APPLICATIONS OF NBI-ME IN ESOPHAGEAL LESIONS
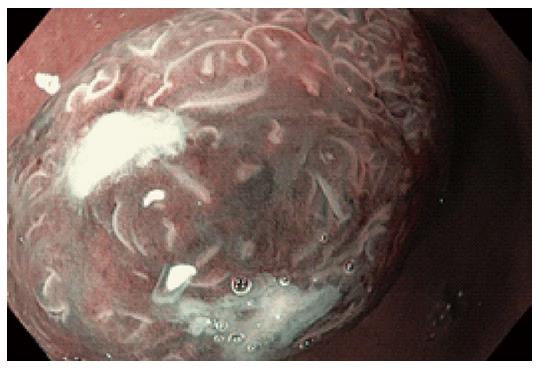
Magnifying endoscopy with NBI of normal esophagus enables visualization of capillary vessels of mucosa (intra-epithelial papillary capillary loop, IPCL) and submucosal vascularity (branching vessels) (Figure 1A). In reflux esophagitis, dilated, elongated IPCLs have been detected on NBI endoscopy[4]. The examination of the gastroesophageal (GE) junction and lower esophagus using NBI and magnification in patients with symptomatic GERD has allowed the detection of modified mucosa and vascularity: micro-erosions, an increased vascularity at the GE junction, an increased number, and dilatation and tortuosity of IPCLs[5].
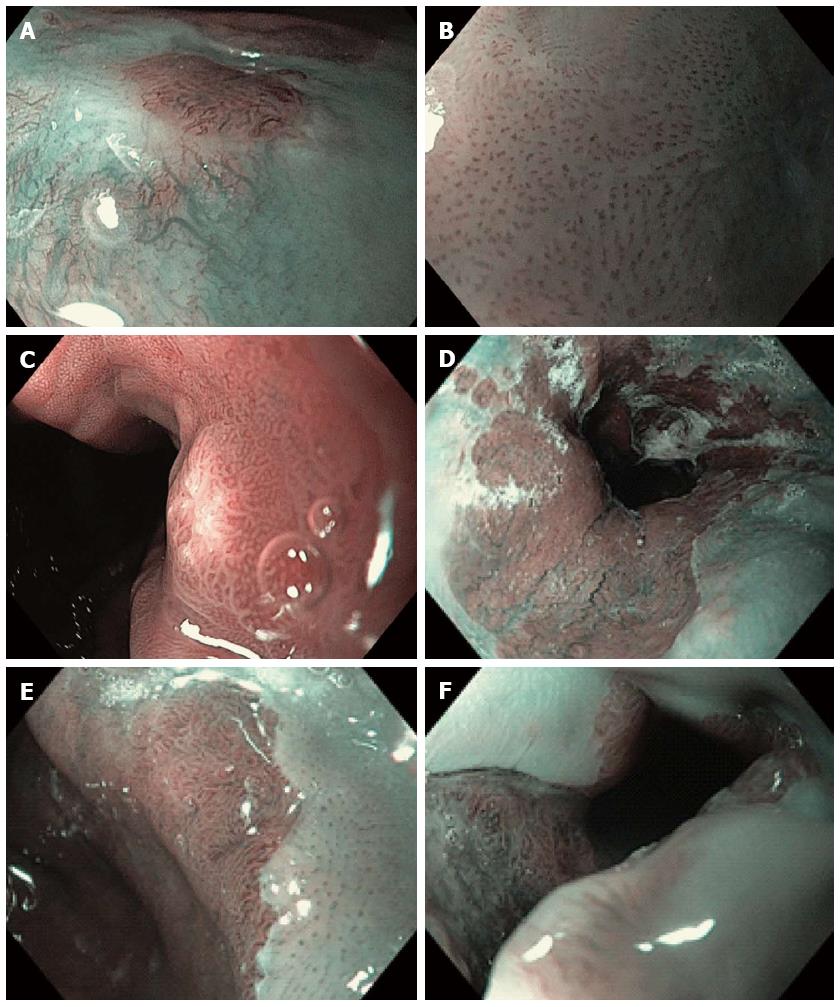
Figure 1 Narrow band imaging with magnification endoscopy images of the esophagus.
A: Normal esophageal mucosa: branching vessel network and intra-epithelial papillary capillary loop (IPCL) surrounding an island of Barrett’s esophagus (BE); B: IPCL type V1: dilatation of intra-epithelial papillary capillary loop, irregular caliber, and form variation; C: Round pits with regular microvasculature corresponding with columnar mucosa; D: Non-dysplastic BE: flat-type mucosa with regular long branching vessels; E: Non-dysplastic BE: regular villous/ridge mucosal pattern; F: Dysplastic BE: distorsion of mucosal pattern and irregular vascular pattern.
Five different IPCL patterns have been described in association with different esophageal features, from normal mucosa to modified mucosa due to inflammation, dysplasia or cancer: type I corresponds to normal mucosa (Figure 1A), type II to inflammation, type III corresponds to borderline lesions, often related to low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia, type IV (Figure 2A) and V corresponds to high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia (HGIN) or carcinoma[6]. Dilation, tortuosity, irregularity in vessels caliber and form, destruction of IPCLs and replacement with tumor vessels are vascular features associated with esophageal carcinoma. The assessment of IPCLs and submucosal vascularity allows the detection of superficial squamous carcinoma and also the prediction of the depth of invasion[7]. The utility of the estimation of submucosal invasion in clinical practice influences the decision of performing endoscopic therapy.
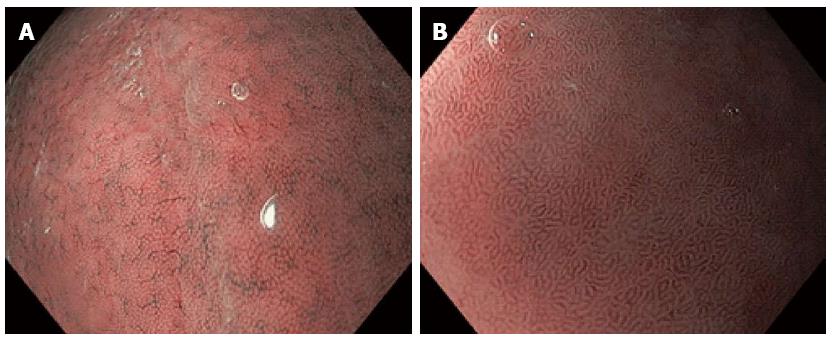
Figure 2 Narrow band imaging with magnification endoscopy images of normal gastric mucosa.
A: Round pits surrounded by the subepithelial capillary network (SECN) and collecting venules (CVs) in normal corporeal mucosa; B: Coil-shaped appearance of SECN, without the visualization of the CVs in normal antral mucosa.
Magnifying NBI endoscopic diagnosis of Barrett’s esophagus
The surveillance of Barrett’s esophagus (BE) for early detection of adenocarcinoma continues to represent a challenge in clinical practice due to the large number of random biopsies required and to sampling errors. New endoscopic techniques improve the visualization of Barrett mucosa and improve the detection of dysplasia and early cancer by targeting biopsies from areas with modified pattern. Numerous reports have described mucosal and vascular features displayed in BE.
Chromoendoscopy and magnifying endoscopy has been used for better detection of specialized intestinal metaplasia (SIM) and early neoplasia in BE[8-10]. However, the dye application alters the visualization of vascular patterns. Additional time is required for better fixation of the dye on the tissue surface, followed by repeated water rinses and suctions to remove excess dye. NBI technique has the advantage of identification of both vascular and mucosal patterns without dye application, is easier to perform, and adds useful information about the mucosal morphology.
Different mucosal patterns have been described that can be detected at the GE junction during magnifying NBI endoscopy: rounded, circular (Figure 1C) or oval crypts (columnar mucosa), flat (Figure 1D), villous (Figure 1E), and gyrus-shaped patterns [intestinal metaplasia (IM)][11]. Apart from these regular patterns, the identification of an irregular, disrupted mucosal pattern raises the suspicion of a dysplastic/cancerous lesion. The second element that should be evaluated is the vascular pattern: the presence of a regular pattern with normal-appearing vessels or an irregular pattern with abnormal blood vessels. In non-dysplastic BE a regular vascular pattern is associated with the regular villous/gyrus-like pattern or with flat-type mucosa (Figure 1D, E). Areas presenting an irregular mucosal pattern or abnormal blood vessels (irregular, dilated, corkscrew type vessels) are suspicious for the presence of high-grade dysplasia (HGD) or cancer (Figure 1F).
The significance of the detection of irregular mucosal and vascular patterns and abnormal blood vessels for the diagnosis of HGIN by using NBI-ME was previous outlined by Kara et al[12] (94% sensitivity, 76% specificity, 64% PPV and 98% NPV for HGIN). Other studies have reported the sensitivity, specificity and positive predictive value (PPV) of ridge/villous pattern for diagnosis of IM (93.5%, 86.7% and 94.7% respectively) and the sensitivity, specificity and PPV of irregular/distorted pattern for HGD (100%, 98.7% and 95.3% respectively), but also have emphasized the inability to differentiate areas of IM from areas with low-grade dysplasia[13].
The reproducibility and repeatability of a simplified classification of mucosal and vascular patterns visualized in BE by experts and non-NBI-experts endoscopists was reported by Singh et al[14]. They have described four different patterns on NBI-ME: type A- round pits with regular microvasculature (Figure 1C) corresponded with columnar mucosa without IM (PPV and NPV were 100% and 97% respectively); type B- villous/ridge pits with regular microvasculature and type C-absent pits with regular microvasculature (Figure 1D, E) corresponded with IM (PPV and NPV were 88% and 91% respectively); type D-distorted pits with irregular microvasculature (Figure 1F) was associated with HGD (PPV and NPV were 81% and 99% respectively)[14].
Due to the multiplicity of classification systems, the clinical utility of NBI-ME in the assessment of BE is still under evaluation. In a study performed by Alvarez Herrero et al[15], a simplified classification of mucosal and vascular patterns (regular patterns in nondysplastic BE, irregular patterns in dysplastic BE) has shown a moderate interobserver agreement and a disappointing rate for correctly identifying HGIN/early cancer (67% and 71% of the images with HGIN/early cancer were correctly identified). The limitations of the available classification systems concerning accuracy in identification of SIM and dysplasia, as well as limited interobserver agreement, are arguments that the surveillance protocol of BE based on random 4-quadrant biopsies and biopsies from suspicious areas, cannot be yet replaced[16]. A targeted NBI-ME examination of suspicious areas previously identified on white light endoscopy (WLE), such as mucosal irregularities, depressed areas, ulcerations, or nodules, is useful for the delineation of modified mucosal or vascular patterns and for the guidance of directed biopsies.
NBI-ME has also successfully been used as an adjunct for therapeutic procedures. The method has proved to be helpful in targeting and delineating areas with early Barrett’s neoplasia, previously identified by high-resolution endoscopy and autofluorescence imaging, for endoscopic mucosal resection[17]. The trimodal imaging evaluation, which combines high-resolution WLE, autofluorescence, and NBI could be an alternative to dye-spraying techniques for the detection and the lateral spread assessment of early cancer before endoscopic therapy.
Applications of NBI-ME in gastric lesions
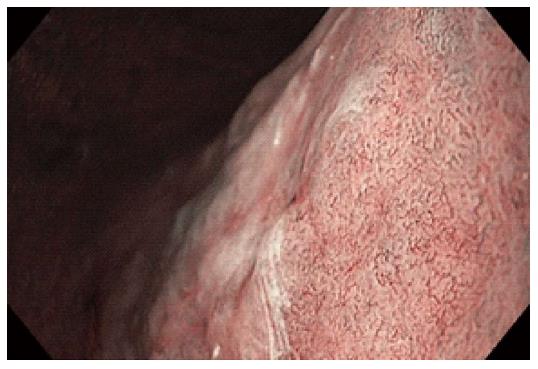
The normal gastric mucosa displays particular features in the corpus and antrum on NBI-ME. A regular arrangement of small, round pits surrounded by the subepithelial capillary network (SECN) with a honeycomb appearance and the collecting venules (CVs) are detected in the gastric body (Figure 2A). A coil-shaped appearance of SECN, without the detection of the CVs are specific features associated with normal antral mucosa (Figure 2B). Modified patterns should be evaluated by comparison with these normal mucosal and vascular features. The detection of modified patterns due to inflammatory and atrophic changes of the corporeal mucosa and the interpretation of such endoscopic features could represent a challenge in clinical practice: the enlargement of pits with irregular SECNs in Helicobacter pylori gastritis (Figure 3A), or the detection of oval or tubulovillous pits with coiled or wavy vessels in IM (Figure 3B) and atrophic gastritis (AG)[18]. Targeted biopsies from areas with modified patterns are mandatory for a proper evaluation of the lesions.
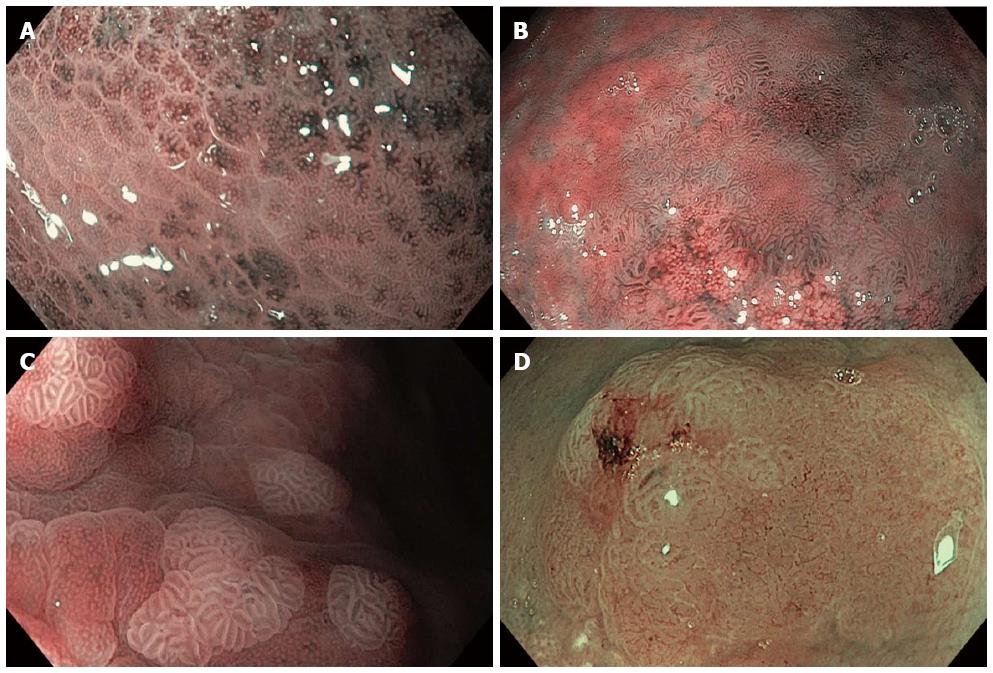
Figure 3 Narrow band imaging with magnification endoscopy images of gastric lesions.
A: Helicobacter pylori gastritis: enlargement of pits, variable vascular density (alternation of lighter and darker areas); B: Extensive areas of intestinal metaplasia (tubulovillous mucosal pattern) and remnant normal gastric body mucosa (small regular and circular pits); C: Areas of intestinal metaplasia: blue whitish slightly raised areas (the light blue crest sign) with regular, tubulovillous mucosal pattern; D: Dysplasia: area with architectural loss of mucosal pattern and irregular vascular pattern.
The detection of blue whitish slightly raised areas, described as the “light blue crest sign” (Figure 3C) was reported to have a good sensitivity (89%), specificity (93%) and accuracy (91%) for the diagnosis of IM[19]. This sign could represent a marker for global gastric atrophy[20]. The detection of extensive and severe atrophy and IM and the detection of dysplasia are important steps in the identification of patients at risk for gastric neoplasia. According to European guidelines, these patients should be included in a surveillance program[21]. Targeted surveillance and directed biopsies guided by NBI-ME for IM and AG mapping could represent a better alternative to a surveillance protocol based on randomly taken biopsies.
Different mucosal and vascular patterns have been reported in association with normal gastric mucosa, preneoplastic and neoplastic gastric lesions. Pimentel-Nunes et al have proposed a classification system for the diagnosis of gastric preneoplastic lesions: pattern A (regular and circular mucosal patterns with regular vascular patterns - Figure 2A) corresponds with normal mucosa (accuracy 83%; 95%CI: 75%-90%), pattern B (regular, ridge or tubulovillous mucosal patterns with regular vessels - Figure 3C) corresponds with IM (accuracy 84%; 95%CI: 77%-91%), and pattern C (absent or irregular mucosal patterns with irregular vascular patterns - Figure 3D) corresponds with dysplasia (accuracy 95%; 95%CI: 90%-99%)[22].
Magnifying NBI endoscopic diagnosis of early gastric cancer
Diagnostic accuracy for early gastric cancer was improved by the development of NBI-ME, which allows the detection of subtle mucosal changes. The estimation of the histology and the delineation of the lateral spread of gastric cancer are possible during endoscopic examination[23-25]. An estimation of the deep of invasion of early gastric cancer was also achieved by NBI endoscopy. The superiority of NBI-ME over WLE for the diagnosis of superficial gastric lesions in a population at high risk of gastric cancer was demonstrated in clinical studies[26].
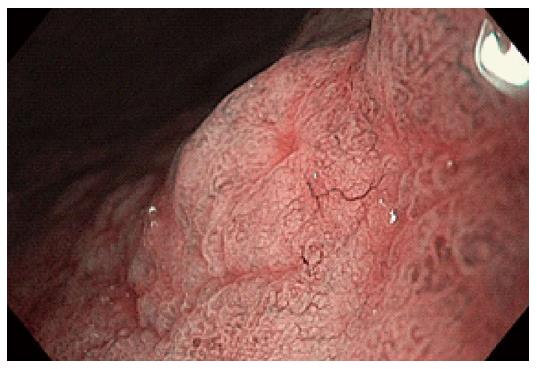
Three criteria have been use by Kaise et al[27] for the detection of superficial gastric cancer: the disappearance of fine mucosal structure, microvascular dilation and heterogeneity in shape of vessels. The sensitivity of these criteria for the diagnosis of cancer was 92.9%, with 94.7% specificity[26]. Yao et al[28] have used a “VS classification”, based on the assessment of microvascular pattern (V) and microsurface pattern (S). They have identified the irregular microvascular pattern and/or the irregular microsurface pattern and the demarcation line as hallmarks of early gastric cancer (Figure 4). The delineation of the lateral margins of differentiated carcinoma prior to endoscopic resection has been performed using NBI-ME[28].
Figure 4 Superficial gastric cancer: Disappearance of microsurface pattern, irregular microvascular pattern with a demarcation line.
Yamada et al[29] have recently reported that the demarcation (DL) line and an irregular microvascular pattern (IMVP) on NBI-ME represent reliable criteria for the diagnosis of small, depressed, early gastric cancer. An irregular margin and a spiny depressed area on conventional WLE represent diagnostic criteria for depressed cancer. The diagnostic accuracy increases by using both methods: the initial detection of a depressed lesion on conventional WLE, followed by magnifying NBI assessment for the presence of DL and IMVP[29]. The combination of conventional WLE with NBI-ME in clinical practice has proved to enhance diagnosis accuracy of small, depressed gastric mucosal cancer (96.6% accuracy, 95.0% sensitivity, and 96.8% specificity)[30].
Regarding the application of NBI-ME in the assessment of elevated gastric lesions, a regular microsurface and microvasculature was detected in adenomas, while the microvascular changes (irregular caliber, meandering, heterogeneity) and the line of demarcation were associated with carcinoma[31]. There are situations when an estimation of the microvascular pattern is difficult, due to a white opaque substance (WOS) within the neoplastic epithelium, which obscures the microvessels (Figure 5). Yao et al[32] have identified the WOS in 0-IIa type neoplasms, and more frequently in adenomas (78%) than in carcinomas (43%). A regular distribution of WOS was detected within adenomas, whereas an irregular distribution was found in carcinomas. Besides the assessment of the microvascular pattern, morphologic analysis of the WOS could represent a valuable optical sign discriminating between adenoma and carcinoma[32].
Figure 5 Gastric adenoma: White opaque substance with regular distribution obscures the subepithelial microvascular pattern.
The demarcation line could also be identified in focal gastritis, but in this situation the regular mucosal and vascular patterns differentiate the lesion from early cancer. Doubtful lesions are better sent for pathologic assessment after endoscopic submucosal dissection.
Distinct vascular patterns are related to different histologic types of cancer. The fine network pattern, appearing as mesh microvessels, correlates with well-differentiated adenocarcinoma, whereas the corkscrew pattern, with isolated and tortuous microvessels, corresponds with undifferentiated adenocarcinoma[33]. Li et al[34] have reported a good sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of NBI-ME in distinguishing between differentiated from undifferentiated adenocarcinoma (92.3%, 89.7%, and 90.4%, respectively) and in differentiation between cancerous and noncancerous lesions (97.3%, 84.4% and 90.2% respectively). The authors have described three distinct patterns associated with different type of gastric lesions and with the depth of cancer invasion. A regular surface and microvascular pattern (type A pattern) corresponds with noncancerous lesions. The type B pattern, consisting of thickened, dilated, irregular vessels, with an asymmetrical distribution, and an irregular surface pattern, corresponds with differentiated adenocarcinoma and intramucosal/superficially invasive cancers. The type C pattern, consisting of the disappearance of the surface pattern, with markedly distorted, sparse, isolated microvessels, or with avascular areas, is indicative of undifferentiated adenocarcinoma or differentiated cancer with deep submucosal invasion[34].
In a recent report, Yagi et al[35] have also emphasized the usefulness of NBI-ME in the evaluation of the depth of submucosal invasion of the carcinoma. They have described the blurry mucosal pattern (BMP) and the irregular mesh vascular pattern (IMP) as endoscopic features suggestive of submucosal invasion of gastric differentiated adenocarcinoma (Figure 6). A mucosal cancer could be estimated by correlating the absence of these NBI-ME criteria (BMP, IMP) with the absence of conventional endoscopic criteria for invasion (extremely uneven or depression, nodularity at the verge, obvious hardening of the wall and unusual elevated non-cancerous mucosa on the verge)[35]. When the margins of early gastric cancer are difficult to identify using chromoendoscopy, NBI-ME represents a reliable alternative to delineate the horizontal extent of the differentiated carcinoma. The difficulty in determining the real extent of undifferentiated cancer still remains a problem, and a proper evaluation by biopsies from the apparently normal mucosa around the lesion is recommended in these situations[36].
Figure 6 Gastric cancer with submucosal invasion: Blurry mucosal pattern and irregular mesh vascular pattern.
Applications of NBI-ME in colonic lesions
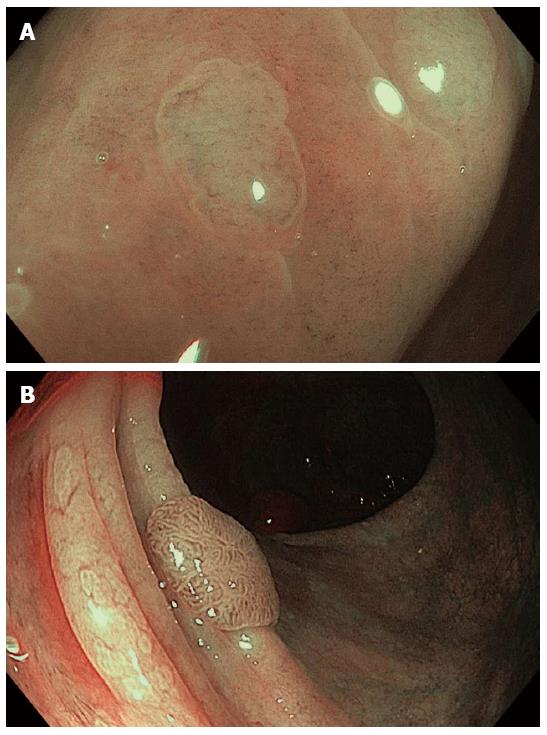
The ability of NBI for the prediction of a polyp’s histology has been reported in different studies. Kudo’s classification system of mucosal pit pattern detected on magnification has included 5 different types: type I- round pits, type II- stellar or papillary pits, type III L- large tubular or roundish pits, type III s- small tubular or roundish pits, type IV- branch-like or gyrus-like pits and type V- non-structural pits[37]. A proper evaluation of a colonic lesion consists in the assessment of mucosal pattern and also of vascular pattern. Sano et al[38] have proposed an evaluation of “capillary pattern” by using NBI colonoscopy with magnification for the differential diagnosis of colorectal lesions: type I- absent meshed brown capillary network (MBCN) in hyperplastic polyps (Figure 7A), type II- regular pattern in adenomatous polyps (Figure 7B), and type III- irregular pattern in cancerous lesions (Figure 7C).
Figure 7 Assessment of colonic lesions by narrow band imaging with magnification endoscopy according to different classification systems.
A: Hyperplastic polyp: absent mesh brown capillary network (Type I MBCN) (Sano classification); a lighter color of the polyp than the background, isolated vessels coursing across the lesion (NICE criteria); B: Adenomatous polyp: regular mesh brown capillary network (Type II MBCN) and Kudo’s Type IV mucosal pattern; the brown color relative to background, thick brown vessels surrounding white structures (NICE criteria); C: Cancerous colonic lesion: irregular mucosal and vascular patterns (Type III MBCN); D: Deep submucosal invasive colorectal cancer: amorphous surface pattern and disrupted vessels (NICE criteria).
According to these diagnostic criteria for mucosal and vascular patterns, specific features on NBI-ME have been described, corresponding with different colonic lesions: type I or II mucosal pattern (round, stellar or papillary pits) and type I vascular pattern (absence of vascular structure) in hyperplastic polyps (Figure 7A); type III or type IV mucosal pattern (tubular or branching pits) and type II vascular pattern (regular vessels) in adenoma (Figure 7B); type V mucosal pattern (disappeared pits) and type III vascular pattern (irregular vessels) in adenocarcinoma (Figure 7C). This combined classification system, based on mucosal and vascular patterns assessment, was used for the prediction of polyp histology. The accuracy of the NBI-ME method has proven to be superior to high-resolution WLE for the prediction of polyp histology[39].
The NBI International Colorectal Endoscopic (NICE) classification has been proposed by an international expert group for the diagnosis of colonic lesions[40]. The classification is based upon the evaluation of lesion color, microvascular architecture, and surface pattern, and can be applied for NBI observation either with or without use of magnification. The similar or lighter color of the polyp compared with the background mucosa, with no vessels or isolated vessels coursing across the polyp surface, the homogenous lack of mucosal pattern, the detection of dark or white spots of uniform size, are features corresponding with hyperplastic polyps (Figure 7A). A browner color of the polyp relative to the background mucosa, the visualization of brown vessels surrounding oval, tubular or branched white structures are features mainly associated with colonic adenomas (Figure 7B). A brown color of the lesion relative to background, sometimes with patchy whiter areas, an absent or amorphous mucosal pattern, and a vascular pattern with disrupted or missing vessels, all represent endoscopic criteria for the diagnosis of deep submucosal invasive colorectal carcinomas according to NICE classification (Figure 7D)[41].
The real time estimation of polyp histology could play an important role in clinical decisions regarding the therapeutic strategy for polyps ≤ 5 mm in size and for the duration of post-polypectomy surveillance intervals. Different cost-saving strategies were previously proposed in this setting. A “resect-and discard” policy was proposed for polyps ≤ 5 mm, which consists in a real-time estimation of polyp histology by NBI, followed by resection without pathologic assessment[42]. The “resect and discard” strategy for diminutive adenomatous polyps could decrease the cost of colonoscopy. The post-polypectomy surveillance intervals could be recommended on the basis of the estimation of polyp histology by NBI and of the pathologic assessment of the larger polyps submitted to histology[43].
The accurate estimation of the histology of the polyps (real-time optical biopsy) could prevent unnecessary polypectomies in cases of diminutive rectosigmoid hyperplastic polyps (“do-not-resect” strategy). On the basis of the evaluation of polyp histology by NBI criteria (color, vessels, pit pattern), experts have demonstrated that leaving diminutive distal hyperplastic polyps in place without pathologic assessment could be a reliable approach in clinical practice[44].
According to the Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI) statement, developed by The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE), the thresholds of endoscopic technology for the assessment of polyps histology are: optical diagnosis for diminutive colorectal polyps combined with pathologic assessment of all other polyps should provide ≥ 90% agreement in determining post-polipectomy surveillance intervals when compared with decisions based on pathology assessment of all polyps, and the recommended NPV for adenomatous histology in diminutive rectosigmoid polyps should be ≥ 90%. After the achievement of PIVI thresholds, the NBI technology could be used to guide the “characterize, resect and discard” strategy in clinical practice[45]. Recent studies have focused on the ability of NBI diagnosis to meet these ASGE thresholds[46,47]. The incorporation of real-time histology in clinical practice still represents a matter of debate[48].
Regarding the widespread use of the aforementioned strategies in clinical practice, the lack of accurate criteria for the differentiation between sessile serrated adenomas (SSAs) and hyperplastic polyps on NBI could represent a real challenge. A type II open-pit pattern (Type II-O), characterized by wider and rounded pits, was identified on magnification to be specific to SSAs[49]. Recent reports from community gastroenterologists have showed that endoscopic features of SSAs under NBI according to NICE classification were intermediate to the patterns observed in hyperplastic polyps and adenomas[50]. The misclassification of SSAs could affect clinical decisions regarding therapeutic strategy and surveillance intervals. The approach to serrated polyps in clinical practice should take into account their malignant potential[51].
Another problem regarding the global use of optical biopsy in practice is related to the level of training and expertise. A high performance level of the optical diagnosis of the polyps using NBI-ME was reported by the experts[47], but these studies were mainly performed in academic centers. Recent studies investigating optical biopsy performance in community practice have shown that the results are not as good as those obtained in the academic setting: only 25% of gastroenterologists assessed polyps with ≥ 90% accuracy. The thresholds for optical biopsy recommended by ASGE were achieved for identification of adenoma (NPV ≥ 90%), but not for the surveillance interval agreement[46]. The level of performance in clinical practice might be improved by training programs including the evaluation of frozen images or videos, real-time optical diagnosis during NBI colonoscopy, as well as creation of computer-aided diagnostic tools[52].