Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Nov 16, 2013; 5(11): 568-573
Published online Nov 16, 2013. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v5.i11.568
Published online Nov 16, 2013. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v5.i11.568
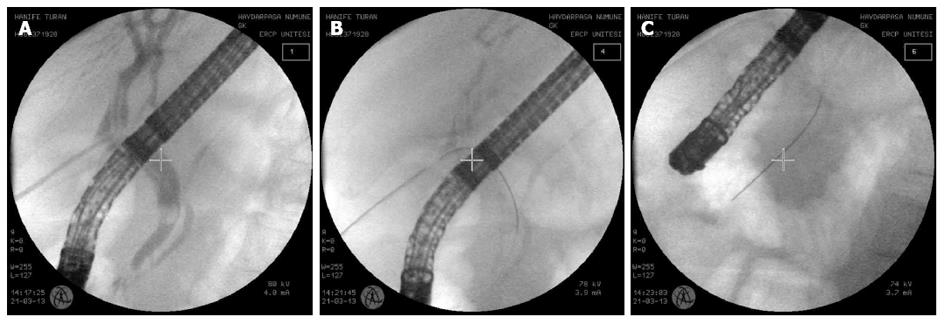
Figure 1 A sterile guide-wire was inserted via the T-tube to the common bile duct stone then to the papilla.
A: Retained stone with a T-tube in the common bile duct; B: The antegrade insertion of a guide-wire through the T-tube; C: The extension of the guide-wire through the papilla into the duodenum.
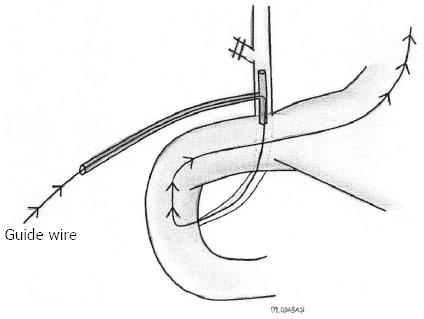
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of a guide-wire.
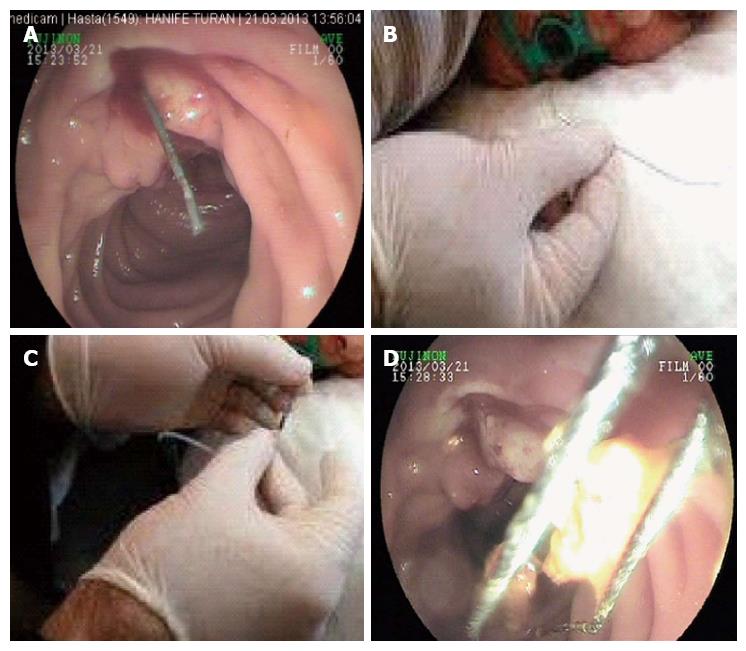
Figure 3 Appearance of the technique.
A: A guide-wire through the papilla during an endoscopic sphincterotomy; B: The guide-wire taken out by a snare; C: The guide-wire inserted in the tip of the sphincterotome, which is inserted via the endoscope channel of the duodenoscope; D: The stone is extracted by a basket catheter.
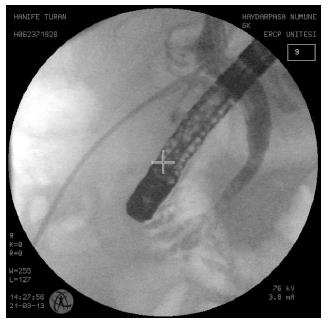
Figure 4 Control images of the common bile duct stone after the extraction of the stone.
- Citation: Odabasi M, Yildiz MK, Abuoglu HH, Eris C, Ozkan E, Gunay E, Aktekin A, Muftuoglu MT. A modified Rendezvous ERCP technique in duodenal diverticulum. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2013; 5(11): 568-573
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v5/i11/568.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v5.i11.568