Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Mar 25, 2016; 8(6): 288-294
Published online Mar 25, 2016. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v8.i6.288
Published online Mar 25, 2016. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v8.i6.288
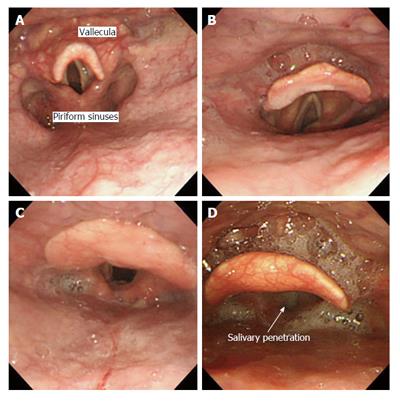
Figure 1 Endoscopic images of Hyodo-Komagane score.
Salivary pooling in vallecula and piriform sinuses. A: A-0 no pooling; B: A-1 pooling at the only vallecula; C: A-2 pooling in vallecula and piriform sinuses and no penetration into larynx; D: A-3 pooling in vallecula and piriform sinuses and penetration into larynx.
Figure 2 Test jelly used in this study (Isotonic jelly®, Nutri Co.
, Ltd., Yokkaichi, Japan).
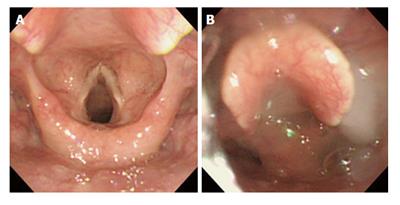
Figure 3 Endoscopic image of Hyodo-Komagane score.
A: Before swallowing of test jelly; B: D-3 pharyngeal residues remain and penetrate into larynx after swallowing of test jelly.
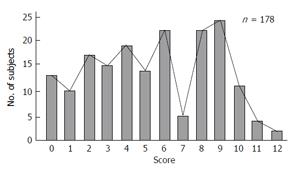
Figure 4 Distribution of a new scoring (Hyodo-Komgane score) in 178 patients undergoing endoscopic evaluation of swallowing.
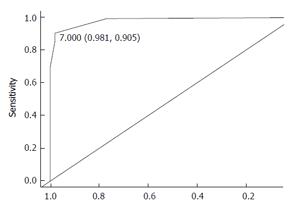
Figure 5 Receiver operating characteristic curve to evaluate the prediction capability of the Hyodo-Komgane score for successful oral intake of pureed diets.
- Citation: Sakamoto T, Horiuchi A, Makino T, Kajiyama M, Tanaka N, Hyodo M. Determination of the cut-off score of an endoscopic scoring method to predict whether elderly patients with dysphagia can eat pureed diets. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2016; 8(6): 288-294
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v8/i6/288.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v8.i6.288