Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jul 16, 2010; 2(7): 237-243
Published online Jul 16, 2010. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v2.i7.237
Published online Jul 16, 2010. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v2.i7.237
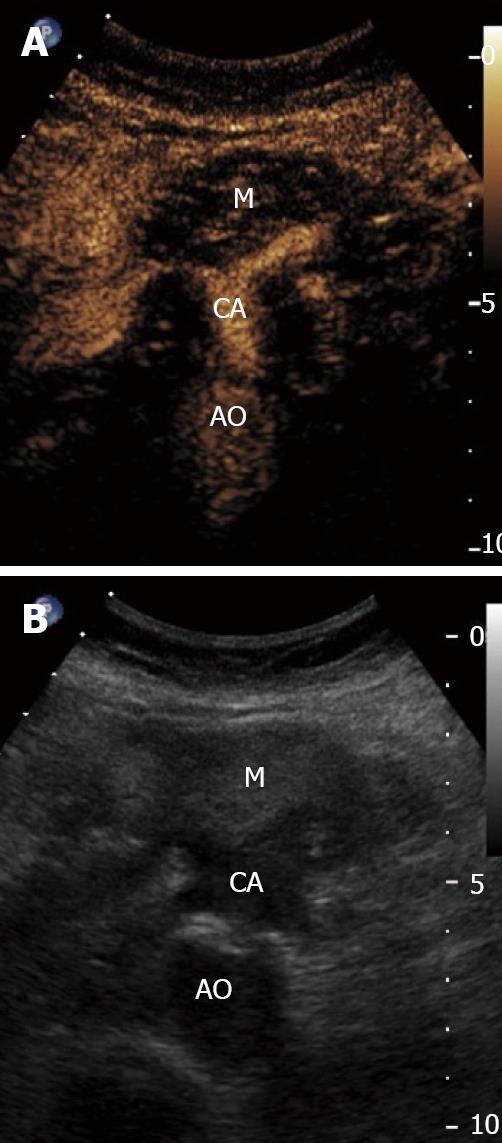
Figure 1 Transabdominal contrast enhanced ultrasound.
A: Hypoechoic lesion in the head of the pancreas on traditional grey-scale ultrasound. B:Vascularity of this lesion after infection of Definity contrast agent. The ultimate diagnosis later proved to be pancreatic adenocarcinoma encasing the celiac axis. AO: aorta; CA: celiac axis; M: mass. Image courtesy of Dr. Stephanie Wilson, Department of Radiology, University of Calgary.
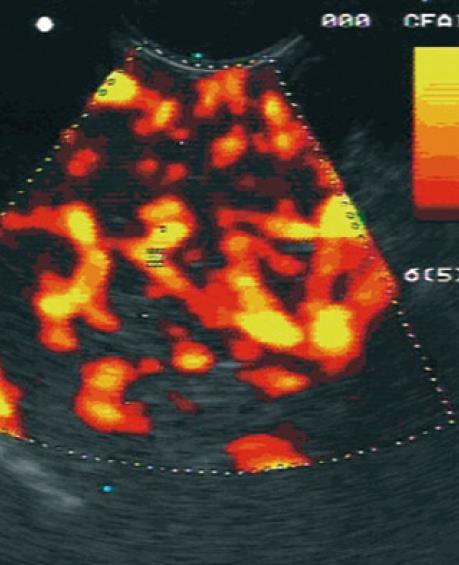
Figure 2 Contrast enhanced endoscopic ultrasound image using SonoVue injection of a focal pancreatic lesion.
The region shows regular vascularization consistent with chronic pancreatitis. Image courtesy of Hocke M et al, World J Gastroenterol 2006[34].
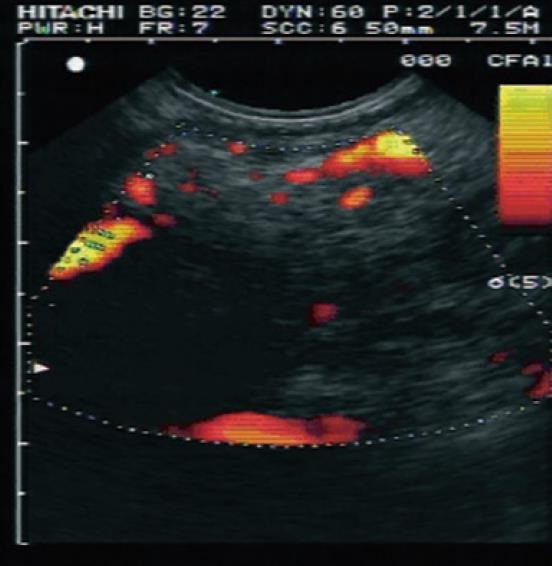
Figure 3 Contrast enhanced endoscopic ultrasound image using SonoVue injection of a focal pancreatic lesion.
This region shows irregular arterial vascularization suggestive of a malignancy (later proven to be ductal adenocarcinoma). Image courtesy of Hocke M et al, World J Gastroenterol 2006[34].
- Citation: Mohamed RM, Yan BM. Contrast enhanced endoscopic ultrasound: More than just a fancy Doppler. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2010; 2(7): 237-243
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v2/i7/237.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v2.i7.237