Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Sep 16, 2017; 9(9): 456-463
Published online Sep 16, 2017. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i9.456
Published online Sep 16, 2017. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i9.456
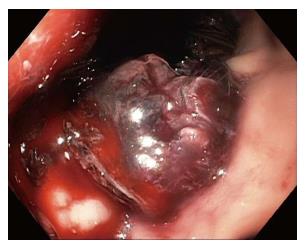
Figure 1 Delayed bleeding after lumen apposing metal stent placement, which required angiographic embolization.
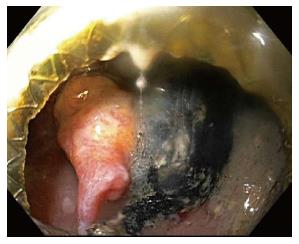
Figure 2 Pulsatile pseudoaneurysm seen on left of screen after endoscopic entry into cyst cavity, several weeks after initial lumen apposing metal stent placement for walled off necrosis.
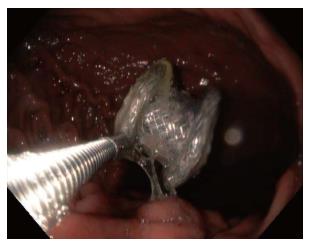
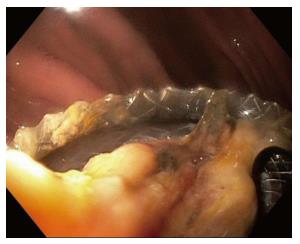
Figure 3 Endoscopic removal of lumen apposing metal stent that migrated into gastric lumen.
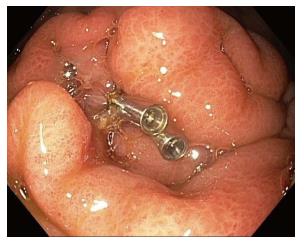
Figure 4 Closure of a perforation in the stomach after lumen apposing metal stents maldeployment and removal (a second gastric location was subsequently chosen for successful lumen apposing metal stents placement).
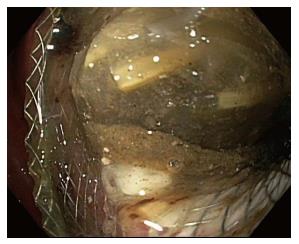
Figure 5 Food debris occluding lumen apposing metal stent lumen.
Figure 6 Necrotic debris occluding lumen apposing metal stent lumen.
- Citation: DeSimone ML, Asombang AW, Berzin TM. Lumen apposing metal stents for pancreatic fluid collections: Recognition and management of complications. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2017; 9(9): 456-463
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v9/i9/456.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v9.i9.456