Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Apr 16, 2010; 2(4): 138-142
Published online Apr 16, 2010. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v2.i4.138
Published online Apr 16, 2010. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v2.i4.138
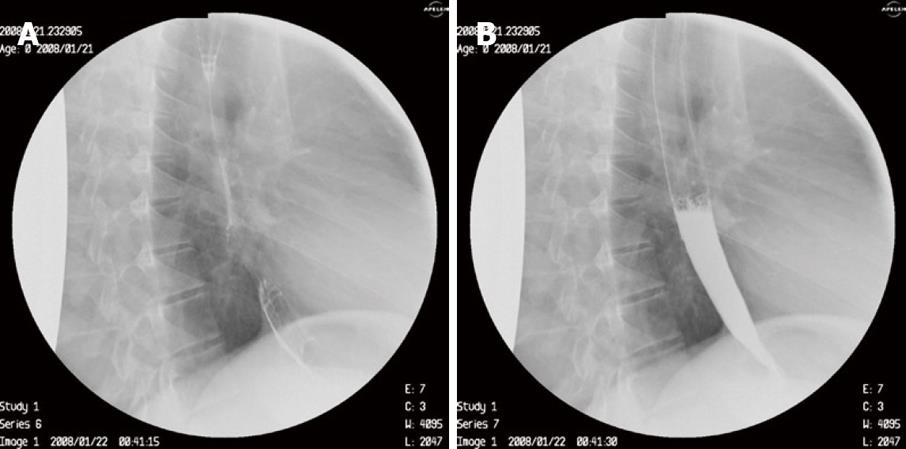
Figure 1 Barium follow through of the esophagus revealing the esophago-bronchial fistula.
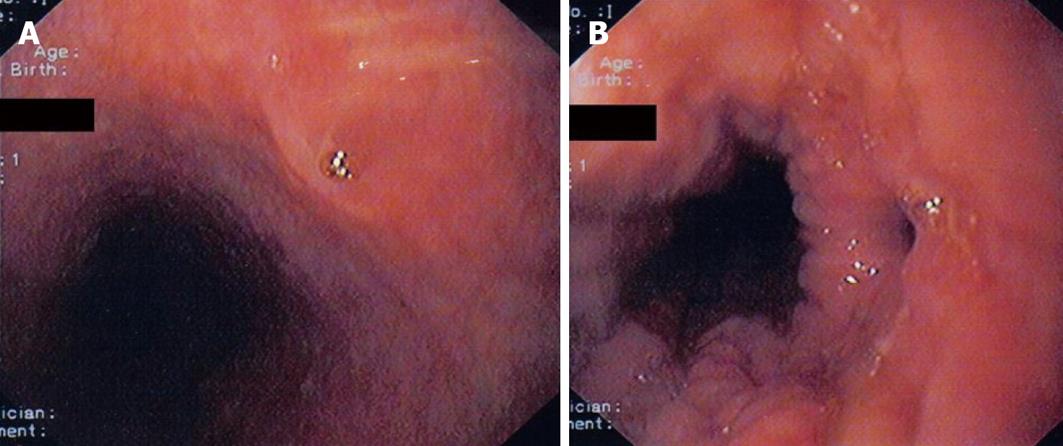
Figure 2 Endoscopic view of the proximal opening (open and closed) of the esophago-bronchial fistula caused by heterotopic gastric mucosa.
A: Closed; B: Open.
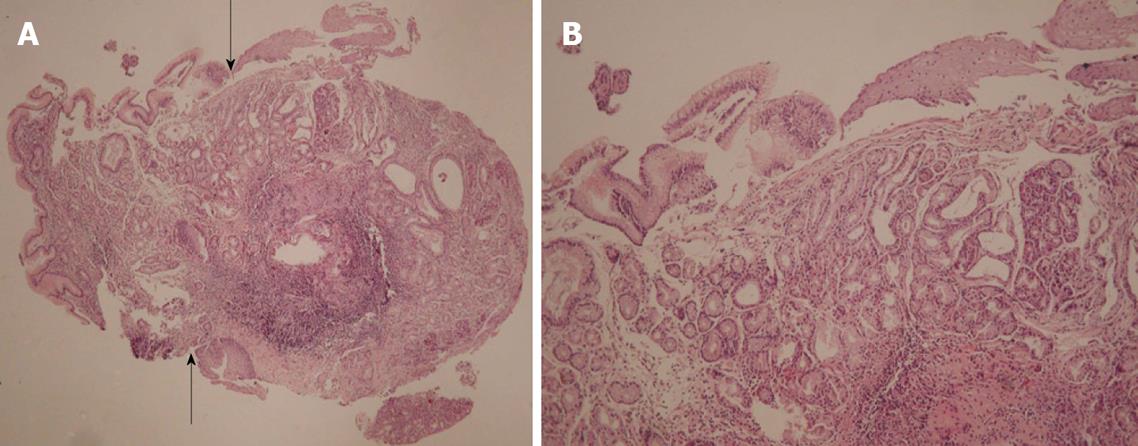
Figure 3 Heterotopic gastric mucosa in middle esophagus.
A: Arrows denote the transition between the columnar foveolar epithelium and the esophageal stratified squamous epithelium (H&E, × 40); B: Columnar epithelium merges with stratified squamous epithelium. At the lamina propria cardiac and fundic-type glands are evident (H&E, × 200).
Figure 4 Gastrograffin follow through 1 mo after endoscopic therapy of esophago-bronchial fistula with glue.
- Citation: Katsanos KH, Christodoulou DK, Kamina S, Maria K, Lambri E, Theodorou S, Tsampoulas K, Vasiliki M, Tsianos EV. Diagnosis and endoscopic treatment of esophago-bronchial fistula due to gastric heterotopy. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2010; 2(4): 138-142
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v2/i4/138.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v2.i4.138