Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jul 16, 2017; 9(7): 304-309
Published online Jul 16, 2017. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i7.304
Published online Jul 16, 2017. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i7.304
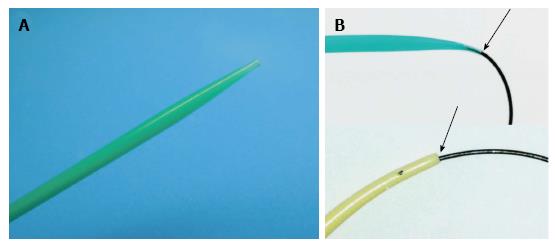
Figure 1 Newly developed dilator, ES Dilator® (Zeon Medical Co.
, Tokyo, Japan), characterized by high pushability and lesser difference in diameters of the inner lumen and the guidewire. A: Tip of the ES Dilator; B: The ES Dilator has a lesser difference between the diameter of the inner lumen and that of the guidewire (upper figure), compared with traditional tapered catheters for ERCP (lower figure). ES Dilator: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
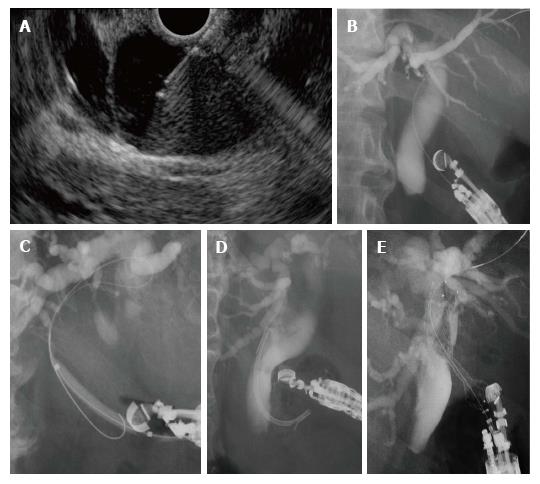
Figure 2 Technique of endoscopic ultrasound-guided choledochoduodenostomy.
A: The extrahepatic bile duct is punctured by a 19-gauge needle under EUS guidance; B: After contrast medium is injected, a guidewire is inserted; C: The puncture tract is dilated with a tapered catheter, a balloon dilator, and/or ES Dilator; D and E; A plastic stent (D) or a metal stent is deployed at the puncture site (E). EUS: Endoscopic ultrasound.
- Citation: Kanno Y, Ito K, Koshita S, Ogawa T, Masu K, Masaki Y, Noda Y. Efficacy of a newly developed dilator for endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2017; 9(7): 304-309
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v9/i7/304.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v9.i7.304