Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Nov 15, 2023; 14(11): 1693-1709
Published online Nov 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i11.1693
Published online Nov 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i11.1693
Figure 1 PRISMA flow diagram of literature search, search strategy, screening, and selection of studies.
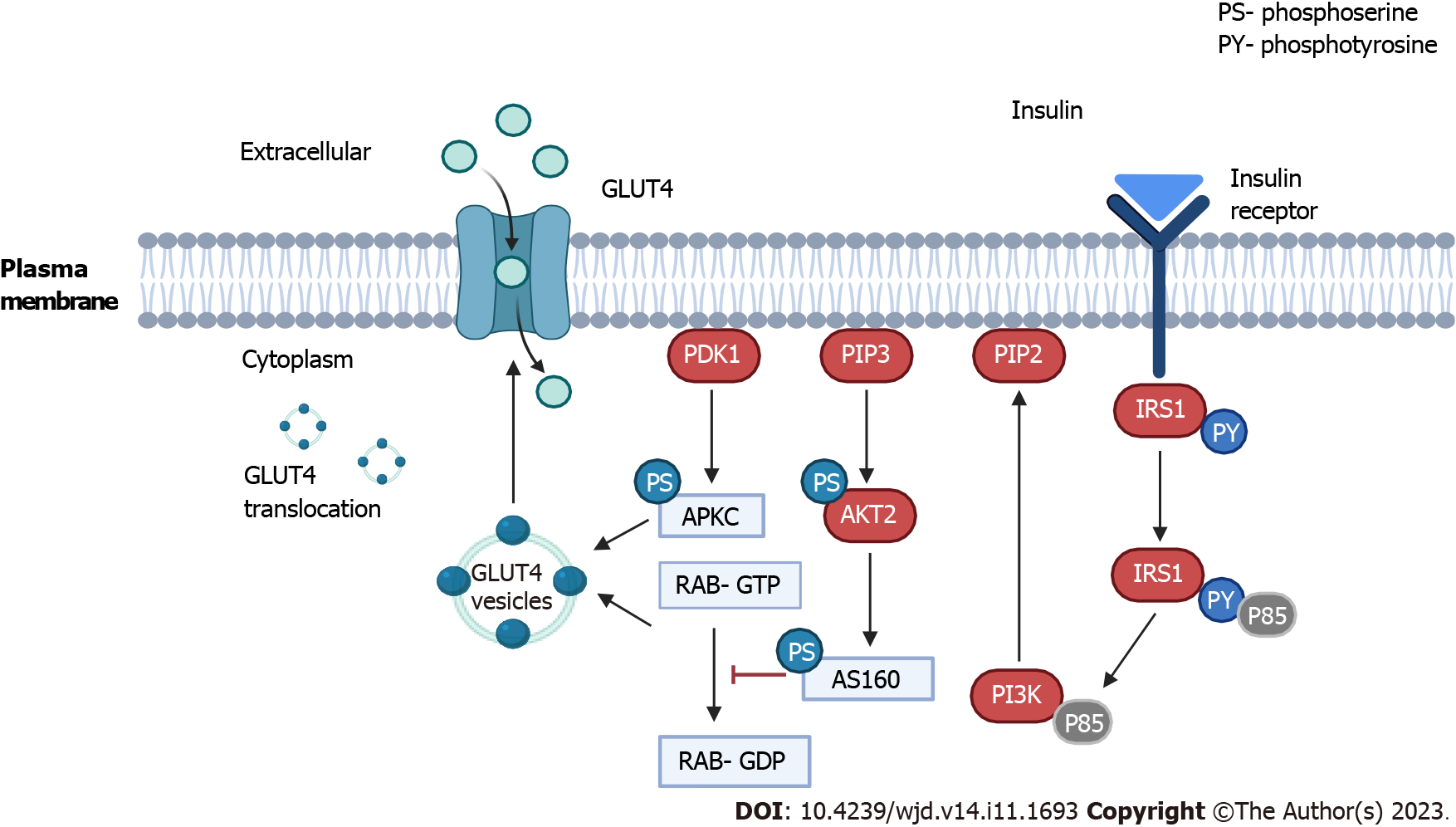
Figure 2 A brief summary of insulin signaling and subsequent glucose transporter 4 translocation that implicate the cellular and molecular mechanisms of gestational diabetes mellitus.
AKT: Protein kinase B; APKC: Atypical protein kinases C; GDP: Guanosine diphosphate; GLUT4: Glucose transporter 4; GTP: Guanosine triphosphate; IRS: Insulin receptor substrate; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase; PDK1: Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1.
Figure 3 Brief summary of leptin signaling pathways, in which leptin can bind to the leptin receptor and activate JAK2, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, and MAPK via phosphorylation of different sites on the leptin receptor and subsequent reaction to downstream molecules to exert its anorexigenic effect.
AgRP: Agouti-related peptide; AKT: Protein kinase B; IRS: Insulin receptor substrate; NPY: Neuropeptide Y; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase; POMC: Polypeptide pro-opiomelanocortin; PTP1B: Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B; SOCS3: Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
Figure 4 Brief summary of the nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway.
As suppressors, the inhibitory regulators of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) can bind to the NF-κB dimers to form a complex, which remains sequestered and inactive in the cytoplasm of non-stimulated cells. Under the status of insulin resistance, proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα) and toll-like receptors are increased to initiate the phosphorylation and degradation of inhibitory regulators of NF-κB to expose a nuclear localization sequence on the NF-κB proteins. Thus, the NF-κB dimers translocate to the nucleus to regulate gene transcription and induce inflammatory cascades. IκB: Inhibitory regulators of nuclear factor-kappa B; TLR: Toll-like receptor.
- Citation: Lim PQ, Lai YJ, Ling PY, Chen KH. Cellular and molecular overview of gestational diabetes mellitus: Is it predictable and preventable? World J Diabetes 2023; 14(11): 1693-1709
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i11/1693.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i11.1693