Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jul 25, 2015; 7(9): 860-871
Published online Jul 25, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i9.860
Published online Jul 25, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i9.860
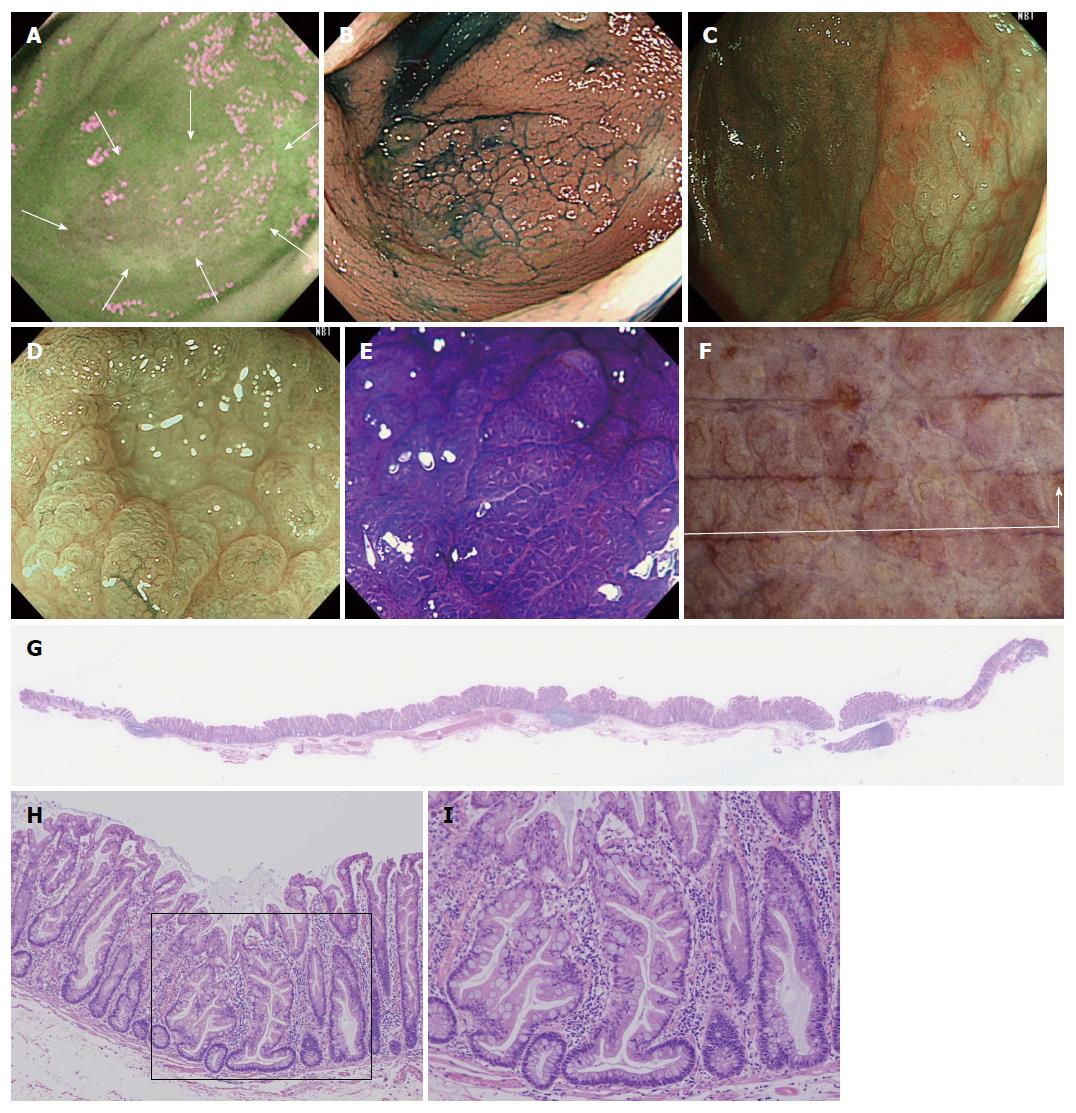
Figure 2 A case of sessile serrated adenoma/polyp without cytological dysplasia (scope: CF: FH260AZI).
A: AFI imaging. The flat elevated polyp is approximately 37 mm in diameter as is located in cecum. No change to magenta of the tumor relative to the surrounding normal mucosa can be observed (inside white arrows); B: Indigocarmine spraying endoscopic finding. The structure of the granular surface is clearly revealed by chromoendoscopy; C: NBI observation, non-magnified. A red cap is covering the surface of the tumor; D: NBI observation, magnified. Small black dots can be observed in the tumor. This finding indicates that this tumor possesses the characteristic of SSA/P; E: Crystal violet staining under magnified observation. Type II open pits (II-O pits) containing with normal type II pits are shown in the tumor; F: Stereoscopic finding. The tumor was excised by the ESD method. The tumor was cut into12 pieces; G: HE staining, whole specimen findings from section #4; H: Low power view of the HE staining findings. The tumor contains serrated glands in the mucosal layer; I: High power view of the HE staining findings. Typical histological findings for SSA/P. The crypt exhibits an “inverted T” type. NBI: Narrow band imaging; SSA/P: Sessile serrated adenoma/polyp; AFI: Auto fluorescence imaging.
- Citation: Saito S, Tajiri H, Ikegami M. Serrated polyps of the colon and rectum: Endoscopic features including image enhanced endoscopy. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2015; 7(9): 860-871
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v7/i9/860.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v7.i9.860