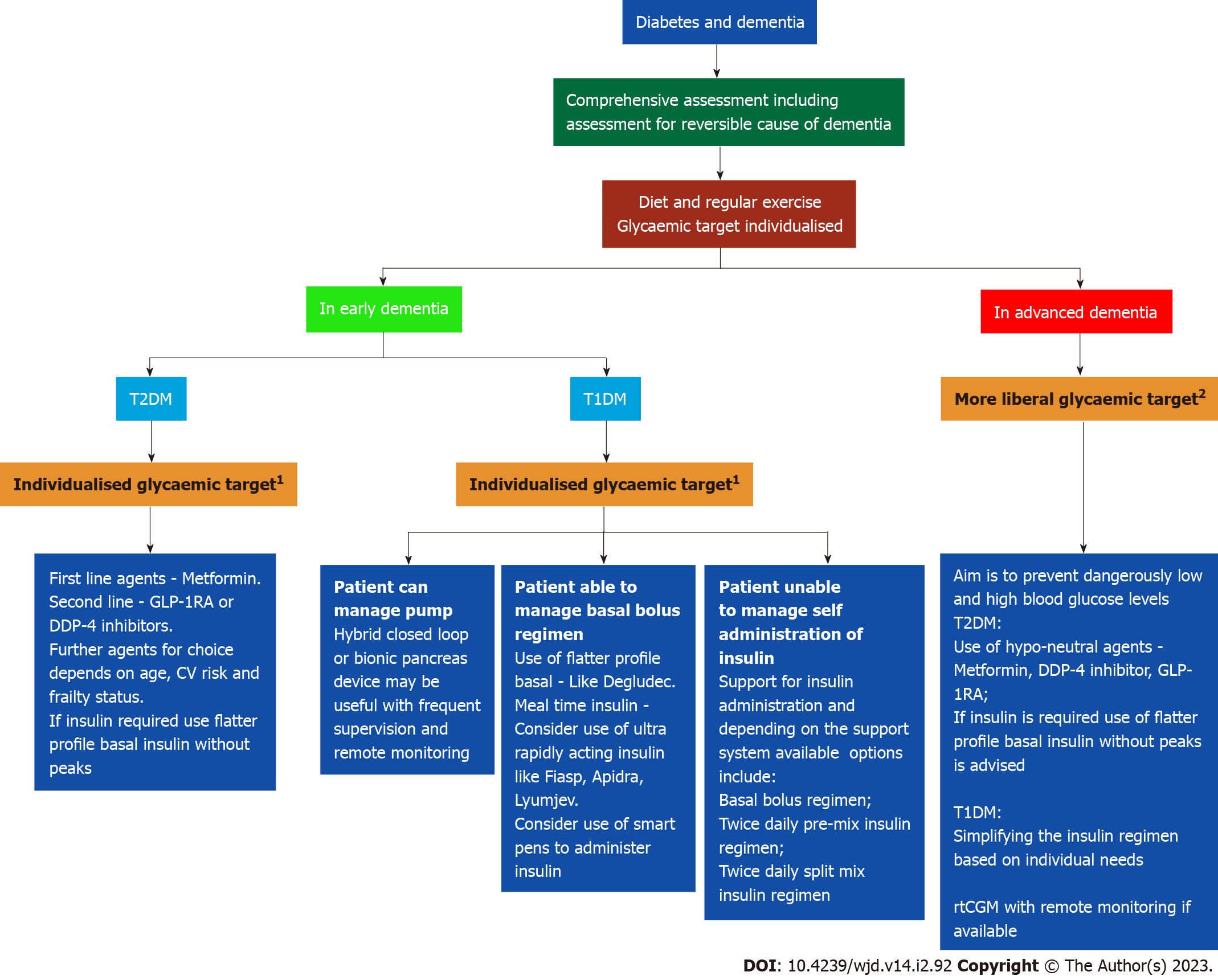
Figure 3 Practical approach to the management of patient with diabetes and dementia.
1Glycaemic target according to comorbidities to avoid marked glycaemic variability, hypo- and hyperglycaemia. 2Target glucose 7-12 mmol/L ideally (but can range between 5-16 mmol/L especially while on insulin). T1DM: Type 1 diabetes mellitus; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; GLP-1RA: Glucagon like insulinotropic peptide-receptor agonist; DPP-4: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4; CV: Cardiovascular; rtCGM: Real-time continuous glucose monitoring.
- Citation: Sebastian MJ, Khan SK, Pappachan JM, Jeeyavudeen MS. Diabetes and cognitive function: An evidence-based current perspective. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(2): 92-109
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i2/92.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i2.92