Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jun 25, 2015; 7(7): 688-701
Published online Jun 25, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i7.688
Published online Jun 25, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i7.688
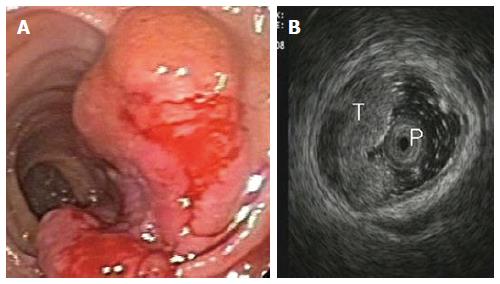
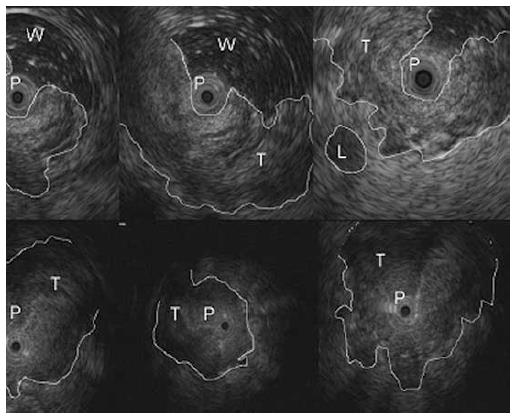
Figure 1 Stage T1 rectal cancer: (A) endoscopic and (B) ultrasonographic view.
Endoscopic ultrasound with radial miniprobe (12 MHz), showing a small tumor located within the mucosa and superficial submucosal layers, and preservation of the outer layers of the rectal wall. T: Tumor; P: Radial probe.
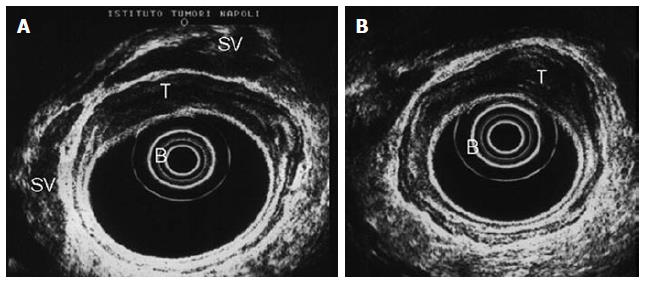
Figure 2 Stage T2 rectal cancer: Ultrasonographic view.
The tumor infiltrated the entire wall, without invading the smooth outer margin of the muscularis propria (fourth layer). Endoscopic ultrasound with radial array transducer UM 20 (7.5-12 MHz). B: Ballon; T: Tumor; SV: Seminal vesicles.
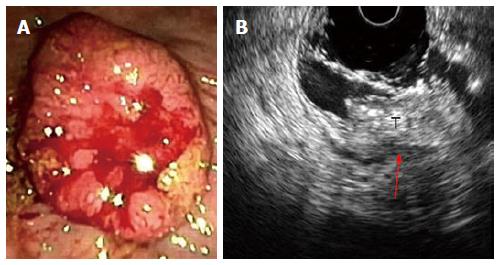
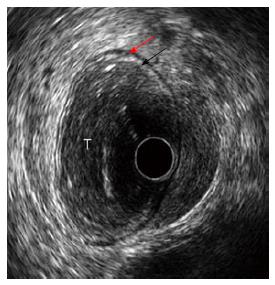
Figure 3 Stage T3 rectal cancer: (A) endoscopic and (B) ultrasonographic view.
Endoscopic ultrasound with radial array transducer UM160 (5-20 MHz), showing increased wall thickness for the presence of a mass with inhomogeneous echogenicity, invading all the layers of the wall and minimal infiltration of the perirectal fat. T: Tumor; Red arrow: Infiltration of the perirectal fat.
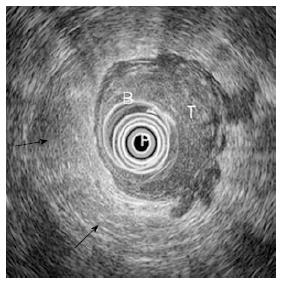
Figure 4 Stage T3 rectal cancer: Ultrasonographic view.
Endoscopic ultrasound shows advanced cancer of the rectum with large hypoechoic and inhomogeneous thickening of the rectal wall, loss of the five-layered wall structure and deep infiltration of the perirectal fat. Endoscopic ultrasound with radial array transducer UM160 (5-20 MHz). B: Ballon; P: Transducer; T: Tumor; Black arrow: Perirectal fat.
Figure 5 Stage T4 rectal cancer: Miniprobe ultrasonographic view.
Endoscopic ultrasound with radial miniprobe (12 MHz) shows an advanced, stenotic rectal cancer with large hypoechoic and inhomogeneous thickening of the rectal wall, loss of the five-layered wall structure and invasion of adjacent organs. T: Tumor; P: Miniprobe; L: Metastatic lymph node; W: Water.
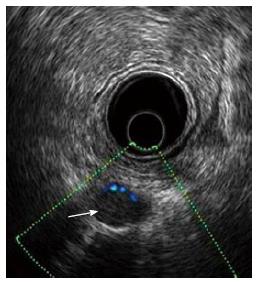
Figure 6 Perirectal metastatic lymph node: Ultrasonographic view.
Endoscopic ultrasound with radial array transducer UM160 (5-20 MHz). White arrow: Perirectal metastatic lymph node.
Figure 7 Stage T1 rectal cancer: miniprobe ultrasonographic view.
Endoscopic ultrasound with radial miniprobe (12 MHz), showing a small tumor located within the mucosa and superficial submucosal layers, with preservation of the outer layers of the rectal wall. T: Tumor; Red arrow: Muscularis propria layer; Black arrow: Submucosa layer.
- Citation: Marone P, Bellis M, D’Angelo V, Delrio P, Passananti V, Girolamo ED, Rossi GB, Rega D, Tracey MC, Tempesta AM. Role of endoscopic ultrasonography in the loco-regional staging of patients with rectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2015; 7(7): 688-701
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v7/i7/688.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v7.i7.688