Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. May 16, 2015; 7(5): 481-495
Published online May 16, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i5.481
Published online May 16, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i5.481
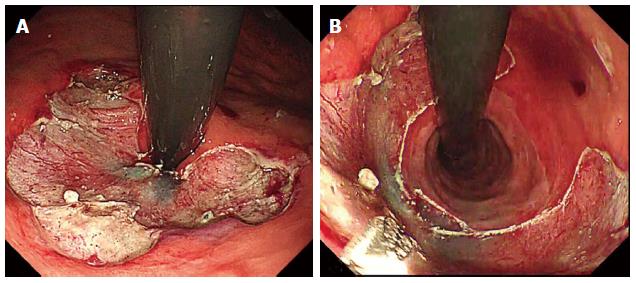
Figure 1 Completed antireflux mucosectomy.
A: View on expiration; B: View on inspiration.
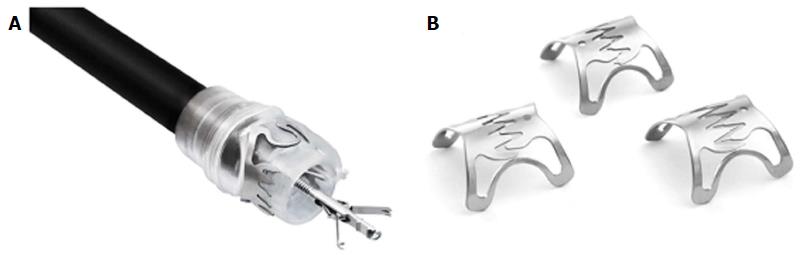
Figure 2 The over the scope clip device.
A: Clip mounted onto the distal tip of an endoscope with Twin Grasper projecting from the working channel; B: The different over-the-scope clip tooth configurations available. (With permission from OVESCO Endoscopy, Germany).
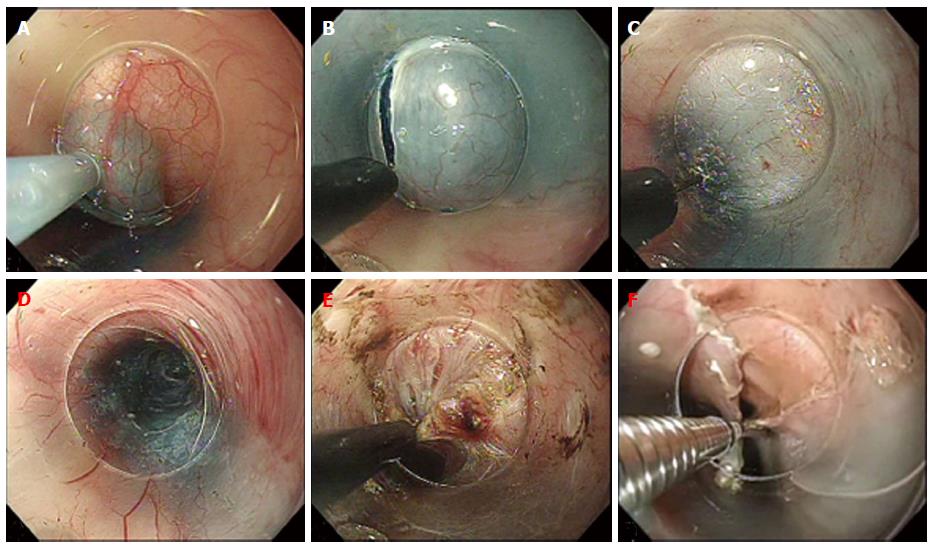
Figure 3 Steps in Per-oral endoscopic myotomy.
A: Submucosal injection; B: Mucosal incision; C: Submucosal tunneling; D: Completed tunnel; E: Circular muscle myotomy; F: Closure of mucosal incision.
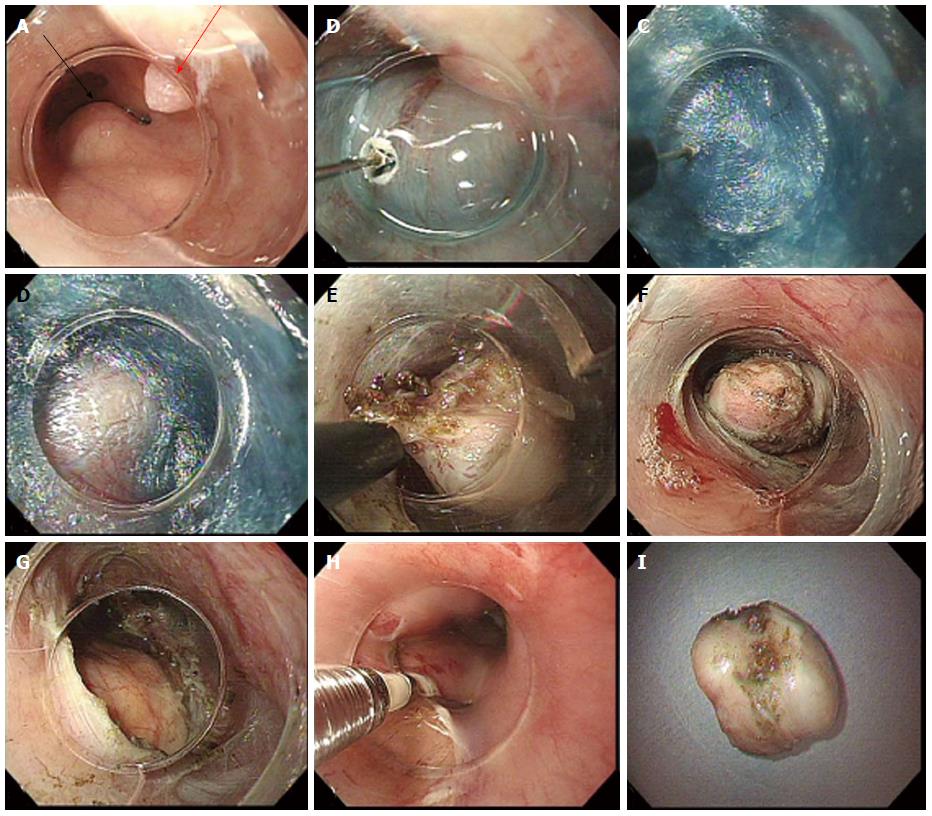
Figure 4 Per-oral endoscopic tumor resection of Leiomyoma.
A: Subepithelial tumor (SET) (black arrow) and incidental papilloma (red arrow); B: Mucosal incision with TT knife; C: Creation of submucosal tunnel; D: First encounter with SET in tunnel; E: Dissection of tumor; F: Dissected SET; G: Completed full thickness resection; H: Closure of incision; I: Extracted SET with intact capsule.
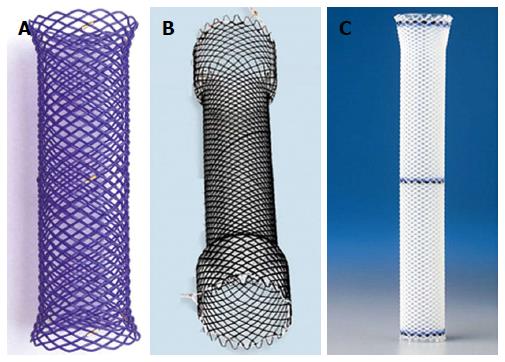
Figure 5 Examples of biodegradable stent, fully covered self-expandable metal stent and self-expandable plastic stent.
A: Biodegradable stent (ELLA-CS, Czech Republic) composed of polydioxanone monofilament; B: Fully covered Evolution® stent composed of nitinol silicone coating (Cook, United States); C: Fully covered silicon constructed Polyflex® stent (Boston Scientific, United States).
- Citation: Bechara R, Inoue H. Recent advancement of therapeutic endoscopy in the esophageal benign diseases. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2015; 7(5): 481-495
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v7/i5/481.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v7.i5.481