Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. Aug 15, 2022; 13(8): 622-642
Published online Aug 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i8.622
Published online Aug 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i8.622
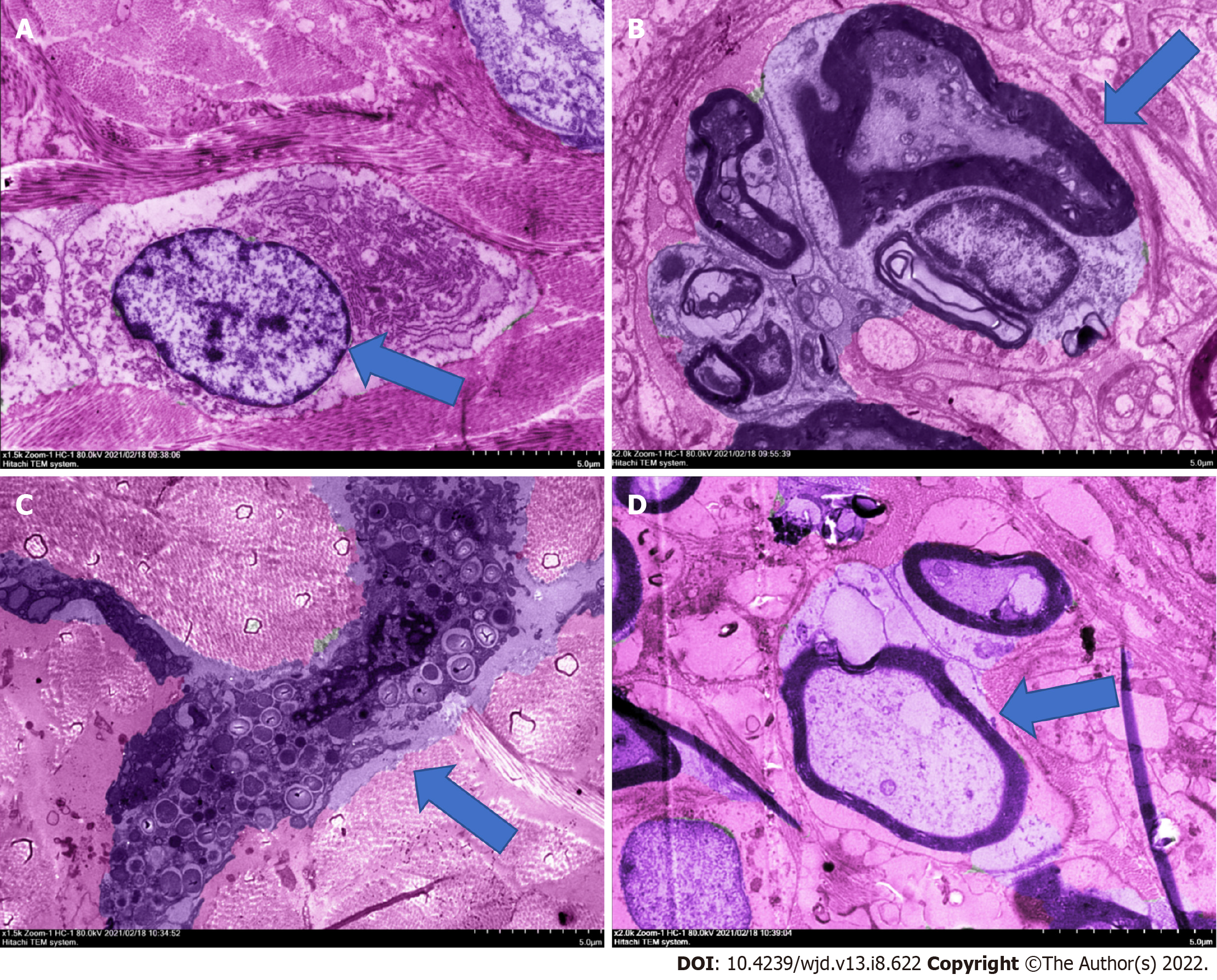
Figure 1 Hematoxylin-eosin staining electron micrograph of rat diabetic foot ulcer.
A: The fibroblasts of blank group; B: The neuritis of model group; C: Mast cells of powder group; D: Nerve cells of powder group. The mice treated with powder had good fibroblasts function, mature granulation tissue, and restored nerve cells. The thickness of the stratum corneum and the integrity of the epidermis were good, showing a good state of recovery, and intact lymphocytes would be observed, but there were a few mast cells. Ruyi Jinhuang powder promoted the healing of diabetic foot ulcers in rats by affecting fibroblasts and nerve cells.
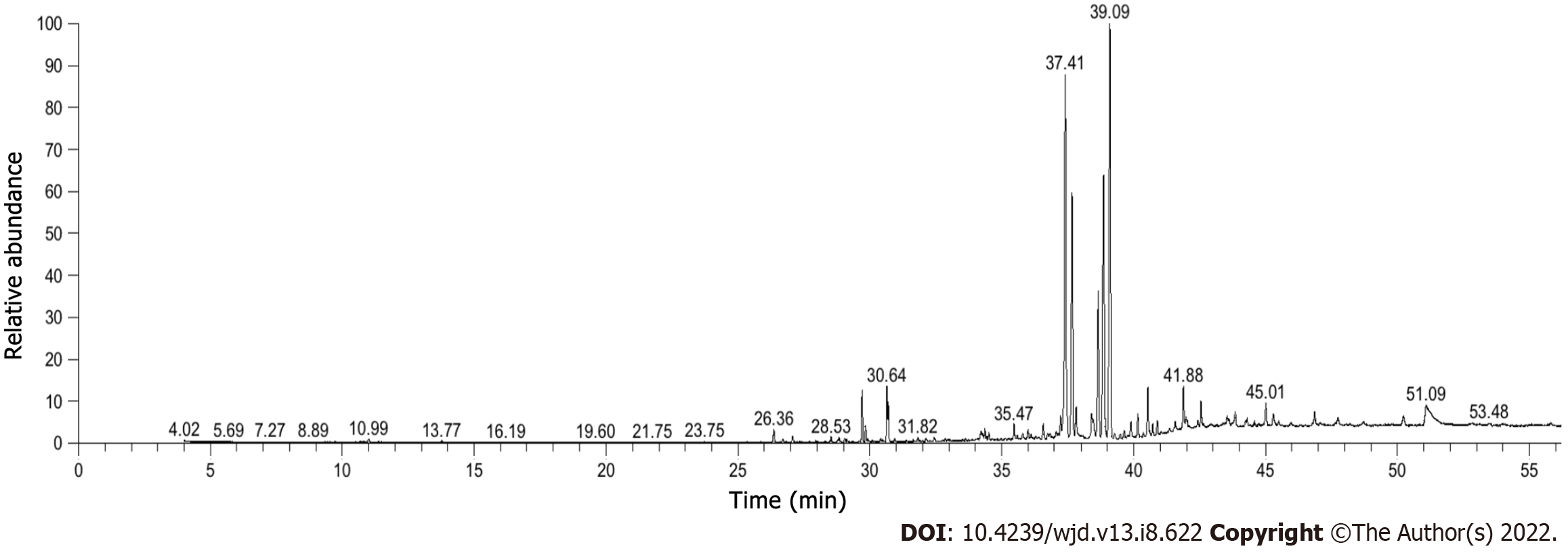
Figure 2 The total ion flow diagram of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry.
Among them, the higher components were ar-turmerone 24.33%, tumerone 20.74%, agarospirol 13.80%, β-eudesmol 9.06%, palmitic acid 2.31%, (E) atlantone 2.23%, β-quadruphellandrene 1.95%, methyloleate 1.87%, α-zingiberene 1.86%, and methylmitate 1.75%.
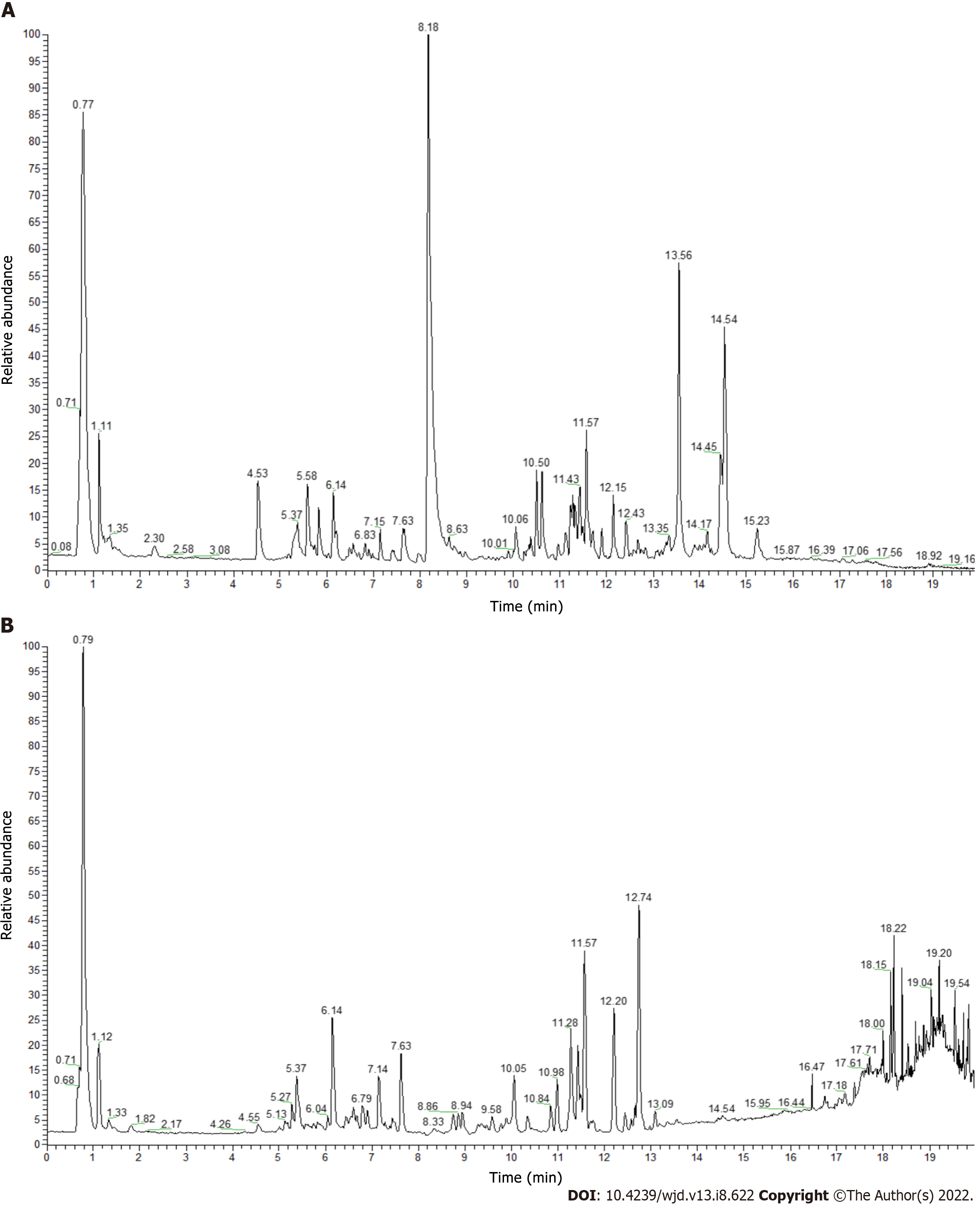
Figure 3 Ultra-performance liquid chromatography ion flow diagram of Ruyi Jinhuang powder.
A: Positive ion flow diagram; B: Negative ion flow diagram. Among them, the components with high levels were α,α-trehalose 409.04% (No. 6), curcumin 307.20% (No. 37), berberine 232.25% (No. 24), (3R,5R)-1,3,5-trihydroxy-4-{[(2E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-propenoyl]oxy}cyclohexanecarboxylic acid 201.34% (No. 16), bisdemethoxycurcumin 153.92% (No. 33), genistein 153.83% (No. 39), demethoxycurcumin 151.99% (No. 35), and citricol acid 145.29% (No. 9).
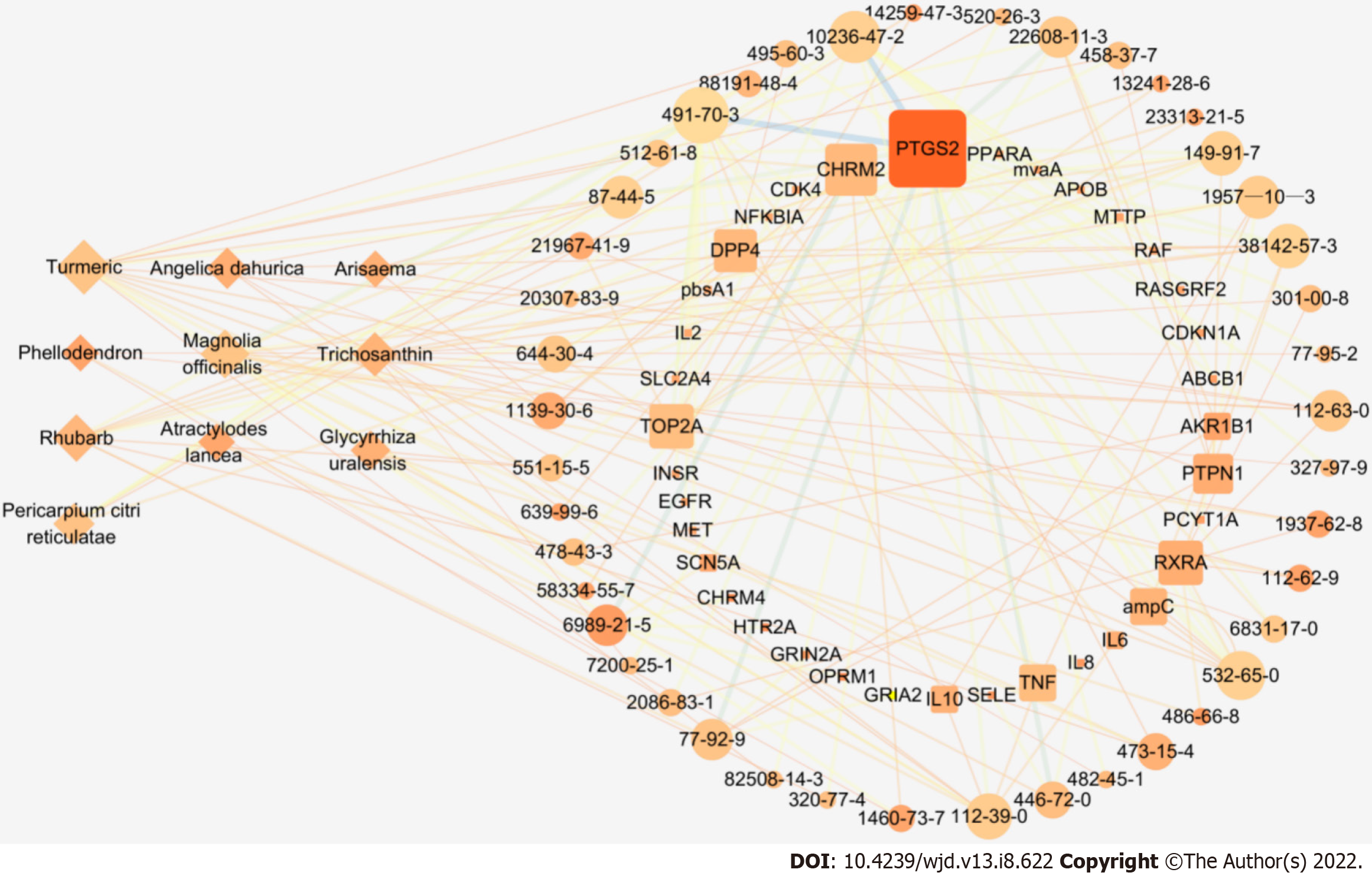
Figure 4 The “traditional Chinese medicine-ingredient-target” network of Ruyi Jinhuang powder topology diagram.
There are a total of 89 nodes and 186 edges; diamonds represent ten herbs of Ruyi Jinhuang powder, circles represent 43 related chemical components (represented in the form of CAS number), squares represent 36 target targets (represented in the form of GenecardID), nodes indicate that the greater Degree value, the darker color indicates the greater Closness value, and the thicker lines indicate the greater Betweenness value.
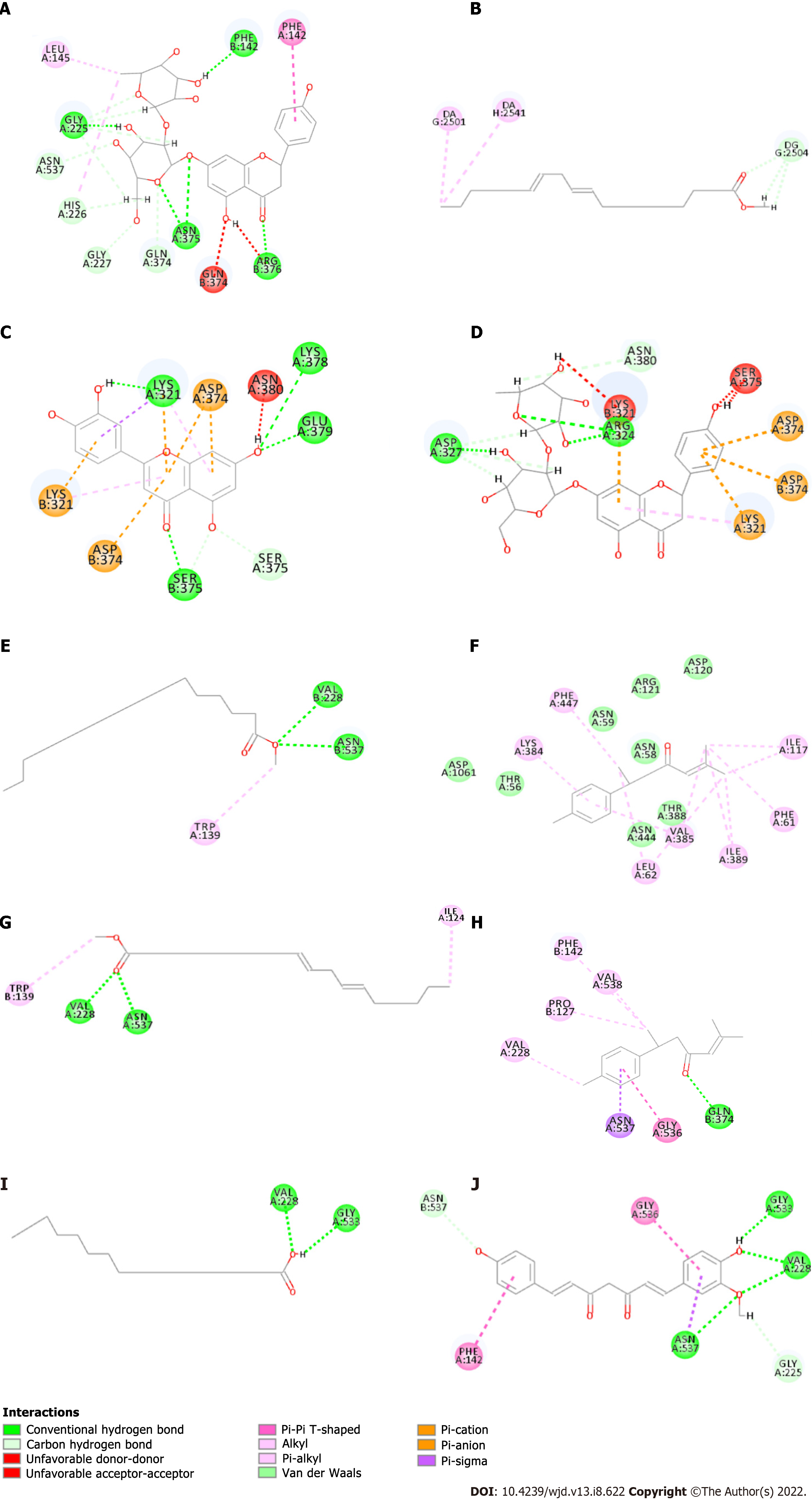
Figure 5 The virtual docking of bioactive ingredients from Ruyi Jinhuang powder for diabetic foot ulcer targets.
A and D: The virtual docking of naringin with post-transcriptionalgenesilencing (PTGS2) and Topoisomerase II alpha (TOP2A); B and G: The virtual docking of methyl linoleate with Retinoid X Receptor alpha and PTGS2; C: The docking of Luteolin and TOP2A; E: The docking of Methyl palmitate and PTGS2; F and H: The virtual docking of ar-Turmeric with Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptor M2 and PTGS2; I: The virtual docking of palmitic acid and PTGS2. J represents the virtual docking of demethoxycurcumin and PTGS2.
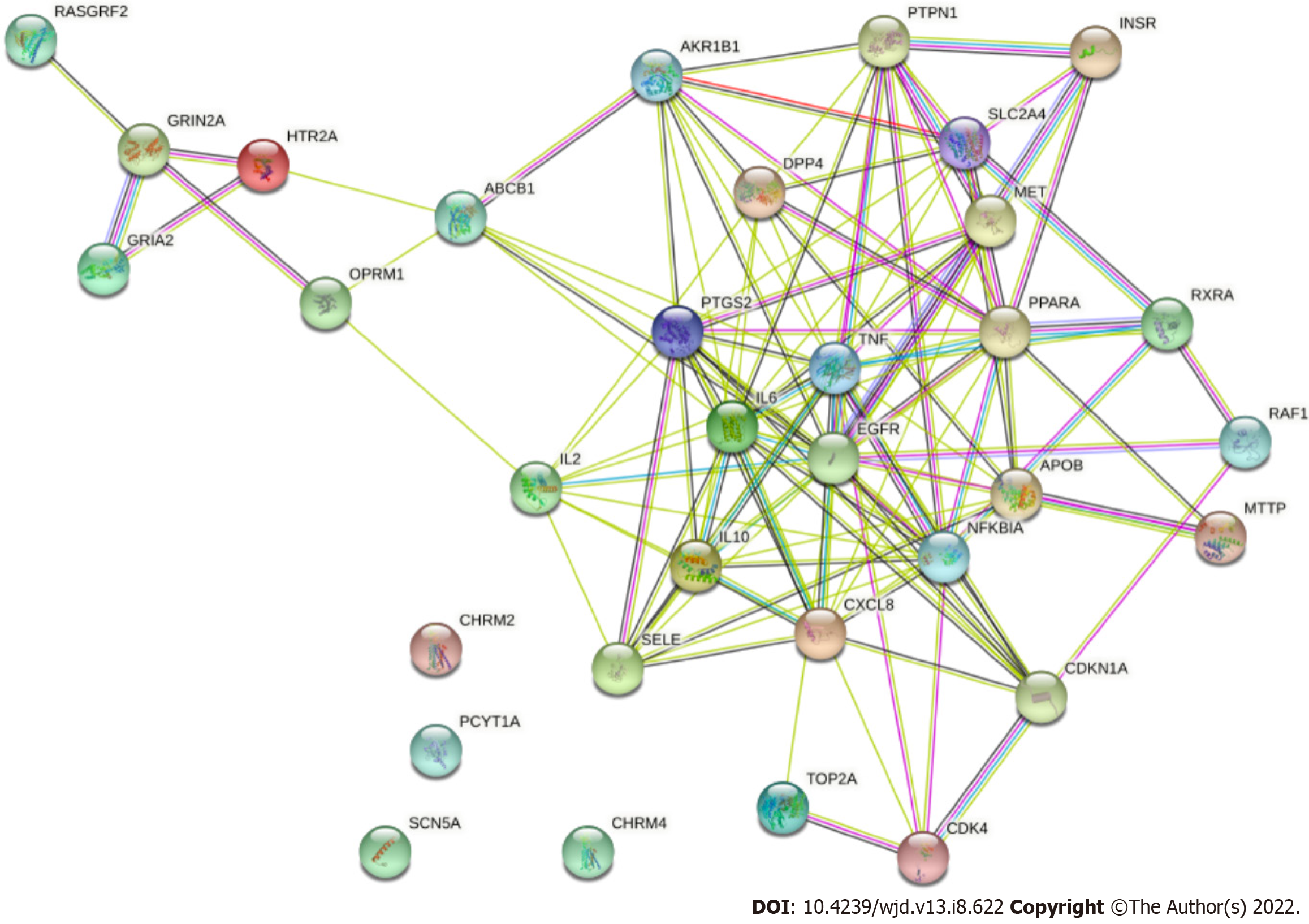
Figure 6 Interaction diagram of target proteins.
The edges with different colors represent different association relationships. Among the 36 targets, except for Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptor M2 (CHRM2), CHRM4, Choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase A and Sodium channel protein type 5 subunit alpha, the remaining 32 target proteins are closely related to each other and may participate in multiple pathways.
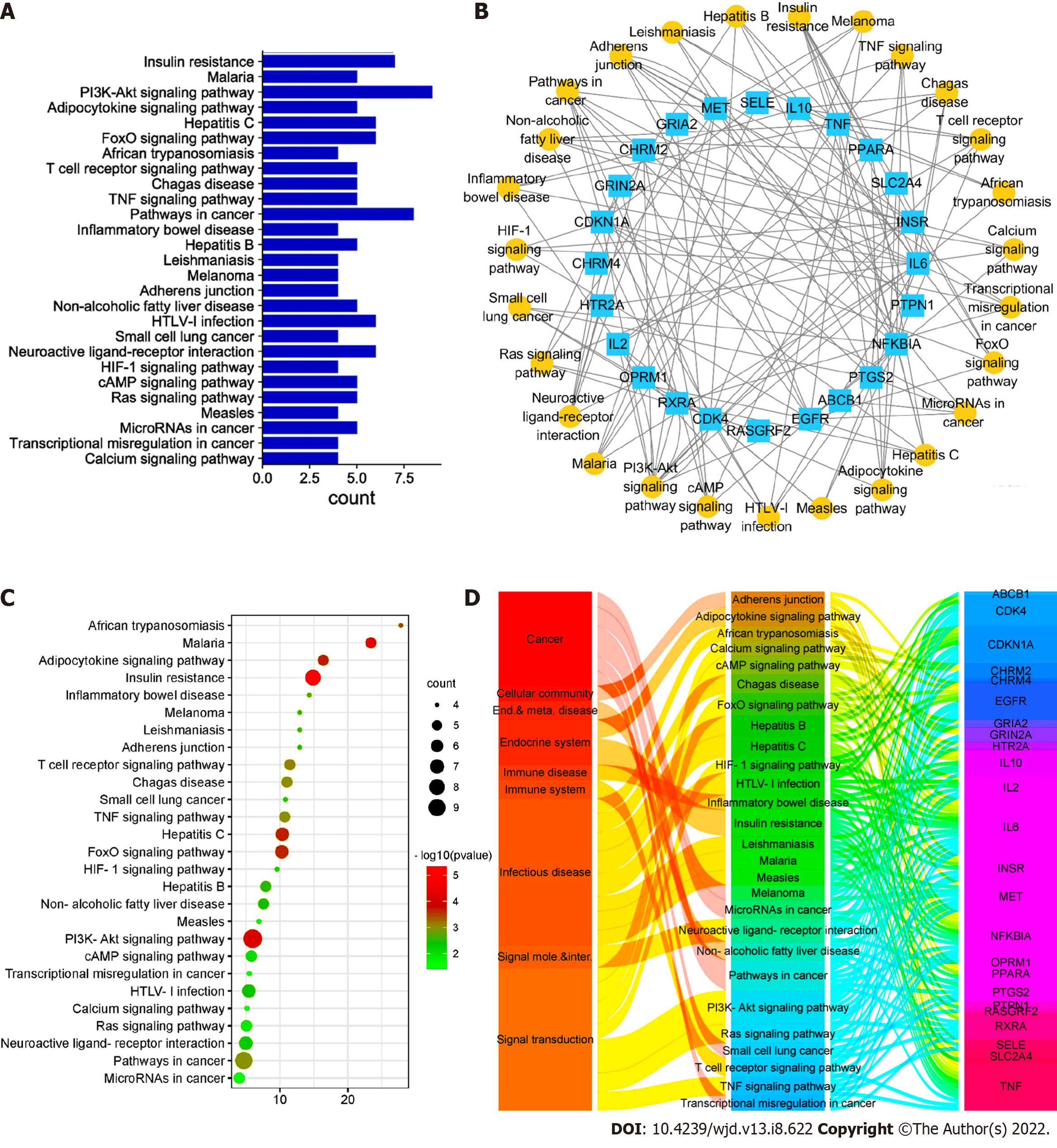
Figure 7 Target-pathway diagram of Ruyi Jinhuang powder-diabetic foot ulcer.
A: A bar graph of Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) signal pathway enrichment. The left side is the pathway name, and the right side is the number of targets contained; B: The target-path network relationship diagram. The yellow circle represents 27 pathways, and the blue square represents 36 targets; C: An enriched bubble diagram of the KEGG signaling pathway. The left side is the pathway name, and the abscissa is the fold enrichment. The bubble size corresponds to the number of targets contained, and the color category corresponds to the P value; D: The correspondence diagram of pathway categories. The first column is the ownership of the pathway, the second column is the pathway, and the third column is the target.
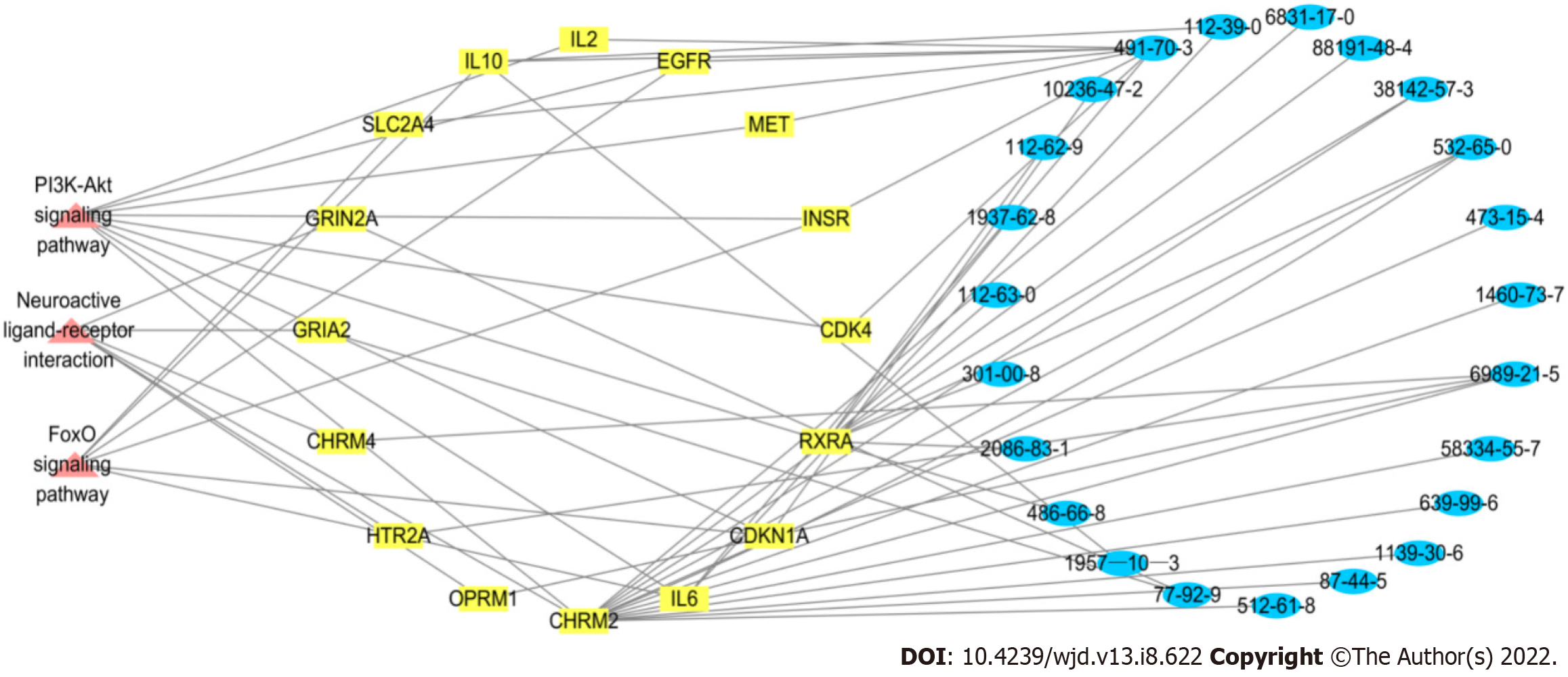
Figure 8 Critical pathway-target-component network relationship diagram of Ruyi Jinhuang powder.
Pink represents the pathway, yellow represents the target and blue represents the components. It was shown that Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptor M2 and Retinoid X Receptor alpha are common targets of the three pathways. Luteolin, atractylenone and arylodone are the key components in the three pathways.
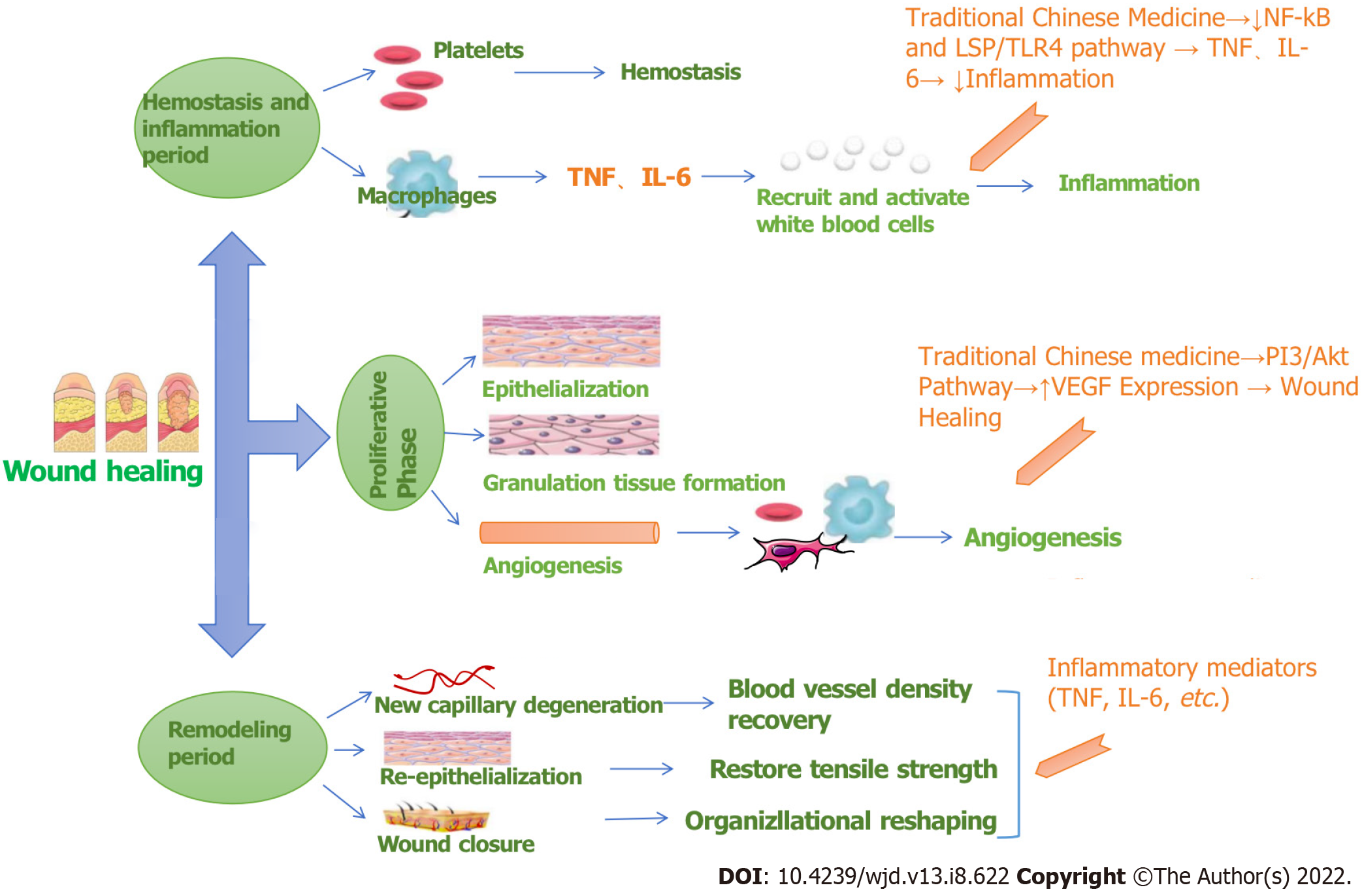
Figure 9 Wound healing mechanism diagram.
TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; NF-kB: Nuclear factor-kappaB.
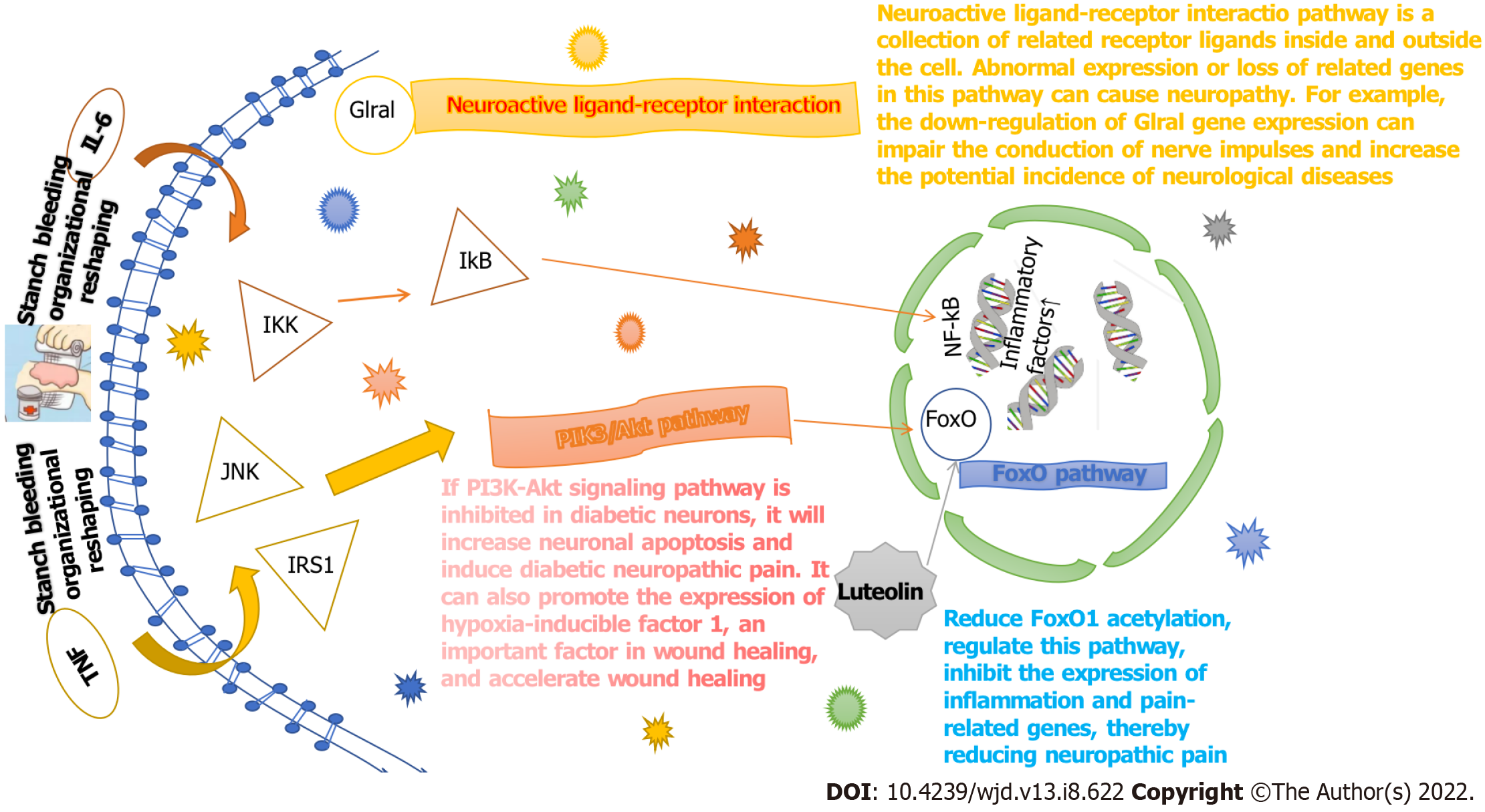
Figure 10 Target pathway mechanism of Ruyi Jinhuang powder.
TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; NF-kB: Nuclear factor-kappaB; IKK: IkappaB kinase; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; IkB: Inhibitor kB; IRS1: Insulin receptor substrate-1.
- Citation: Li XY, Zhang XT, Jiao YC, Chi H, Xiong TT, Zhang WJ, Li MN, Wang YH. In vivo evaluation and mechanism prediction of anti-diabetic foot ulcer based on component analysis of Ruyi Jinhuang powder. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(8): 622-642
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i8/622.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i8.622