Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2021; 12(4): 499-513
Published online Apr 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i4.499
Published online Apr 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i4.499
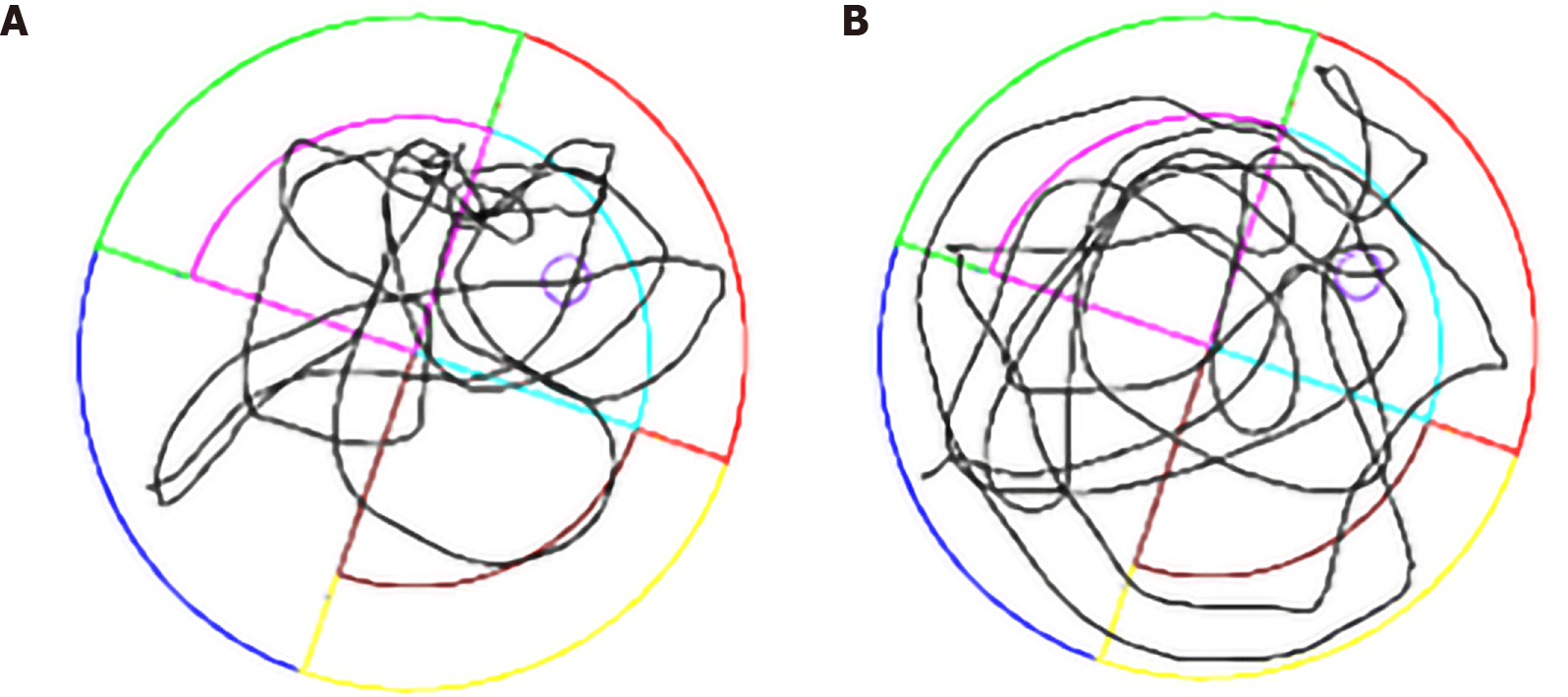
Figure 1 Representative swimming trajectories of rats.
A: Control group; B: Comparison with the control group, the swimming trajectory of the rats in the type 2 diabetes mellitus group was more chaotic.
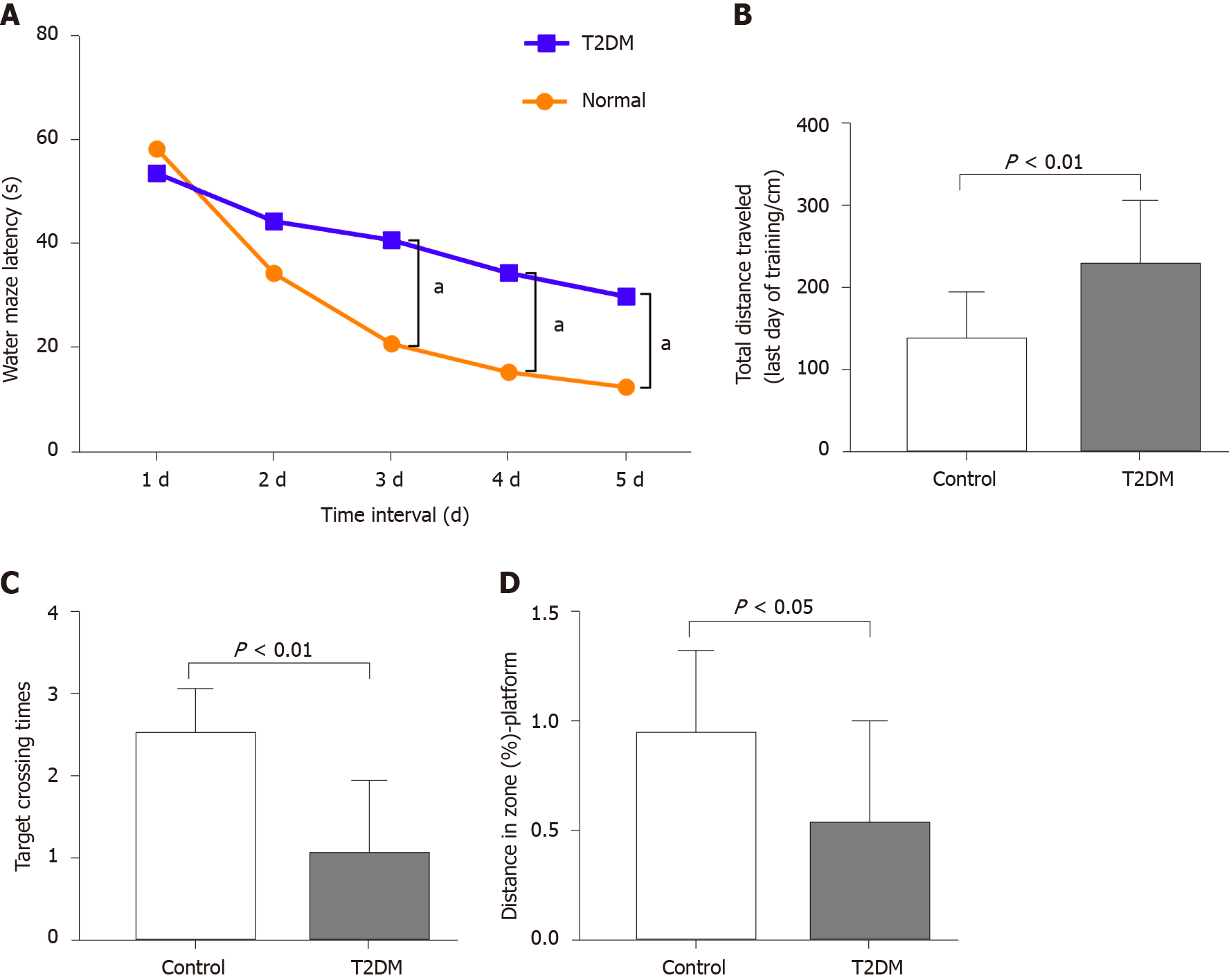
Figure 2 Results of the Morris water maze test of each group.
A: Latency time on the third, fourth, and fifth day (aP < 0.05); B: The total distance reach the platform was recorded in the hidden platform tests on the fifth day (P < 0.01); C: Number of crossing times of the target platform within 2 min (P < 0.01); D: Effects of different groups on the distance in zone-platform (P < 0.05). T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
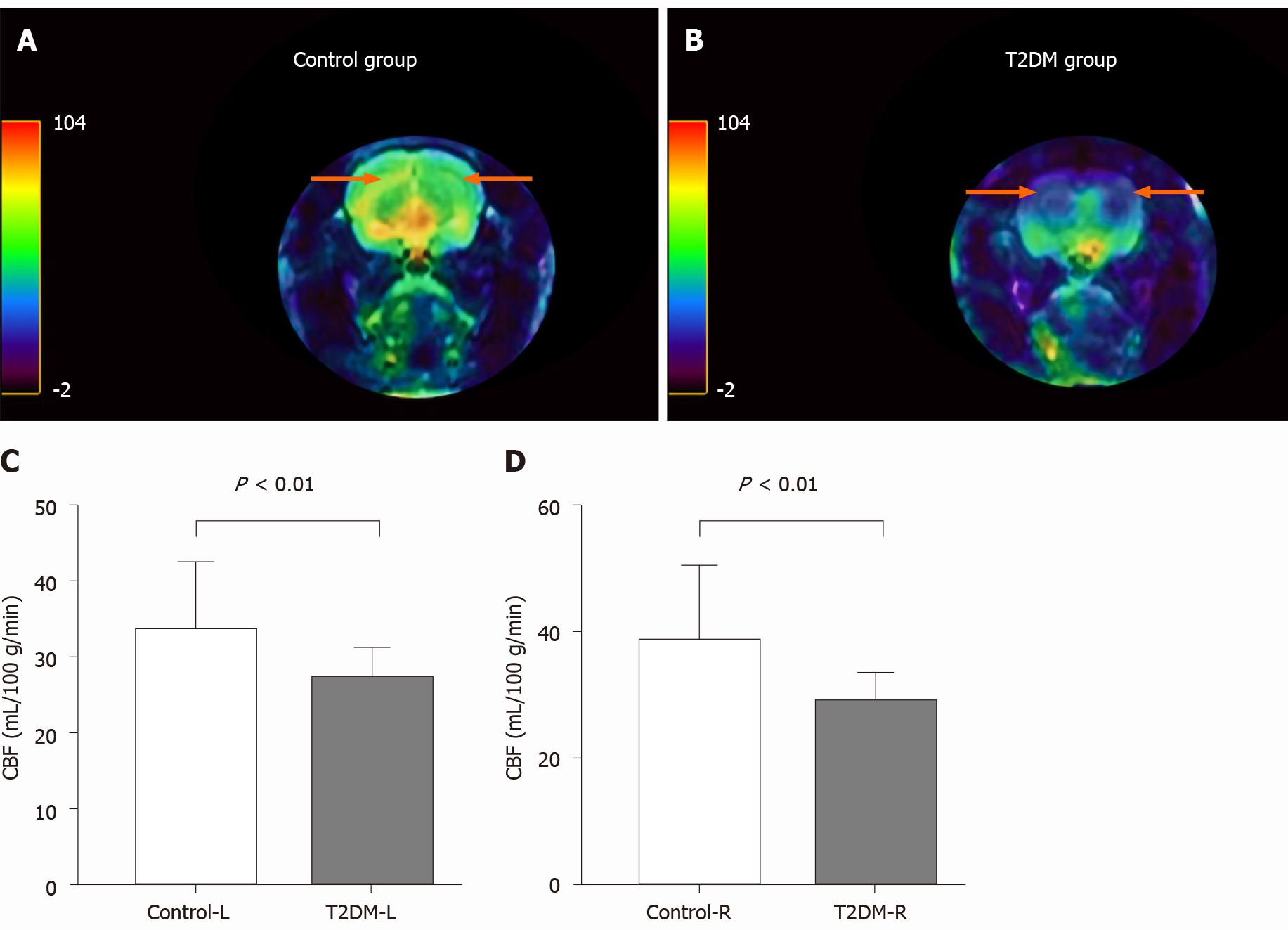
Figure 3 Comparison of cerebral blood flow in hippocampal area between type 2 diabetes mellitus group and control group.
A: Representative cerebral blood flow (CBF) images of the bilateral hippocampus area (orange arrow) in the control group; B: Representative CBF images of the bilateral hippocampus area (orange arrow) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) group; C: Significantly different CBF values between the control and T2DM groups in the left hippocampus (P < 0.01); D: Significantly different CBF between the control and T2DM groups in the right hippocampus (P < 0.01).
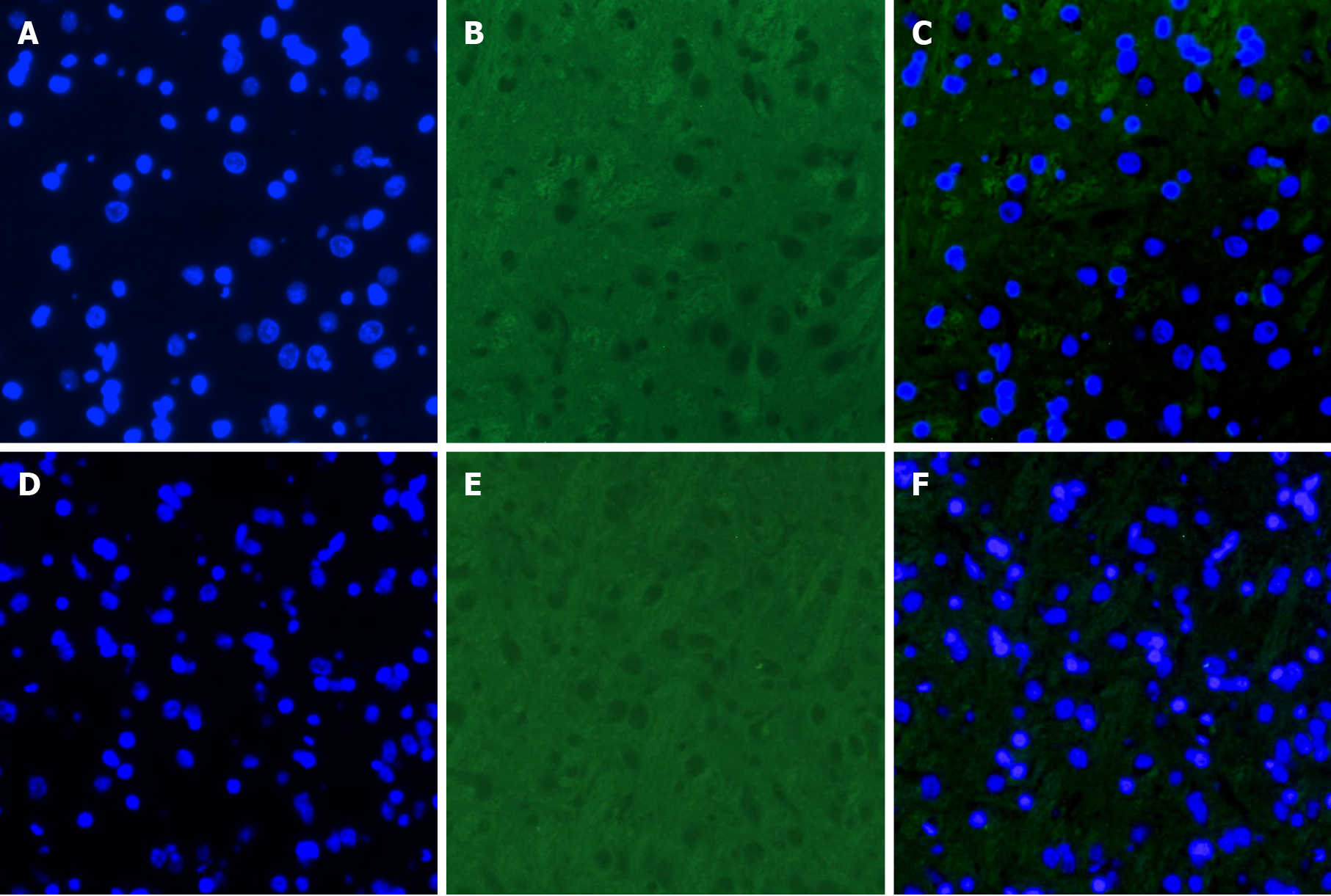
Figure 4 Images of vascular endothelial growth factor immunofluorescence staining of the hippocampus in each group.
A: Nucleus in the type 2 diabetes mellitus group (blue); B: Vascular endothelial growth factor levels in the type 2 diabetes mellitus group (green); C: Merged image for the type 2 diabetes mellitus group; D: Nucleus in the control group (blue); E: Vascular endothelial growth factor levels in the control group (green); F: Merged image for the control group. Scale bar, 100 µm.
Figure 5 Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor was lower in the type 2 diabetes mellitus group than in the control group (P < 0.
05). T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
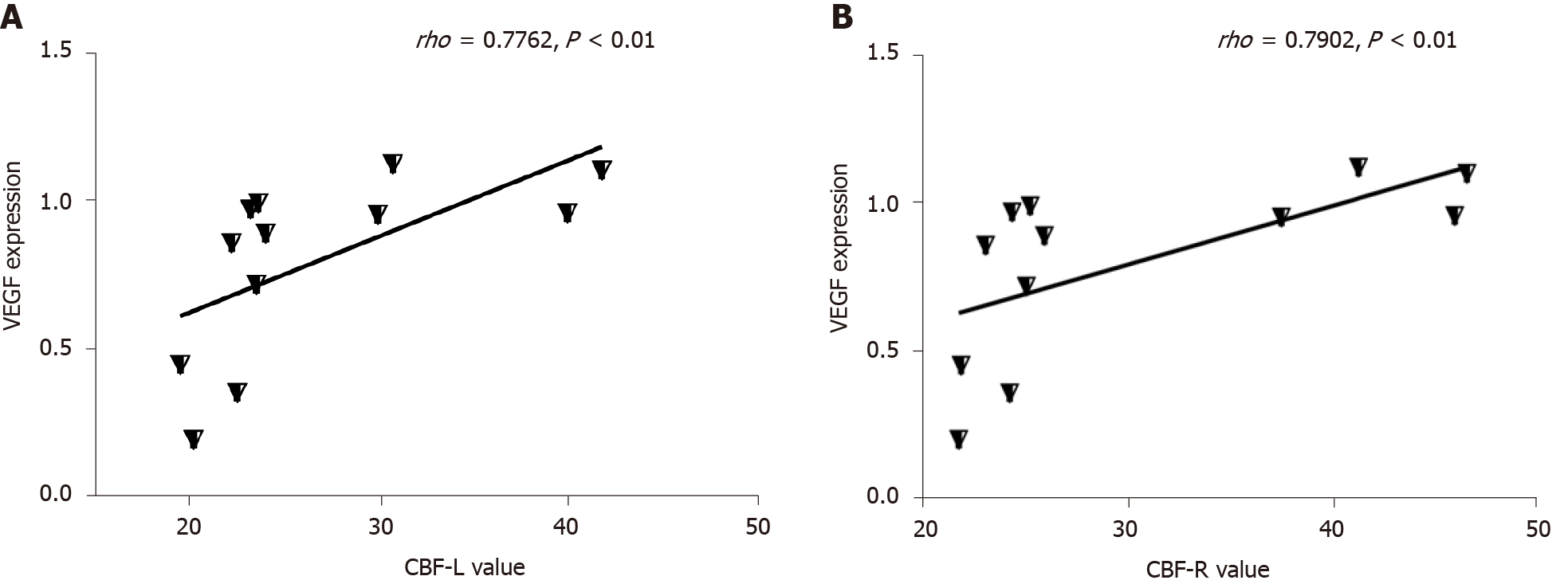
Figure 6 Good relationship was found between cerebral blood flow value and vascular endothelial growth factor expression among the type 2 diabetes mellitus group.
A: Positive correlation between left cerebral blood flow (CBF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) (rho = 0.7762, P < 0.01); B: Positive correlation between right CBF and VEGF (rho = 0.7902, P < 0.01). Unit for CBF value is mL/min/100 g. T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
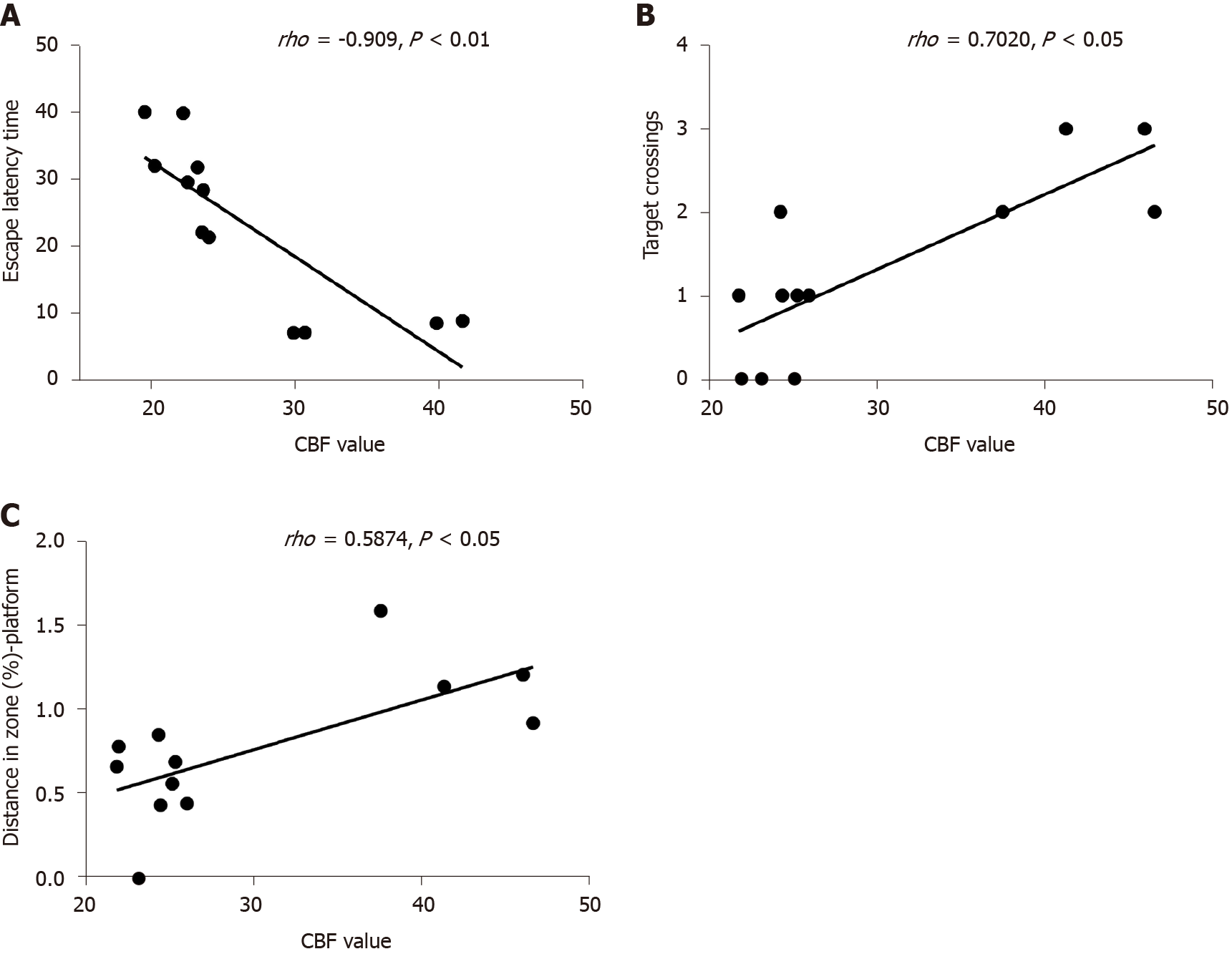
Figure 7 Correlation between cerebral blood flow value and cognitive dysfunction.
A: The escape latency negatively correlated with the cerebral blood flow (CBF) value (P < 0.01); B: The number of rats crossing the platform positively correlated with the CBF value (P < 0.05); C: A significant positive correlation was found between CBF and distance in the zone target (rho = 0.587, P < 0.05).
- Citation: Shao JW, Wang JD, He Q, Yang Y, Zou YY, Su W, Xiang ST, Li JB, Fang J. Three-dimensional-arterial spin labeling perfusion correlation with diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction and vascular endothelial growth factor in type 2 diabetes mellitus rat. World J Diabetes 2021; 12(4): 499-513
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v12/i4/499.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v12.i4.499