Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Dec 16, 2012; 4(12): 532-544
Published online Dec 16, 2012. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v4.i12.532
Published online Dec 16, 2012. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v4.i12.532
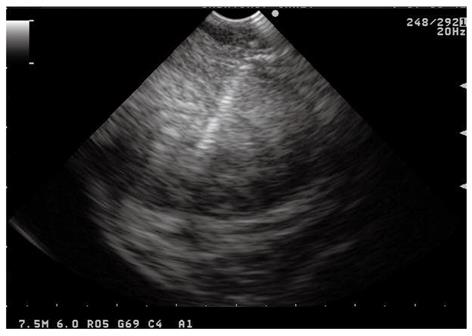
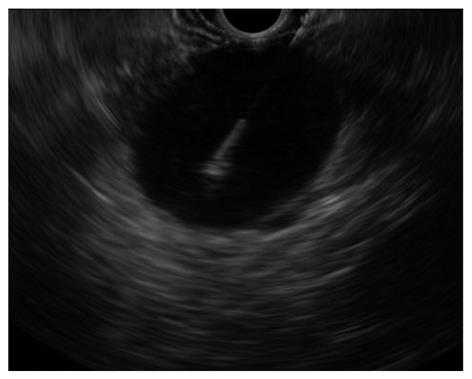
Figure 1 Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration performed using the forward-viewing endoscopic ultrasound scope of a large perirectal lesion suspicious for rectal cancer recurrence.
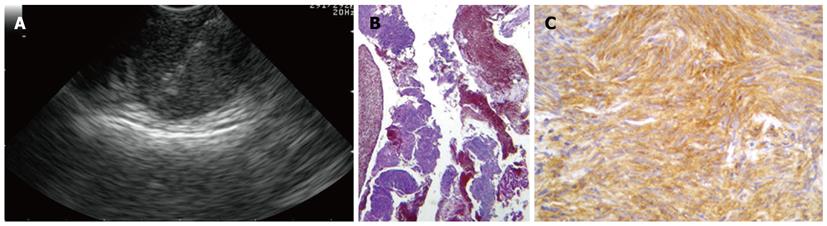
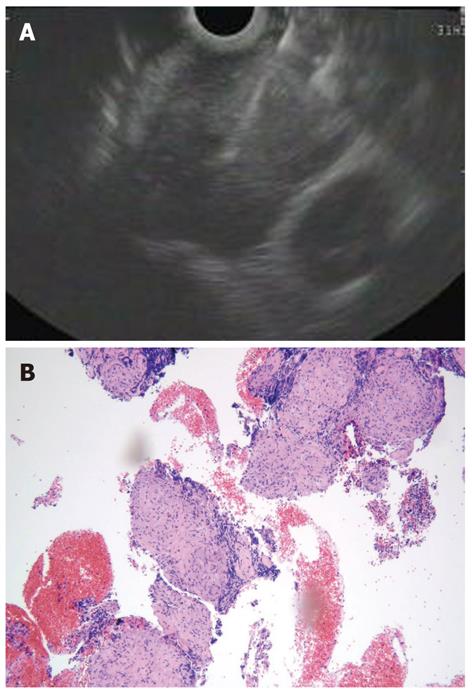
Figure 2 Subepithelial lesions.
A: Endoscopic ultrasound-fine needle tissue acquisition of a subepithelial lesion using a 19 gauge needle; B, C: Histological examination showed large fragments of neoplastic tissue with solid structure, composed of regular, fused cells with mild atypia, which were intensively immunoreactivity for c-Kit, consistent with gastrointestinal stromal tumor.
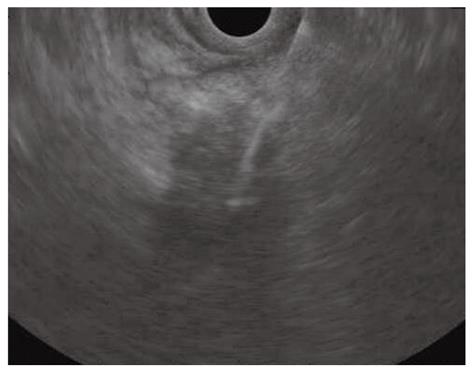
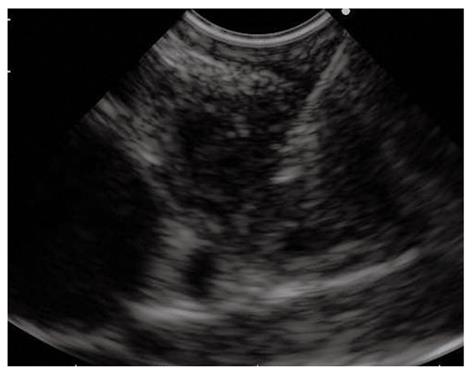
Figure 3 Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of a pancreatic mass of the uncinate process invading the superior mesenteric artery.
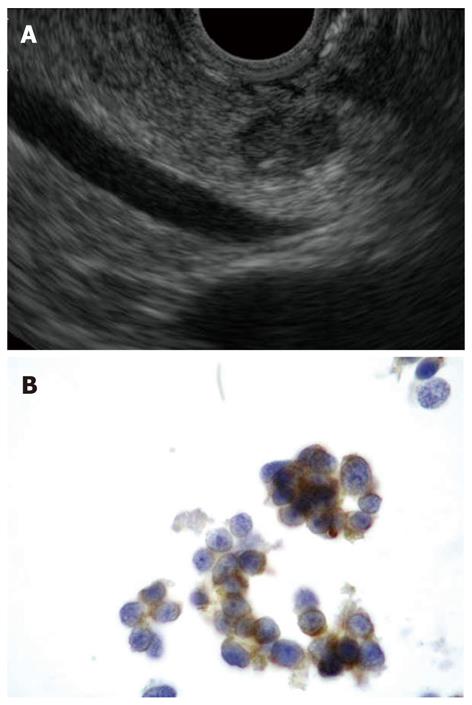
Figure 4 Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.
A: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of a small, hypoechoic, rounded, and well demarcated pancreatic body lesion; B: Diagnosed to be a neuroendocrine tumor by positive immunostaining for synaptophysin (thin layer cytology, 1000 ×).
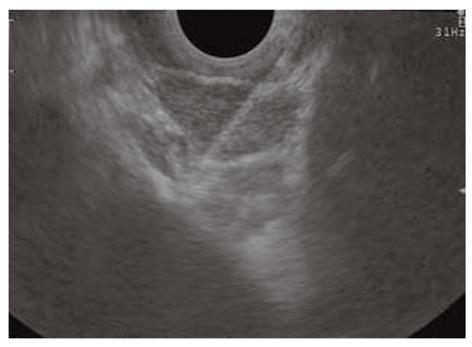
Figure 5 Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of a large pancreatic cystic lesion.
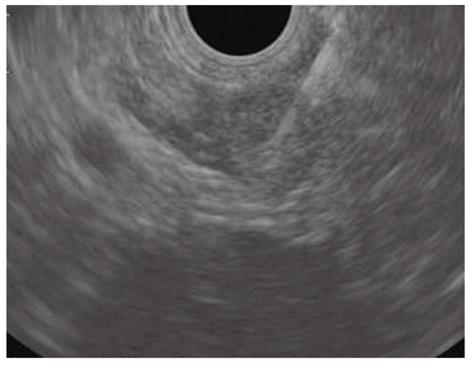
Figure 6 Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of a centimetric lesion causing a hilar biliary stricture performed using the forward viewing endoscopic ultrasound scope.
Figure 7 Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of lymph nodes in the aortic-pulmonary window in a patient with lung cancer.
Figure 8 Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of a left adrenal mass in a patient with lung cancer.
Figure 9 Core biopsy sample can be obtained using the trucut biopsy needle or a standard 19 gauge needle.
A: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration using a 19 gauge needle of a large subcarinal lymph node in a patient without evidence of any lung mass; B: The histological specimen showed non-necrotizing, non confluent granulomas, diagnostic for sarcoidosis (EE = hematoxylin and eosin x 100).
- Citation: Tharian B, Tsiopoulos F, George N, Pietro SD, Attili F, Larghi A. Endoscopic ultrasound fine needle aspiration: Technique and applications in clinical practice. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2012; 4(12): 532-544
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v4/i12/532.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v4.i12.532