Published online Jan 16, 2023. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v15.i1.10
Peer-review started: October 15, 2022
First decision: October 27, 2022
Revised: November 16, 2022
Accepted: December 5, 2022
Article in press: December 5, 2022
Published online: January 16, 2023
Processing time: 85 Days and 15.4 Hours
Ménétrier’s disease is a rare condition characterized by enlarged gastric folds, usually located in the whole body and fundus of the stomach. This report presents an unusual case of localized Ménétrier’s disease elevated by a submucosal lipoma and thus looking like a polypoid mass and causing an episode of upper gas
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy was performed on a 76-year-old male patient after an episode of upper gastrointestinal bleeding, manifesting as fatigue and melena. A large polypoid mass (4 cm × 1 cm) with enlarged mucosal folds was found in the body of the stomach, between the lesser curvature and posterior wall. A small ulcer at the distal end of the mass was identified as the source of the bleeding. Biopsy was negative for neoplasia. Computed tomography showed a submucosal lesion beneath the affected mucosa, most likely a lipoma. The mass was removed en bloc with tunneling endoscopic submucosal dissection. Final pathology de
Localized Ménétrier’s disease can coexist with a submucosal lipoma creating a polypoid mass with risk of bleeding.
Core Tip: We report the first case of localized Ménétrier’s disease coexisting with a submucosal lipoma. The elevation of the affected mucosa made it prone to mechanical damage and caused an episode of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Tunneling endoscopic submucosal dissection proved to be an effective method of resecting such a lesion. Since the remaining mucosa seemed unaffected by the disease, we expect the resection to be curative.
- Citation: Kmiecik M, Walczak A, Samborski P, Paszkowski J, Dobrowolska A, Karczewski J, Swora-Cwynar E. Upper gastrointestinal bleeding as an unusual manifestation of localized Ménétrier’s disease with an underlying lipoma: A case report. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2023; 15(1): 10-18
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v15/i1/10.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v15.i1.10
Ménétrier’s disease is rare; only a few hundred cases have been reported worldwide. Characteristic features of the disease are gastrointestinal symptoms, enlarged gastric folds (usually in the whole body and fundus of the stomach) and protein-losing gastropathy, which manifests as hypoalbuminemia and peripheral edema[1,2]. The disease is associated with a higher risk of developing gastric adenocarcinoma[3].
We report an infrequent case of localized Ménétrier’s disease elevated by an underlying submucosal lipoma, making it look like a polypoid mass. The mass was successfully removed with tunneling endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD).
A 76-year-old White male was referred for esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) after an episode of upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
The patient reported recurrent epigastric pain, transient fatigue and melena.
The patient’s comorbidities were type 2 diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Past medical history was relevant for coronavirus disease 2019, ischemic stroke, appendectomy, viscerocranial abscess and surgically-treated cataract.
The patient had a history of smoking in the past (30 pack-years). However, he had not smoked for 4 years and denied drinking alcohol. There was no relevant family history.
The patient’s height was 183 cm, weight was 80 kg, and body mass index was 23.89. Vitals upon admission were: heart rate, 50 beats/min; blood pressure, 118/48 mmHg; respiratory rate, 14/min; and body temperature, 36 °C. There was no abdominal tenderness and no peripheral edema.
Laboratory results were not relevant. Serum protein or albumin levels were not tested because Ménétrier’s disease was not suspected at the time.
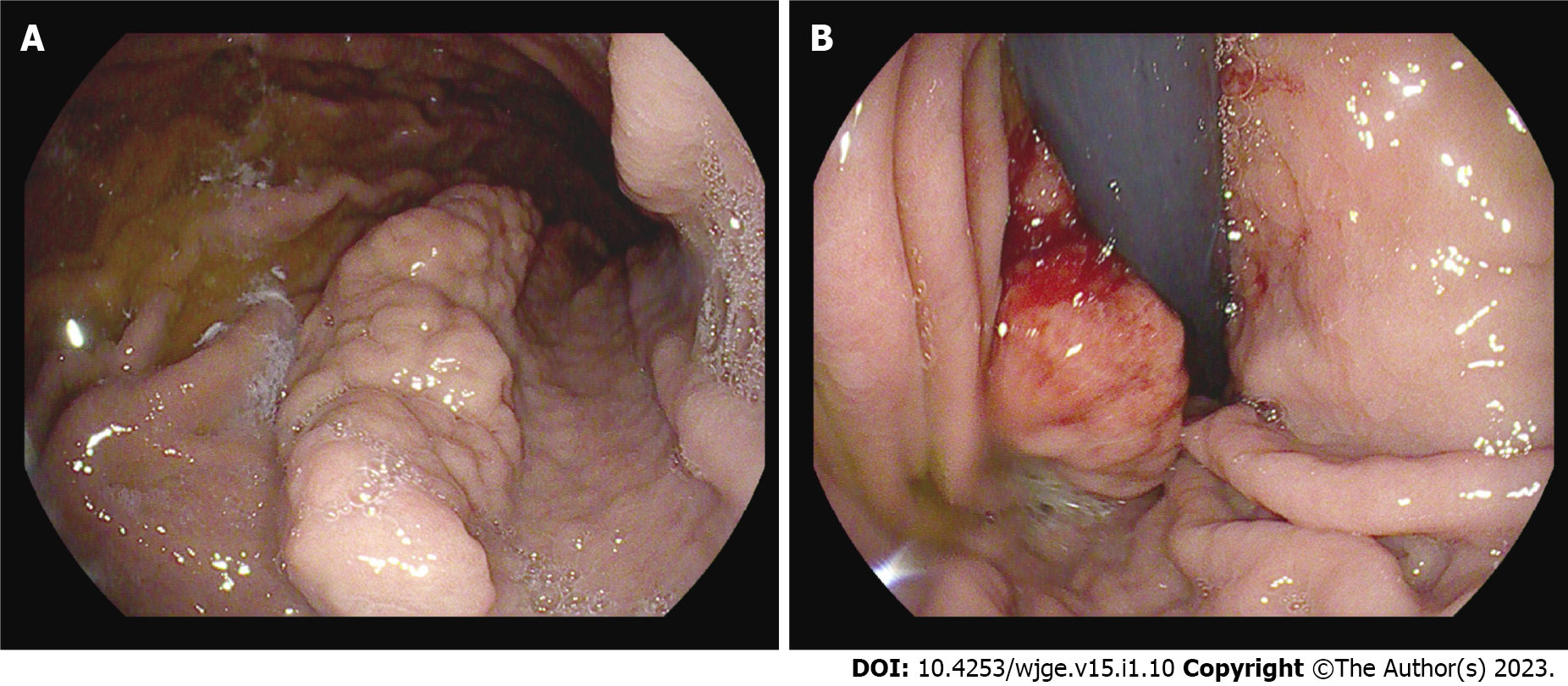
EGD revealed a polypoid mass (4 cm × 1 cm) with enlarged mucosal folds in the body of the stomach between the lesser curvature and posterior wall (Figure 1A). The mass was cohesive and somewhat stiff in contact with the forceps. A small ulcer at the distal end of the mass was identified as the source of the bleeding (Figure 1B). Standard and deep biopsy were taken from the distal end of the mass, and both were negative for neoplasia. Except for the mass, the mucosa was normal, and gastric folds were not enlarged.
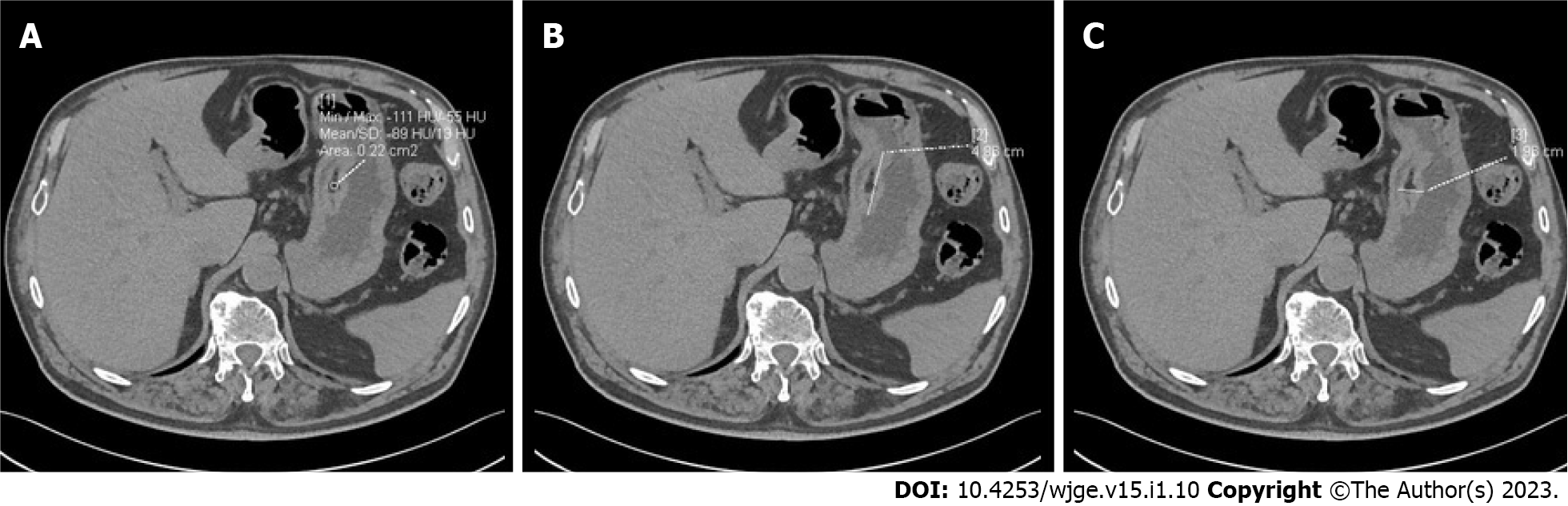
Computed tomography of the abdomen with contrast enhancement showed a submucosal lipoma (49 mm × 19 mm) in the body of the stomach, elevating the mucosa (Figure 2). The stomach was otherwise normal. There was no visible infiltration of surrounding tissue and no enlarged lymph nodes.
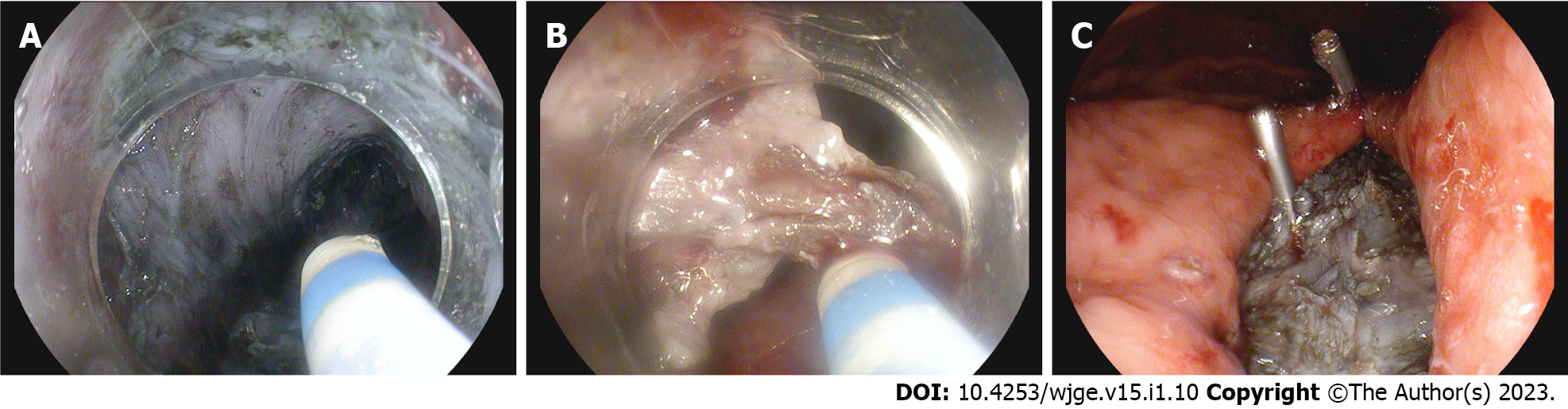
The mass was removed en bloc via tunneling ESD (Figure 3).
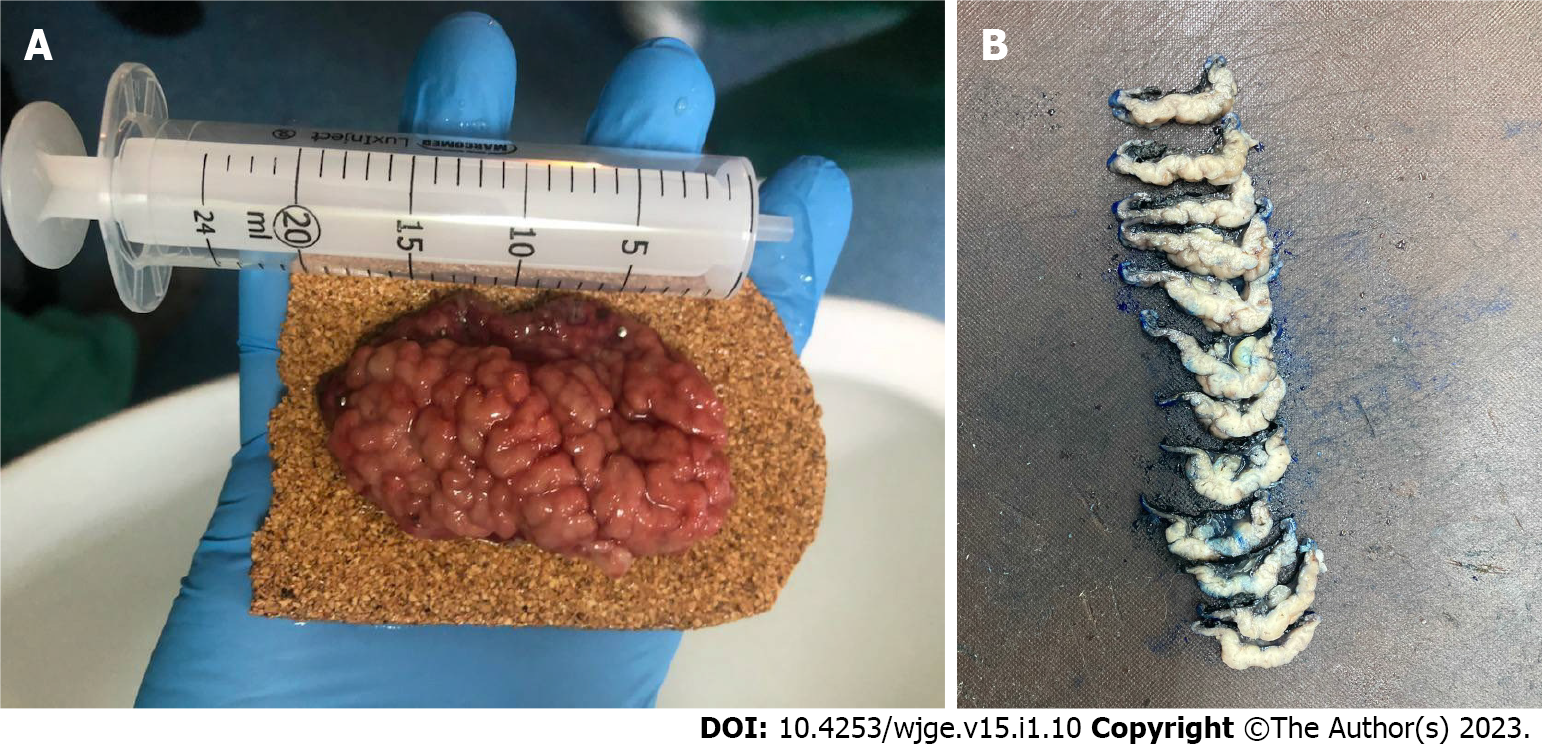
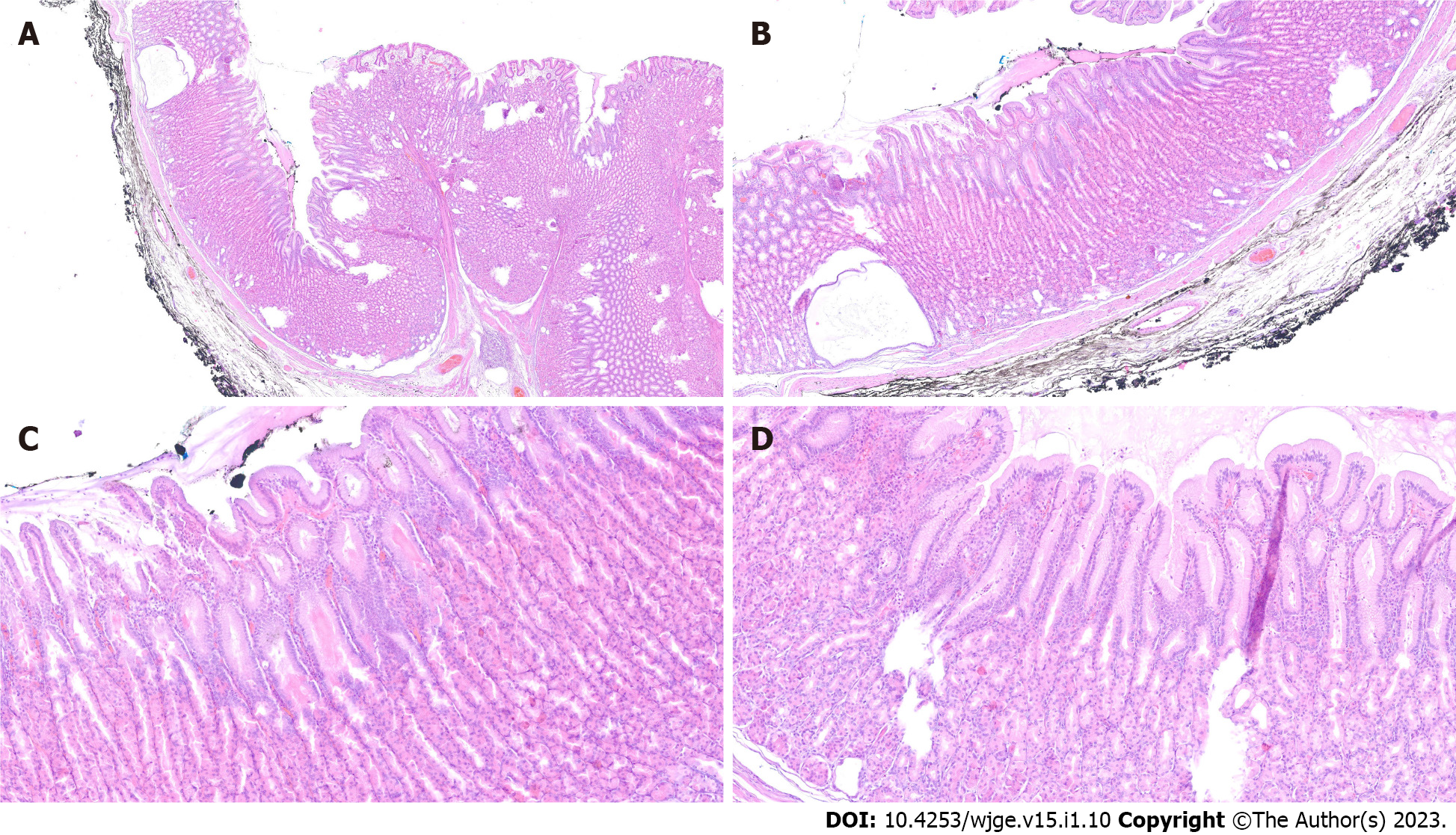
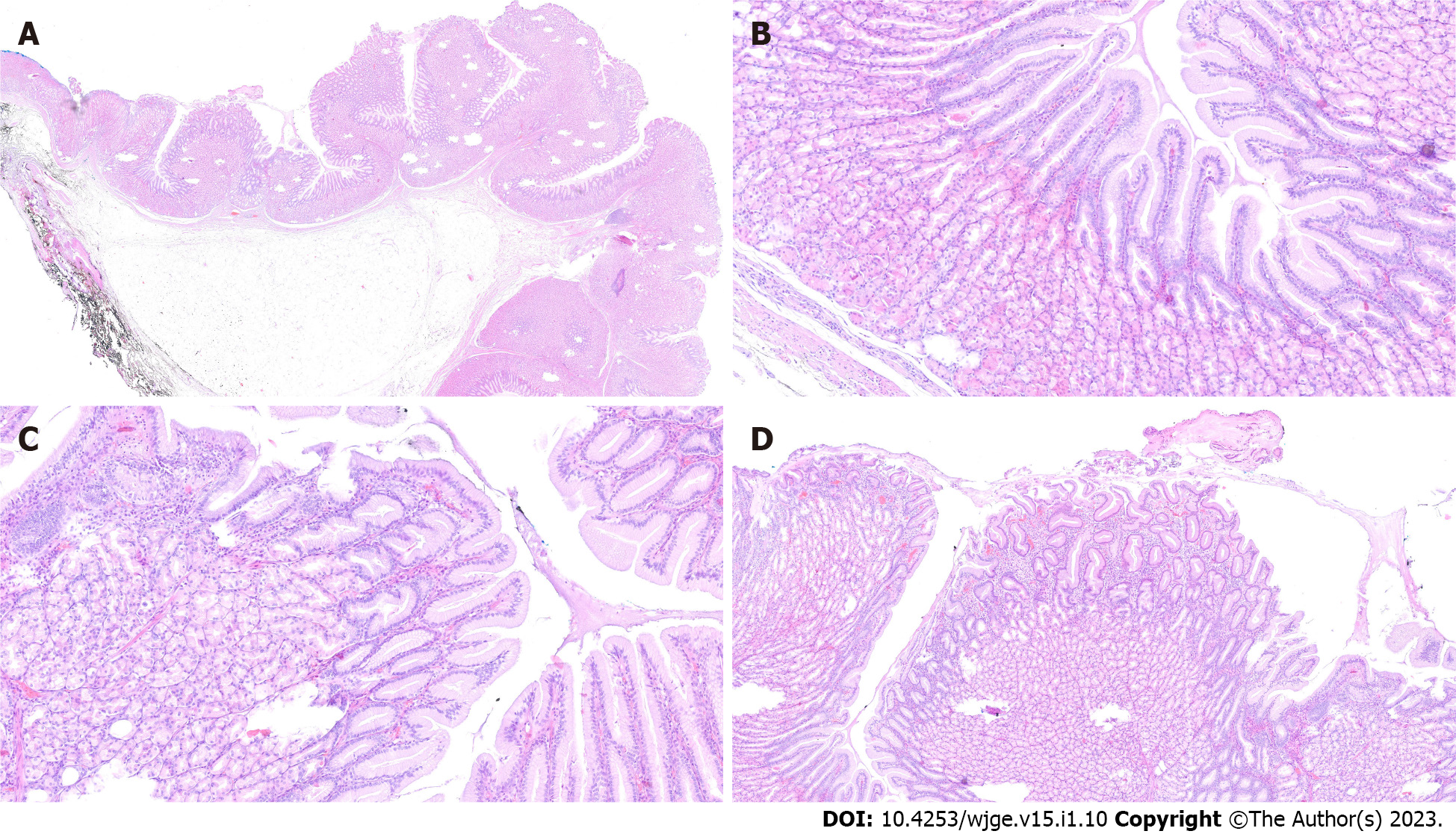
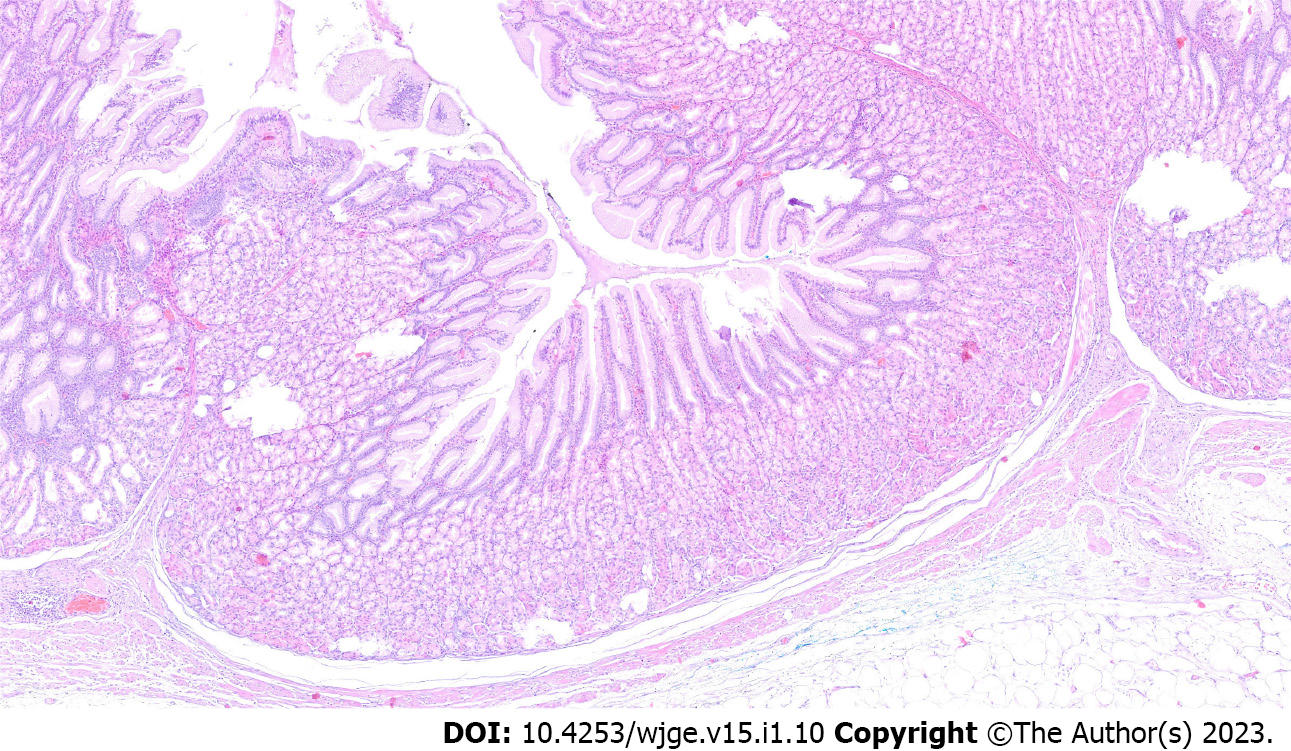
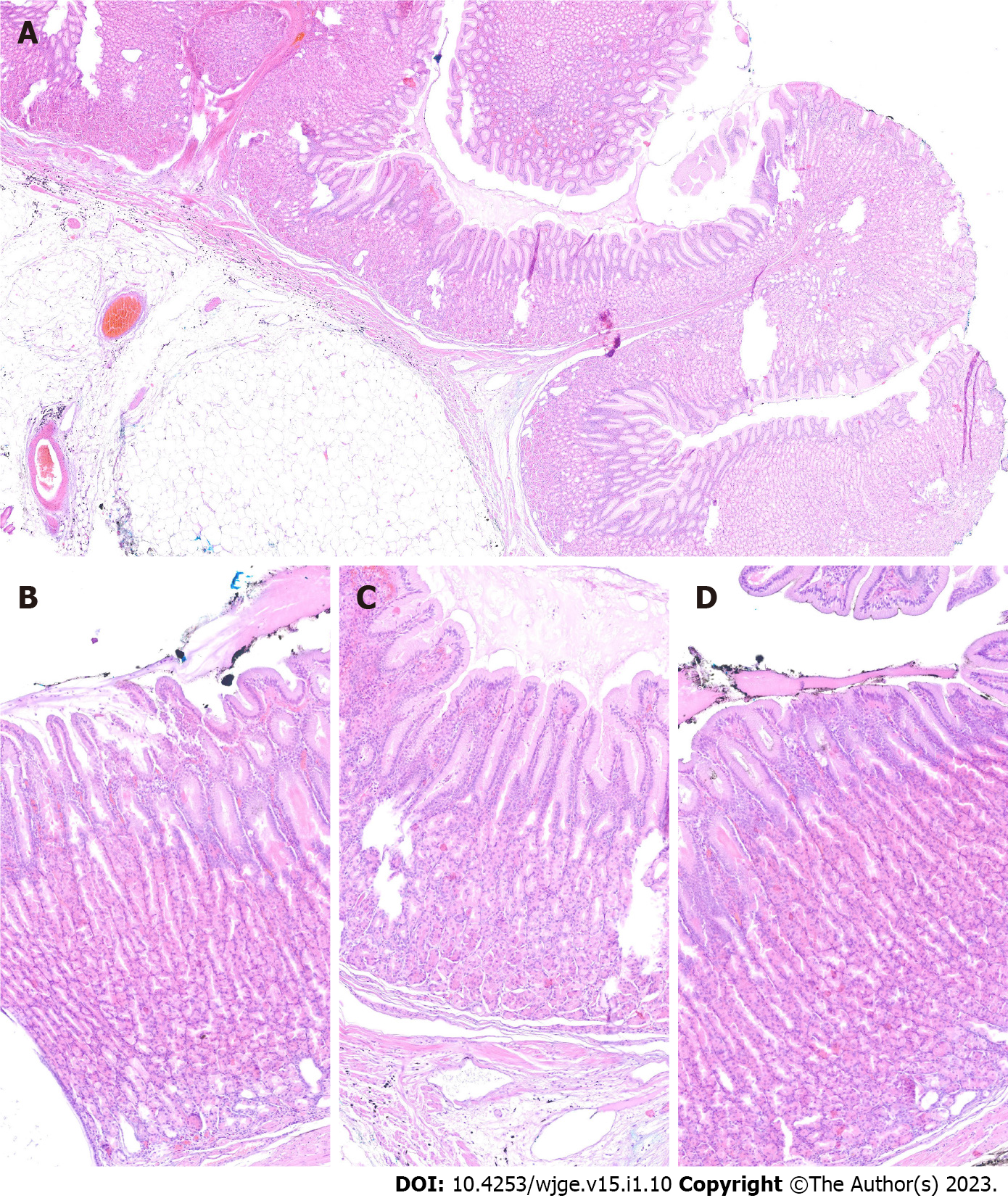
The final diagnosis of Ménétrier’s disease and submucosal lipoma was determined by pathological examination of the resected specimen (Figure 4). Upon macroscopic examination, the gastric mucosa was found to be focally thickened (up to 1.5 cm in width) with tortuous folds and elevation of the surface, which gave the mucosa cobblestone or cerebriform appearance (Figure 5 and Figure 6). Histologically, the dominant feature was foveolar hyperplasia of gastric glands (Figure 7). The surface and glandular mucous cells were elongated, cystically dilated and tortuous, which can be described as a “corkscrew-like appearance” (Figure 5B, Figure 6A, and Figure 8A). Additionally, cystic dilation of the deep glands was observed (Figure 5A). Foveolar hyperplasia was accompanied by oxyntic atrophy with the loss of chief and parietal cells, especially in the area adjacent to cystically dilated deep glands. Muscularis mucosae was focally thickened and branched out to the lamina propria with vertical strands of smooth muscles (Figure 6B). Among microscopic changes of the mucosa, predominant chronic inflammatory infiltrate of low intensity with some scattered eosinophils was present in the lamina propria (Figure 6C). Moreover, a lipoma was identified in the submucosal layer (Figure 6 and Figure 8). This benign lesion was located within the submucosal border without breaching the muscularis mucosae. It simultaneously lifted the mucosal layer, described as an elevation of the surface during the macroscopic examination. The immunohistochemical tests showed no Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection.
The patient’s symptoms subsided after the intervention, and he was scheduled for follow-up EGD.
Clinical symptoms of Ménétrier’s disease are nonspecific and include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, asthenia, anorexia, weight loss and peripheral edema[1,2]. Among these, our patient presented only with recurrent abdominal pain. He was older than most patients at the time of diagnosis since the disease is most often diagnosed between the age of 30 and 60 years. It is diagnosed more frequently in males[1,2].
The etiology of Ménétrier’s disease in most cases is unknown. It is generally considered to be acquired, but a rare familial form has been reported in siblings. Some cases have been linked to H. pylori with regression after treatment of the infection. In our patient, the immunohistochemical test for H. pylori was negative. There is also a subtype occurring in children, associated with cytomegalovirus infection[1,2].
The definite pathophysiology of Ménétrier’s disease is still being investigated. One of the theories is linked to increased production of transforming growth factor-alpha (TGF-α) and as a consequence increased signaling of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). One consequence of TGF-α overexpression is cellular proliferation, which may trigger neoplastic transformation. Studies on mice have shown that TGF-α overexpression in the stomach mucosa showed changes characteristic of Ménétrier’s disease[4-6]. Furthermore, studies on Ménétrier’s disease patients demonstrated a similar mechanism[7,8]. Increased overexpression of TGF-α causes increased signaling of EGFR, a transmembrane receptor with tyrosine kinase activity that further triggers an intracellular signaling cascade, expanding the cell’s proliferation. Immunohistochemical reactions using TGF-α and EGFR are not routinely performed during the diagnostic process as they are not a requirement for the diagnosis of Ménétrier’s disease. However, in the future, it will be worth focusing on the study of the TGF-α and EGFR pathways in order to understand its pathophysiology and consequences.
Initially, Ménétrier’s disease was not suspected in our patient. His symptoms (epigastric pain, fatigue and melena) were not typical for this disease. Gastroscopic and imaging results did not indicate Ménétrier’s disease either. Gastric folds are usually enlarged in the whole body and fundus of the stomach, with antrum spared, although a localized form of the disease has been reported[1,3,9]. In this case, gastric folds were enlarged only on the surface of the mass in the body of the stomach. Biopsy of the affected mucosa usually confirms the diagnosis of Ménétrier’s disease, but in our case it did not show any significant changes in the mucosa. Nevertheless, it helped differentiate the origin of the mass.
Differential diagnosis of Ménétrier’s disease involves a broad spectrum of conditions and requires analysis of clinical symptoms, gastroscopy, imaging and histological results. Ménétrier’s disease should be differentiated from hypertrophic lymphocytic gastritis, hypertrophic hypersecretory gastropathy, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, hyperplastic or hamartomatous polyps, gastric carcinoma, lymphoma and amyloidosis[1,2].
Upper gastrointestinal bleeding has been reported as a rare manifestation of Ménétrier’s disease. The bleeding may present as hematemesis or, like in this case, as melena[10,11]. One patient developed deep vein thrombosis and received anticoagulation therapy, which led to gastrointestinal bleeding[12]. Iron deficiency anemia in patients with Ménétrier’s disease could be a sign of occult bleeding, but iron malabsorption should also be considered[13,14].
Hypoalbuminemia is present in the majority of patients with Ménétrier’s disease (85%), and in some cases causes peripheral edema[1]. Ménétrier’s disease should be considered in differential diagnosis of protein-losing gastropathy/enteropathy, and certain interventions may be necessary to normalize albumin level, such as H. pylori eradication, proton pump inhibitors, H2-blockers, anticholinergic drugs, corticosteroids or octreotide[15]. In this case, albumin level was not obtained during the diagnostic process or preoperative laboratory evaluation. It should be tested if Ménétrier’s disease is suspected or the patient presents with peripheral edema.
Treatment of Ménétrier’s disease usually includes a high-protein diet and supportive medication, but severe cases may require total gastrectomy[1]. Partial gastrectomy has also been performed in selected patients[9,16,17]. The discovery of the role of TGF-α and EGFR overexpression in the pathogenesis of Ménétrier’s disease resulted in experimental treatment with monoclonal antibodies, such as cetuximab[18-20]. To our knowledge, localized Ménétrier’s disease with an underlying submucosal lipoma has never been reported. Tunneling ESD was used for the first time to remove localized Ménétrier’s disease.
Increased risk of gastric cancer in patients with Ménétrier’s disease contributes to increased mortality in this group. In a case-control study of 76 patients by Almazar et al[3], 8.9% of patients with Ménétrier’s disease developed gastric cancer 10 years after the diagnosis vs 3.7% in the control group. The 5-year and 10-year survival rates were 72.7% and 65.0%, respectively (vs 100% in the control group). The authors suggest annual screening for cancer with EGD. Gastrectomy remains the primary treatment option for patients who developed gastric cancer. Recently, two curative endoscopic interventions for early-stage gastric cancer in patients with Ménétrier’s disease have been reported: endoscopic mucosal resection and standard ESD[21,22].
We report a highly unusual case of localized Ménétrier’s disease coexisting with a submucosal lipoma, which created a polypoid mass in the stomach. Successful resection was achieved with tunneling ESD.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: Poland
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Cho JY, South Korea; Tangsuwanaruk T, Thailand S-Editor: Wang JL L-Editor: A P-Editor: Wang JL
| 1. | Lambrecht NW. Ménétrier's disease of the stomach: a clinical challenge. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2011;13:513-517. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 33] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Huh WJ, Coffey RJ, Washington MK. Ménétrier's Disease: Its Mimickers and Pathogenesis. J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50:10-16. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Almazar AE, Penfield JD, Saito YA, Talley NJ. Survival Times of Patients With Menetrier's Disease and Risk of Gastric Cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19:707-712. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Dempsey PJ, Goldenring JR, Soroka CJ, Modlin IM, McClure RW, Lind CD, Ahlquist DA, Pittelkow MR, Lee DC, Sandgren EP. Possible role of transforming growth factor alpha in the pathogenesis of Ménétrier's disease: supportive evidence form humans and transgenic mice. Gastroenterology. 1992;103:1950-1963. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 166] [Cited by in RCA: 149] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Takagi H, Jhappan C, Sharp R, Merlino G. Hypertrophic gastropathy resembling Ménétrier's disease in transgenic mice overexpressing transforming growth factor alpha in the stomach. J Clin Invest. 1992;90:1161-1167. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 107] [Cited by in RCA: 101] [Article Influence: 3.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Takagi H, Fukusato T, Kawaharada U, Kuboyama S, Merlino G, Tsutsumi Y. Histochemical analysis of hyperplastic stomach of TGF-alpha transgenic mice. Dig Dis Sci. 1997;42:91-98. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Bluth RF, Carpenter HA, Pittelkow MR, Page DL, Coffey RJ. Immunolocalization of transforming growth factor-alpha in normal and diseased human gastric mucosa. Hum Pathol. 1995;26:1333-1340. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Romano M, Meise KS, Suozzo R, Sessa G, Persico M, Coffey RJ. Regional distribution of transforming growth factor-alpha and epidermal growth factor in normal and portal hypertensive gastric mucosa in humans. Dig Dis Sci. 1995;40:263-267. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Stamm B. Localized hyperplastic gastropathy of the mucous cell- and mixed cell-type (localized Ménétrier's disease): a report of 11 patients. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997;21:1334-1342. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Dickinson RJ, Axon AT. Haematemesis in Ménétrier's disease. Postgrad Med J. 1979;55:751-752. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Kamal MU, Tariq H, Mehak V, Azam S, Kumar K, Niazi M, Dev A. A Rare Etiology of Abnormally Large Gastric Folds: Menetrier's Disease. Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2019;2019:7927083. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Greenblatt HK, Nguyen BK. Ménétrier's disease presenting as recurrent unprovoked venous thrombosis: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2019;13:14. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Pepa P, Uehara T, Wonaga A, Redondo A, Avagnina A, Mazzocchi O, Antelo P, Waldbaum C, Sorda J. Menetrier's disease. A diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Medicina (B Aires). 2021;81:470-473. [PubMed] |
| 14. | Waisberg DR, de Mello ES, Tustumi F, Szor DJ, Charruf AZ, Fuhro FE, Waisberg J, Dias AR. A case report of diffuse hyperplastic gastropathy with multiple polypoid formations in a patient with pernicious anemia, Helicobacter pylori infection, hypergastrinemia and hypoalbuminaemia: Do not forget of Ménétrier's disease. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2020;77:498-502. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Landzberg BR, Pochapin MB. Protein-Losing Enteropathy and Gastropathy. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2001;4:39-49. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Hsu CT, Ito M, Kawase Y, Sekine I, Ohmagari T, Hashimoto S. Early gastric cancer arising from localized Ménétrier's disease. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1991;26:213-217. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Kim J, Cheong JH, Chen J, Hyung WJ, Choi SH, Noh SH. Menetrier's disease in korea: report of two cases and review of cases in a gastric cancer prevalent region. Yonsei Med J. 2004;45:555-560. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 18. | Fiske WH, Tanksley J, Nam KT, Goldenring JR, Slebos RJ, Liebler DC, Abtahi AM, La Fleur B, Ayers GD, Lind CD, Washington MK, Coffey RJ. Efficacy of cetuximab in the treatment of Menetrier's disease. Sci Transl Med. 2009;1:8ra18. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 41] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Parianos C, Aggeli C, Sourla A, Zografos GN. Total gastrectomy for the treatment of Menetrier's disease persistent to medical therapy: A case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2020;73:95-99. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Toubia N, Schubert ML. Menetrier's Disease. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2008;11:103-108. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Raderer M, Oberhuber G, Templ E, Wagner L, Pötzi R, Wrba F, Hejna M, Base W. Successful symptomatic management of a patient with Ménétrier's disease with long-term antibiotic treatment. Digestion. 1999;60:358-362. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Fukushi K, Goda K, Kino H, Kondo M, Kanazawa M, Kashima K, Kanamori A, Abe K, Suzuki T, Tominaga K, Yamagishi H, Irisawa A. Curative resection with endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer in Helicobacter pylori-negative Ménétrier's disease: A case report. World J Gastroenterol. 2022;28:594-601. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |