Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jan 16, 2010; 2(1): 20-24
Published online Jan 16, 2010. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v2.i1.20
Published online Jan 16, 2010. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v2.i1.20
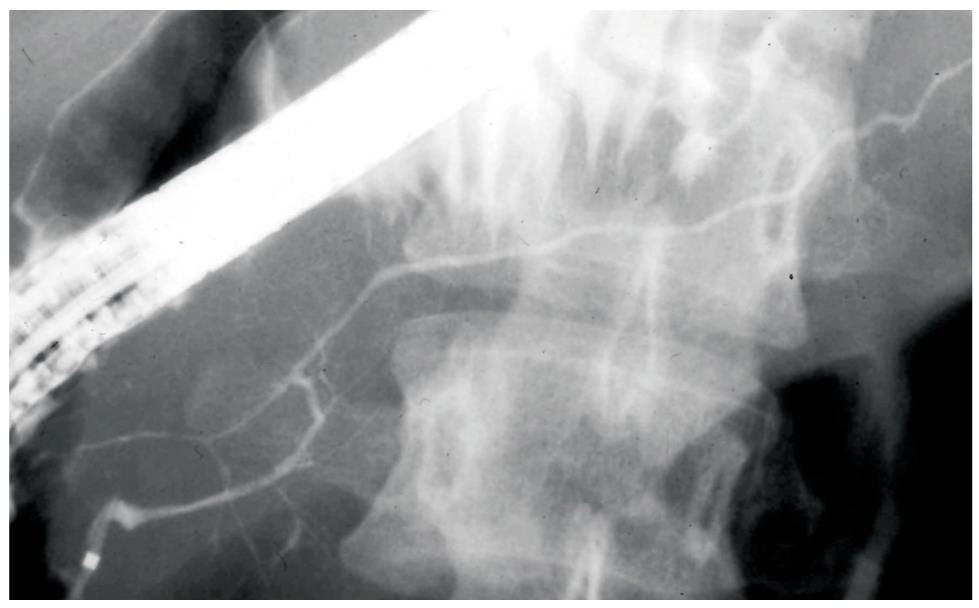
Figure 1 Diffuse irregular narrowing of the main pancreatic duct of an AIP patient on ERP.
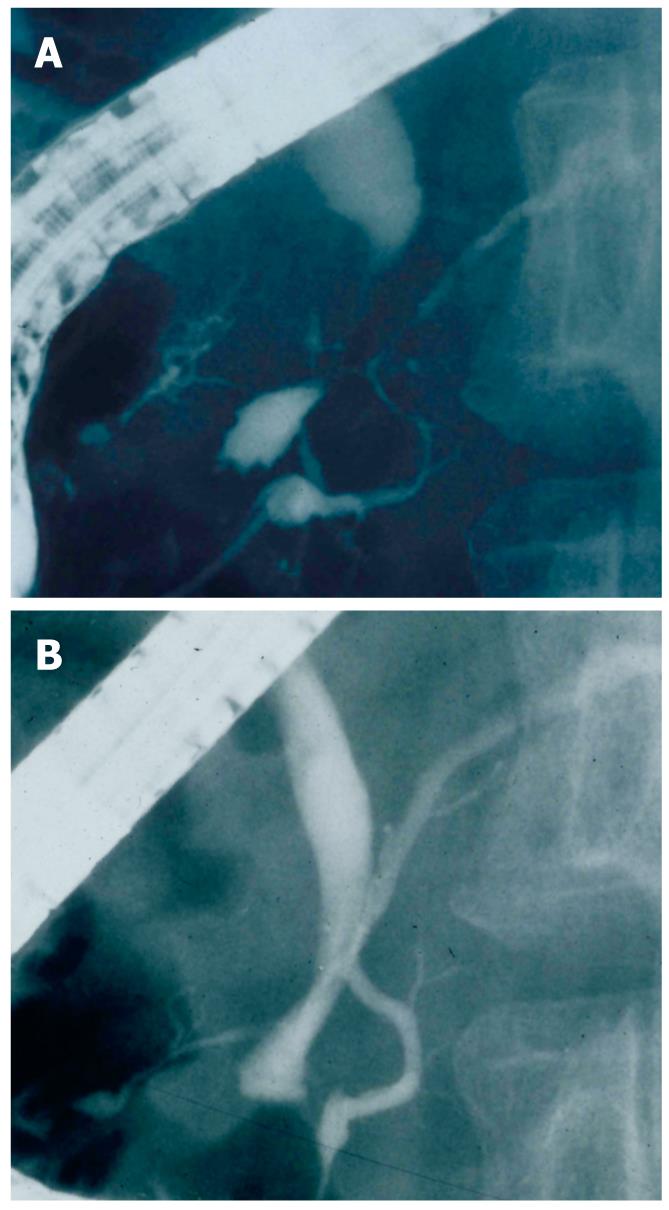
Figure 2 ERCP findings of an AIP patient.
A: Segmental narrowing of the main pancreatic duct and stenosis of the lower bile duct before steroid therapy; B: After steroid therapy, stenosis of the main pancreatic duct and bile duct is improved.
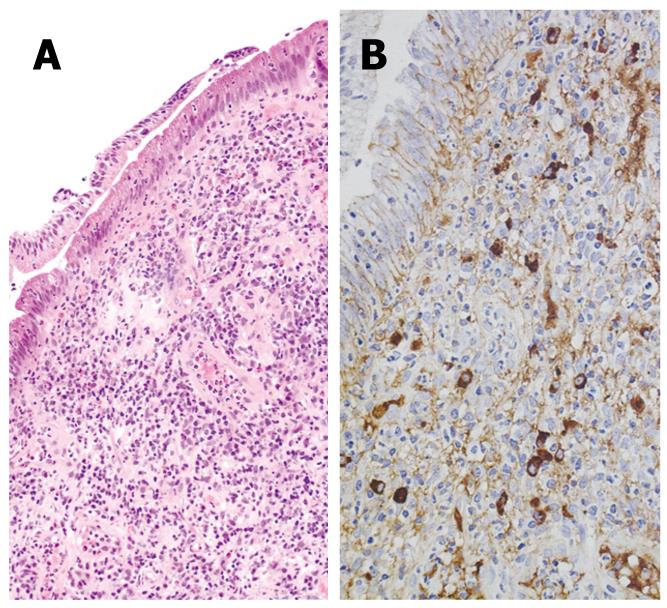
Figure 3 Immunohistochemistry of biopsy specimen taken from the major duodenal papilla of an AIP patient.
A: HE staining showing significant lymphoplasmacytic infiltration; B: IgG4 immunostaining showing significant infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells (10 ≥ 10/HPF).
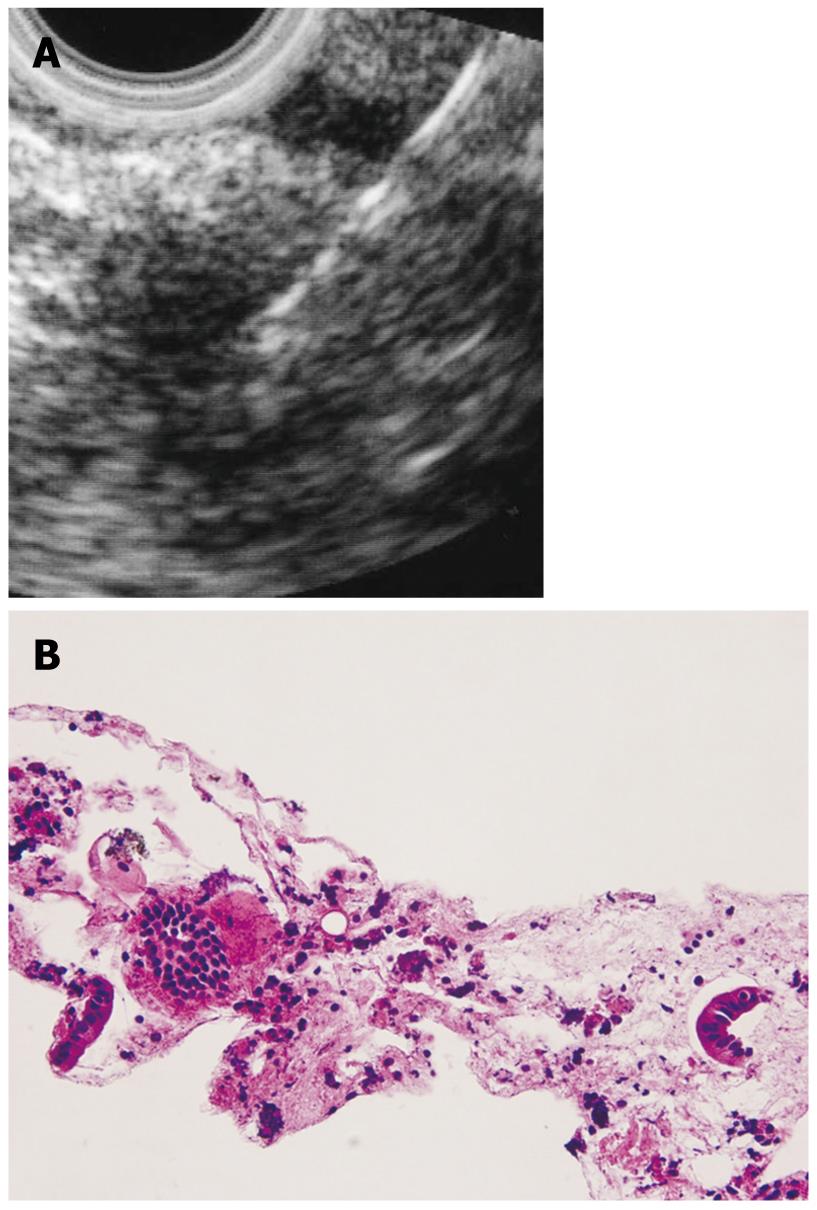
Figure 4 A hypoechoic mass in an AIP patient.
A: Endoscopic ultrasonography finding. EUS-FNA was performed to this mass lesion; B: Histology of the specimen gained by EUS-FNA (HE).
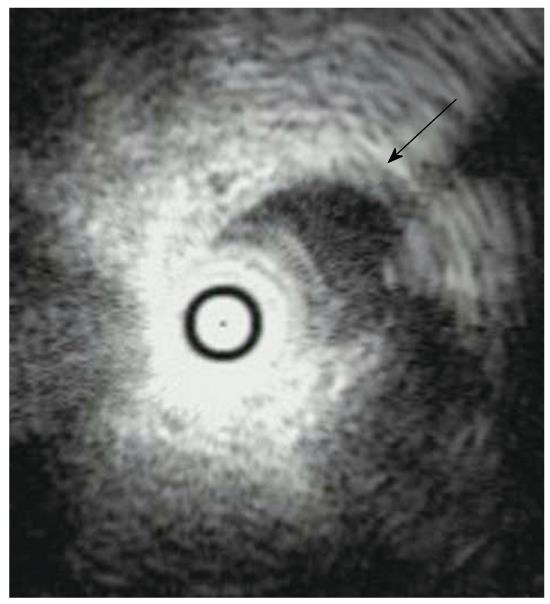
Figure 5 Intraductal ultrasonography finding of an AIP patient showing wall thickening of the common bile duct without stenosis (arrow).
- Citation: Kamisawa T, Anjiki H, Takuma K, Egawa N, Itoi T, Itokawa F. Endoscopic approach for diagnosing autoimmune pancreatitis. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2010; 2(1): 20-24
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v2/i1/20.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v2.i1.20