Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. May 16, 2017; 9(5): 238-242
Published online May 16, 2017. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i5.238
Published online May 16, 2017. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i5.238
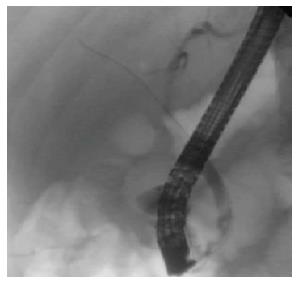
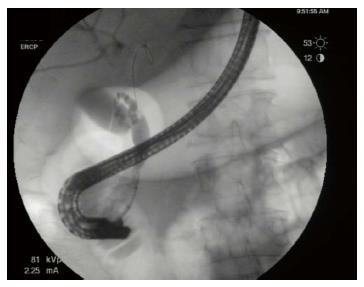
Figure 1 Distal common bile duct stricture on initial cholangiogram.
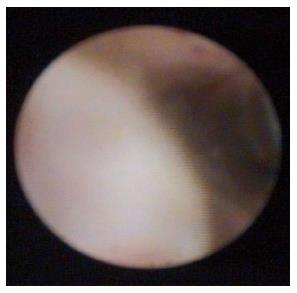
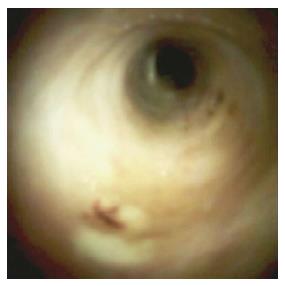
Figure 2 Polypoid lesion seen with SpyGlass™ cholangioscopy.
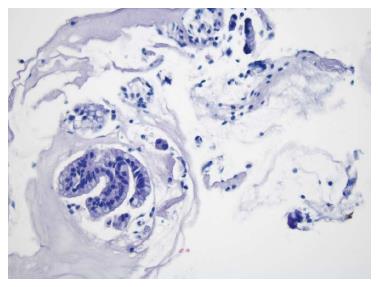
Figure 3 Biliary epithelium with papillary configuration and atypical cells.
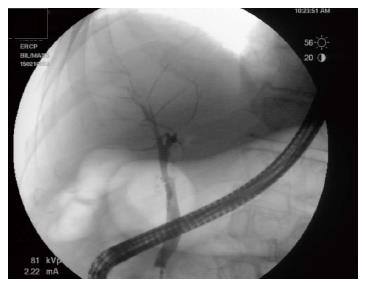
Figure 4 Occlusion cholangiogram performed four months after last radiofrequency ablation treatment, revealing no polypoid lesion or stricture in the distal common bile duct.
Figure 5 Repeat SpyGlass™ cholangioscopy showing no residual polypoid lesion.
Figure 6 Repeat endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography demonstrating a 10 mm distal common bile duct stricture without evidence of a mass lesion.
- Citation: Natov NS, Horton LC, Hegde SR. Successful endoscopic treatment of an intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2017; 9(5): 238-242
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v9/i5/238.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v9.i5.238