Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Diabetes. Aug 15, 2021; 12(8): 1292-1303
Published online Aug 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i8.1292
Published online Aug 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i8.1292
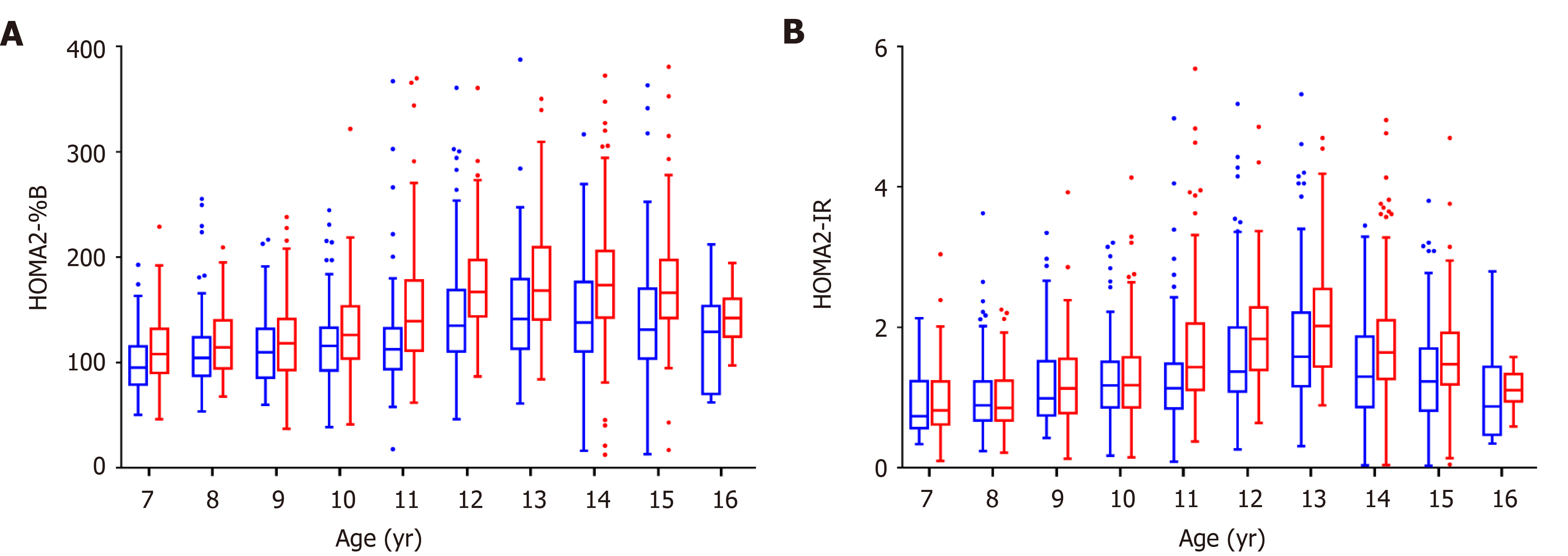
Figure 1 Islet function traits of children and adolescents in the control population by sex.
A: Beta-cell function; B: Insulin resistance. The box plots show the median (horizontal line), interquartile range (box), 5th percentiles (whiskers), 95th percentiles (whiskers), and outliers outside the 5th and 95th percentiles (dots). Red boxes represent female control population and blue boxes represent male control population. HOMA2-%B: Homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function; HOMA2-IR: Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance.
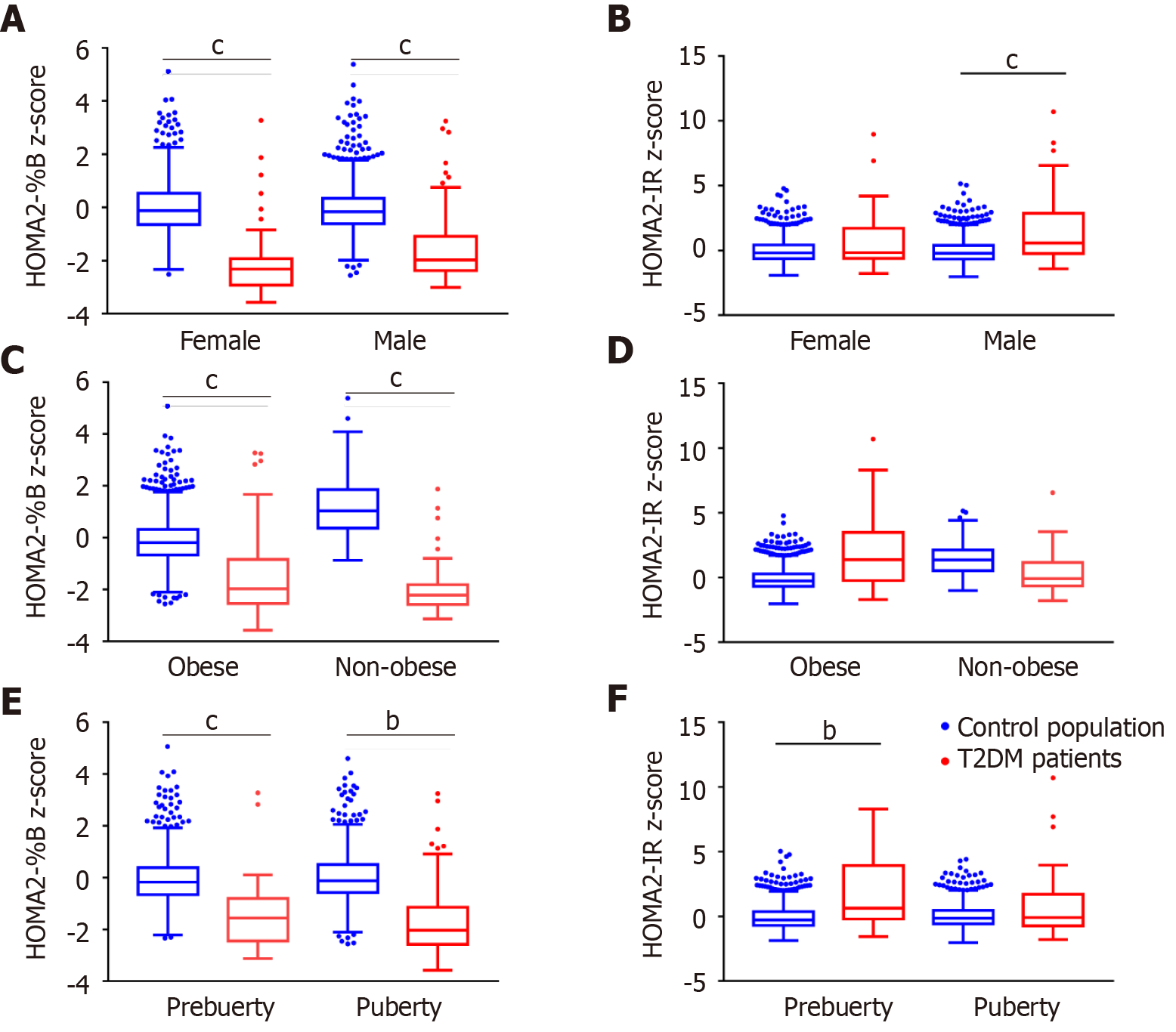
Figure 2 Differences in z-scores of homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function and insulin resistance between type 2 diabetes patients and the control population.
The box plots show the median (horizontal line), interquartile range (box), 5th percentiles (whiskers), 95th percentiles (whiskers), and outliers outside the 5th and 95th percentiles (dots). Red boxes represent type 2 diabetes patients and blue boxes represent the control population. Z-scores of the homeostasis model index were compared between the type 2 diabetes patients and the control population by sex (A and B), obesity status (C and D) and puberty status (E and F). bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; HOMA2-%B: Homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function; HOMA2-IR: Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance.
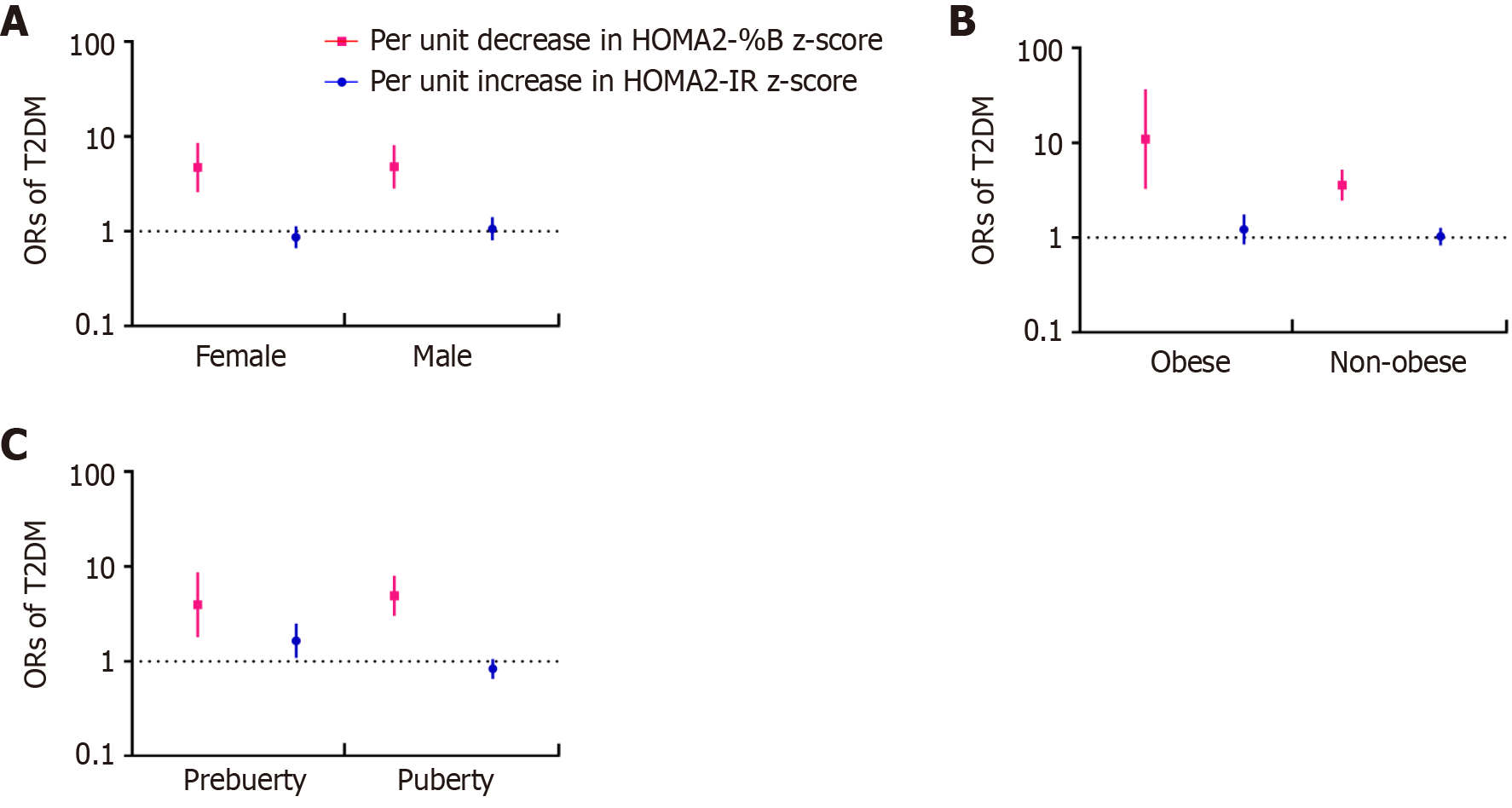
Figure 3 Association of changes in the homeostasis model index with risk of type 2 diabetes by sex, obesity status, and puberty status.
Error bars indicate 95%CIs. Red squares represent the association of per unit decrease in homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function z-score with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Blue circles represent the association of per unit increase in homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance z-score with T2DM. A: Age, Tanner stage, T2DM family history, body mass index (BMI) z-score, and lipid profile were adjusted; B: Sex, age, Tanner stage, T2DM family history, and lipid profile were adjusted; C: Sex, age, T2DM family history, BMI z-score, and lipid profile were adjusted. T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; HOMA2-%B: Homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function; HOMA2-IR: Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance.
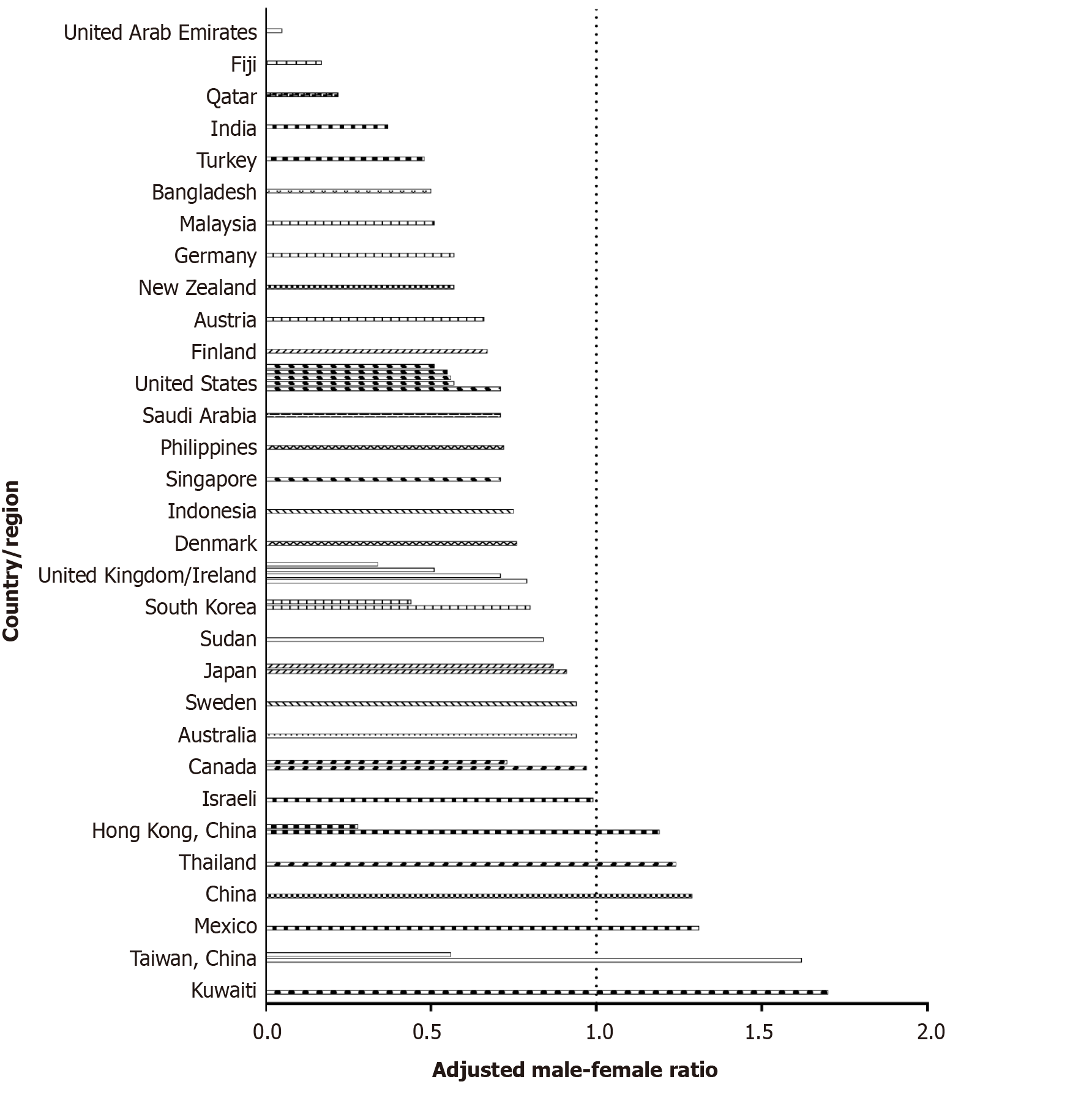
Figure 4 Adjusted male-female ratio of children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes mellitus from different countries and regions.
The adjusted male-female ratio was calculated by dividing the male-female ratio of the study population by the male-female ratio of the population of the country/region.
- Citation: Xu ZR, Du HW, Cui LW, Zheng RX, Li GM, Wei HY, Lu FY, Chen LL, Wu CS, Zhang SX, Zhang SL, Liu F, Zhang MY, Pei Z, Sun CJ, Wu J, Luo FH. Association of β-cell function and insulin resistance with pediatric type 2 diabetes among Chinese children. World J Diabetes 2021; 12(8): 1292-1303
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v12/i8/1292.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v12.i8.1292